Webservice总结
一.神秘的webservice
Web service是一个平台独立的,低耦合的,自包含的、基于可编程的web的应用程序,可使用开放的XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)标准来描述、发布、发现、协调和配置这些应用程序,用于开发分布式的互操作的应用程序。Web Service技术, 能使得运行在不同机器上的不同应用无须借助附加的、专门的第三方软件或硬件, 就可相互交换数据或集成。依据Web Service规范实施的应用之间, 无论它们所使用的语言、 平台或内部协议是什么, 都可以相互交换数据。Web Service是自描述、 自包含的可用网络模块, 可以执行具体的业务功能。Web Service也很容易部署, 因为它们基于一些常规的产业标准以及已有的一些技术,诸如标准通用标记语言下的子集XML、HTTP。Web Service减少了应用接口的花费。Web Service为整个企业甚至多个组织之间的业务流程的集成提供了一个通用机制。
二.webservice技术支持
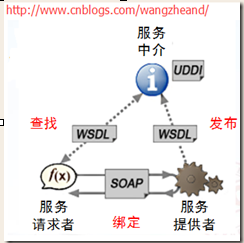
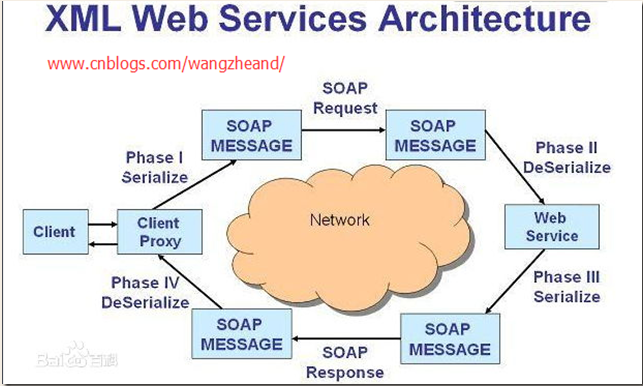
(详情可参考webservice的百度百科)
Web Service平台需要一套协议来实现分布式应用程序的创建。任何平台都有它的数据表示方法和类型系统。要实现互操作性,Web Service平台必须提供一套标准的类型系统,用于沟通不同平台、编程语言和组件模型中的不同类型系统。这些协议有:
XML和XSD
可扩展的标记语言(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)是Web Service平台中表示数据的基本格式。除了易于建立和易于分析外,XML主要的优点在于它既与平台无关,又与厂商无关。XML是由万维网协会(W3C)创建,W3C制定的XML SchemaXSD 定义了一套标准的数据类型,并给出了一种语言来扩展这套数据类型。
Web Service平台是用XSD来作为数据类型系统的。当你用某种语言如VB. NET或C# 来构造一个Web Service时,为了符合Web Service标准,所有你使用的数据类型都必须被转换为XSD类型。如想让它使用在不同平台和不同软件的不同组织间传递,还需要用某种东西将它包装起来。这种东西就是一种协议,如 SOAP。
SOAP
SOAP即简单对象访问协议(Simple Object Access Protocol),它是用于交换XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)编码信息的轻量级协议。它有三个主要方面:XML-envelope为描述信息内容和如何处理内容定义了框架,将程序对象编码成为XML对象的规则,执行远程过程调用(RPC)的约定。SOAP可以运行在任何其他传输协议上。例如,你可以使用 SMTP,即因特网电子邮件协议来传递SOAP消息,这可是很有诱惑力的。在传输层之间的头是不同的,但XML有效负载保持相同。
Web Service 希望实现不同的系统之间能够用“软件-软件对话”的方式相互调用,打破了软件应用、网站和各种设备之间的格格不入的状态,实现“基于Web无缝集成”的目标。
WSDL
Web Service描述语言WSDL 就是用机器能阅读的方式提供的一个正式描述文档而基于XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)的语言,用于描述Web Service及其函数、参数和返回值。因为是基于XML的,所以WSDL既是机器可阅读的,又是人可阅读的。
UDDI
UDDI 的目的是为电子商务建立标准;UDDI是一套基于Web的、分布式的、为Web Service提供的、信息注册中心的实现标准规范,同时也包含一组使企业能将自身提供的Web Service注册,以使别的企业能够发现的访问协议的实现标准。
三.为什么需要Web服务
Web服务为Internet上应用程序之间的交互提供了方便
Web服务也减轻了企业级应用中出现的异构系统的整合危机
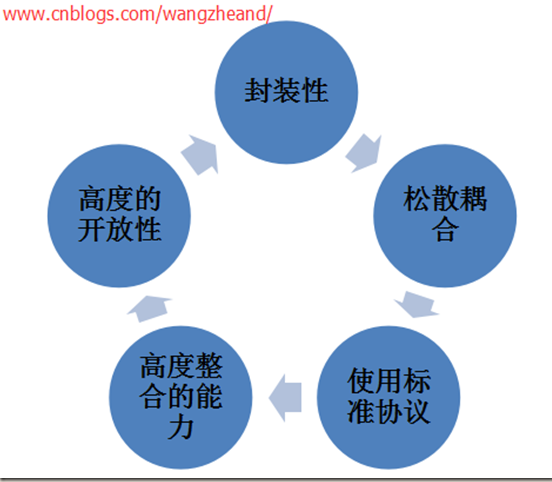
Web服务的优势包括:
四.web广泛用到的技术
-
.NET: 不同应用程序间共享数据与数据交换
他们的特点是其开放性,跨平台性,开放性正是Web services的基础。
五.Web服务在项目中的使用
1.使用JAX-WS发布和调用web服务
(JAX-WS--->web服务标准,jdk中的一个组件,集成了JAXB,本质上其实是Scoket编程)
01.发布自己的ws服务
源码介绍:
HelloService.java
package cn.myservice;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
public class
HelloService {
public void say(String name){
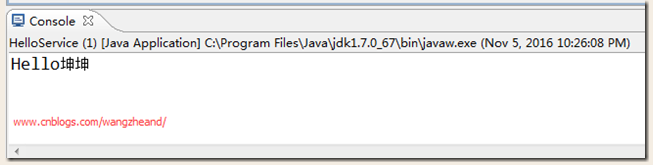
System.out.println("Hello"+name);
}
public static void main(String[]
args) {
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:50000/hello", new HelloService());
System.out.println("server is listening ....");
}
}
运行效果:
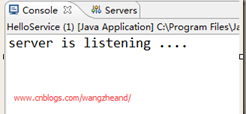
现在我们的局域网上都可以访问我发布的(http://localhost:50000/hello)这个服务了
效果:
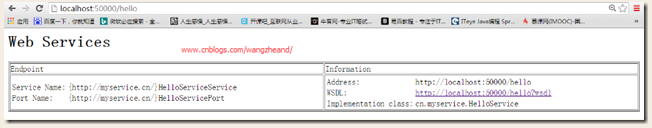
02.书写代码调用
其中我们myservice包中的类我们是不需要自己去写的,我们可以使用jdk中的wsimport.exe利用我们cmd命令给我们生成(当然是在保证我们的jdk安装,环境变量配置成功的情况下)
操作如下:
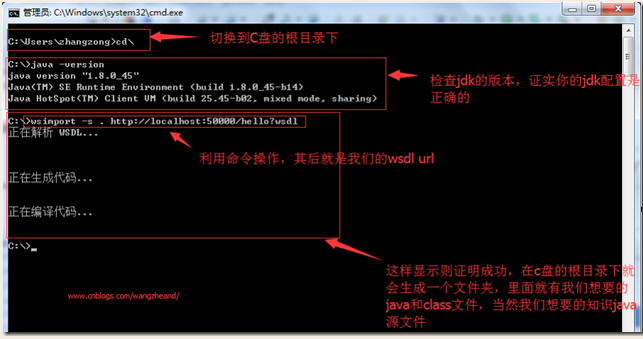
这时,我们来看看我们的c盘根目录:
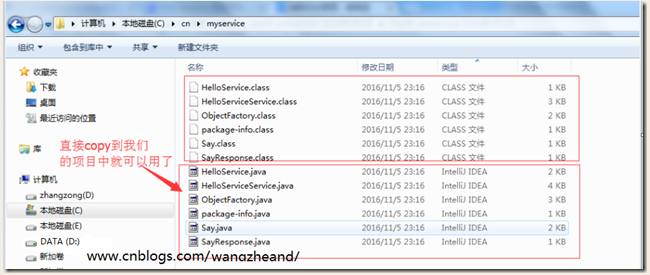
源码介绍:
1.HelloService.java
package cn.myservice;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSeeAlso;
import javax.xml.ws.Action;
import javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper;
import javax.xml.ws.ResponseWrapper;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.2.9-b130926.1035
* Generated source version: 2.2
*
*/
@WebService(name = "HelloService", targetNamespace = "http://myservice.cn/")
@XmlSeeAlso({
ObjectFactory.class
})
public interface HelloService {
/**
*
* @param arg0
*/
@WebMethod
@RequestWrapper(localName = "say", targetNamespace = "http://myservice.cn/", className = "cn.myservice.Say")
@ResponseWrapper(localName = "sayResponse", targetNamespace = "http://myservice.cn/", className = "cn.myservice.SayResponse")
@Action(input = "http://myservice.cn/HelloService/sayRequest", output = "http://myservice.cn/HelloService/sayResponse")
public void say(
@WebParam(name = "arg0", targetNamespace = "")
String arg0);
}
2.HelloServiceService.java
package cn.myservice;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceException;
import
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature;
/**
* This class was generated
by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.2.9-b130926.1035
* Generated source
version: 2.2
*
*/
@WebServiceClient(name = "HelloServiceService",
targetNamespace = "http://myservice.cn/", wsdlLocation =
"http://localhost:50000/hello?wsdl")
public class HelloServiceService
extends Service
{
private final static URL
HELLOSERVICESERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
private final static
WebServiceException HELLOSERVICESERVICE_EXCEPTION;
private final static
QName HELLOSERVICESERVICE_QNAME = new QName("http://myservice.cn/",
"HelloServiceService");
static {
URL url = null;
WebServiceException e = null;
try {
url
= new URL("http://localhost:50000/hello?wsdl");
} catch
(MalformedURLException ex) {
e = new WebServiceException(ex);
}
HELLOSERVICESERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION = url;
HELLOSERVICESERVICE_EXCEPTION = e;
}
public
HelloServiceService() {
super(__getWsdlLocation(),
HELLOSERVICESERVICE_QNAME);
}
public
HelloServiceService(WebServiceFeature... features) {
super(__getWsdlLocation(), HELLOSERVICESERVICE_QNAME, features);
}
public HelloServiceService(URL wsdlLocation) {
super(wsdlLocation, HELLOSERVICESERVICE_QNAME);
}
public
HelloServiceService(URL wsdlLocation, WebServiceFeature... features) {
super(wsdlLocation, HELLOSERVICESERVICE_QNAME, features);
}
public HelloServiceService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName);
}
public
HelloServiceService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName, WebServiceFeature...
features) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName, features);
}
/**
*
* @return
* returns
HelloService
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloServicePort")
public HelloService getHelloServicePort() {
return super.getPort(new
QName("http://myservice.cn/", "HelloServicePort"), HelloService.class);
}
/**
*
* @param features
* A list of
{@link javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature} to configure on the proxy. Supported
features not in the <code>features</code> parameter will have their
default values.
* @return
* returns HelloService
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloServicePort")
public HelloService
getHelloServicePort(WebServiceFeature... features) {
return
super.getPort(new QName("http://myservice.cn/", "HelloServicePort"),
HelloService.class, features);
}
private static URL
__getWsdlLocation() {
if (HELLOSERVICESERVICE_EXCEPTION!= null) {
throw HELLOSERVICESERVICE_EXCEPTION;
}
return HELLOSERVICESERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
}
}
3.ObjectFactory.java
package cn.myservice;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBElement;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElementDecl;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRegistry;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
/**
* This object contains factory methods for each
* Java
content interface and Java element interface
* generated in the cn.myservice
package.
* <p>An ObjectFactory allows you to programatically
*
construct new instances of the Java representation
* for XML content. The
Java representation of XML
* content can consist of schema derived
interfaces
* and classes representing the binding of schema
* type
definitions, element declarations and model
* groups. Factory methods for
each of these are
* provided in this class.
*
*/
@XmlRegistry
public class ObjectFactory {
private final static QName
_SayResponse_QNAME = new QName("http://myservice.cn/", "sayResponse");
private final static QName _Say_QNAME = new QName("http://myservice.cn/",
"say");
/**
* Create a new ObjectFactory that can be used
to create new instances of schema derived classes for package: cn.myservice
*
*/
public ObjectFactory() {
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link SayResponse }
*
*/
public SayResponse createSayResponse() {
return new
SayResponse();
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link
Say }
*
*/
public Say createSay() {
return
new Say();
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link
JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link SayResponse }{@code >}}
*
*/
@XmlElementDecl(namespace = "http://myservice.cn/", name =
"sayResponse")
public JAXBElement<SayResponse>
createSayResponse(SayResponse value) {
return new
JAXBElement<SayResponse>(_SayResponse_QNAME, SayResponse.class, null,
value);
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link
JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link Say }{@code >}}
*
*/
@XmlElementDecl(namespace = "http://myservice.cn/", name = "say")
public JAXBElement<Say> createSay(Say value) {
return
new JAXBElement<Say>(_Say_QNAME, Say.class, null, value);
}
}
4.Say.java
package cn.myservice;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>say complex
type的 Java 类。
*
* <p>以下模式片段指定包含在此类中的预期内容。
*
* <pre>
* <complexType name="say">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction
base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
*
<sequence>
* <element name="arg0"
type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string" minOccurs="0"/>
*
</sequence>
* </restriction>
*
</complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name =
"say", propOrder = {
"arg0"
})
public class Say {
protected String arg0;
/**
* 获取arg0属性的值。
*
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link
String }
*
*/
public String getArg0() {
return arg0;
}
/**
* 设置arg0属性的值。
*
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*
*/
public void
setArg0(String value) {
this.arg0 = value;
}
}
5.SayResponse.java
package cn.myservice;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import
javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>sayResponse
complex type的 Java 类。
*
* <p>以下模式片段指定包含在此类中的预期内容。
*
*
<pre>
* <complexType name="sayResponse">
*
<complexContent>
* <restriction
base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
*
<sequence>
* </sequence>
*
</restriction>
* </complexContent>
*
</complexType>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "sayResponse")
public class SayResponse {
}
6.MyTest.java(测试类)
package cn.test;
import cn.myservice.HelloService;
import
cn.myservice.HelloServiceService;
public class MyTest {
public
static void main(String[] args) {
HelloServiceService service = new
HelloServiceService();
HelloService port =
service.getHelloServicePort();
port.say("坤坤");
}
}
7.运行效果