Python模块与包
1. 模块与包
1.1 模块的概念
随着程序代码越写越多,在一个文件里代码就会越来越长,越来越不容易维护。为了编写可维护的代码,我们把很多函数分组,分别放到不同的文件里,这样,每个文件包含的代码就相对较少,很多编程语言都采用这种组织代码的方式。在Python中,一个.py文件就称之为一个模块(Module)。
1.2 模块的优势
提高代码的可维护性。
编写代码不必从零开始。当一个模块编写完毕,就可以被其他地方引用。在编写程序的时候,也经常引用其他模块,包括Python内置的模块和来自第三方的模块。
避免函数名和变量名冲突。相同名字的函数和变量完全可以分别存在不同的模块中,因此,我们自己在编写模块时,不必考虑名字会与其他模块冲突。但是也要注意,尽量不要与内置函数名字冲突。
1.3 模块的分类
python标准库
第三方模块
应用程序自定义模块
1.4 模块导入的方法
import 语句 //推荐
from…import 语句 //推荐
From…import* 语句 //推荐
from modname import * //此种不推荐
1.5 包的概念
包是指包含__init__.py的模块文件的文件夹,一个包内可以有多个py模块文件,调用包就是执行包下的__init__.py文件(__init__.py可以是空文件,也可以有Python代码)。
1.6 包的优势
A包和B包的目录下的py文件名可以重复,举个例子,A和B包下都存在hello.py,那么引用A包的hello.py模块时候,需要import A.hello.py,引用B包同样就是B.hello.py。
1.7 模块的搜索路径
模块的查找顺序是:内存中已经加载的模块->内置模块->sys.path路径中包含的模块。
如果sys.path中因为没有路径而找不到相关模块,可以使用如下方法进行添加路径。
import sys,os M_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) sys.path.append(M_DIR)
1.8 关于__name__的值
当程序本身被执行的时候__name__ == '__main__',否则__name__ == 'filename本身'。
2 常用模块
2.1 time模块
在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间:
- 时间戳(timestamp):通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。我们运行“type(time.time())”,返回的是float类型。
- 格式化的时间字符串(Format String)
- 结构化的时间(struct_time):struct_time元组共有9个元素共九个元素:(年,月,日,时,分,秒,一年中第几周,一年中第几天,夏令时)
import time #--------------------------我们先以当前时间为准,让大家快速认识三种形式的时间 print(time.time()) # 时间戳:1487130156.419527 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X")) #格式化的时间字符串:'2017-02-15 11:40:53' print(time.localtime()) #本地时区的struct_time print(time.gmtime()) #UTC时区的struct_time

%a Locale’s abbreviated weekday name. %A Locale’s full weekday name. %b Locale’s abbreviated month name. %B Locale’s full month name. %c Locale’s appropriate date and time representation. %d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31]. %H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23]. %I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12]. %j Day of the year as a decimal number [001,366]. %m Month as a decimal number [01,12]. %M Minute as a decimal number [00,59]. %p Locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM. (1) %S Second as a decimal number [00,61]. (2) %U Week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Sunday are considered to be in week 0. (3) %w Weekday as a decimal number [0(Sunday),6]. %W Week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Monday are considered to be in week 0. (3) %x Locale’s appropriate date representation. %X Locale’s appropriate time representation. %y Year without century as a decimal number [00,99]. %Y Year with century as a decimal number. %z Time zone offset indicating a positive or negative time difference from UTC/GMT of the form +HHMM or -HHMM, where H represents decimal hour digits and M represents decimal minute digits [-23:59, +23:59]. %Z Time zone name (no characters if no time zone exists). %% A literal '%' character. 格式化字符串的时间格式
其中计算机认识的时间只能是'时间戳'格式,而程序员可处理的或者说人类能看懂的时间有: '格式化的时间字符串','结构化的时间' ,于是有了下图的转换关系
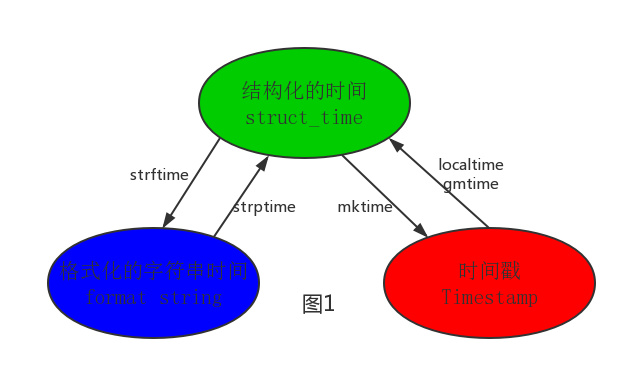
#--------------------------按图1转换时间 # localtime([secs]) # 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。 time.localtime() time.localtime(1473525444.037215) # gmtime([secs]) 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。 # mktime(t) : 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。 print(time.mktime(time.localtime()))#1473525749.0 # strftime(format[, t]) : 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和 # time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如果元组中任何一个 # 元素越界,ValueError的错误将会被抛出。 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))#2016-09-11 00:49:56 # time.strptime(string[, format]) # 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。 print(time.strptime('2011-05-05 16:37:06', '%Y-%m-%d %X')) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2011, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=16, tm_min=37, tm_sec=6, # tm_wday=3, tm_yday=125, tm_isdst=-1) #在这个函数中,format默认为:"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y"。
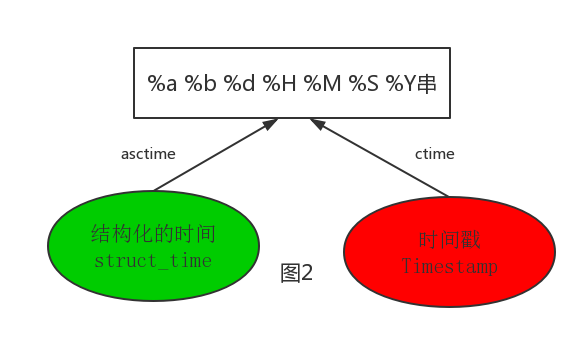
#--------------------------按图2转换时间 # asctime([t]) : 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:'Sun Jun 20 23:21:05 1993'。 # 如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。 print(time.asctime())#Sun Sep 11 00:43:43 2016 # ctime([secs]) : 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为 # None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。 print(time.ctime()) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 print(time.ctime(time.time())) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016
2.2 random模块
import random print(random.random())#(0,1)----float 大于0且小于1之间的小数 print(random.randint(1,3)) #[1,3] 大于等于1且小于等于3之间的整数 print(random.randrange(1,3)) #[1,3) 大于等于1且小于3之间的整数 print(random.choice([1,'23',[4,5]]))#1或者23或者[4,5] print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2))#列表元素任意2个组合 print(random.uniform(1,3))#大于1小于3的小数,如1.927109612082716 item=[1,3,5,7,9] random.shuffle(item) #打乱item的顺序,相当于"洗牌" print(item)

import random def make_code(n): res='' for i in range(n): s1=chr(random.randint(65,90)) s2=str(random.randint(0,9)) res+=random.choice([s1,s2]) return res print(make_code(9)) 生成随机验证码
2.3 OS模块
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.') os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..') os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录 os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 os.remove() 删除一个文件 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息 os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/" os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n" os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 win下为;,Linux下为: os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix' os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 os.environ 获取系统环境变量 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
在Linux和Mac平台上,该函数会原样返回path,在windows平台上会将路径中所有字符转换为小写,并将所有斜杠转换为饭斜杠。 >>> os.path.normcase('c:/windows\\system32\\') 'c:\\windows\\system32\\' 规范化路径,如..和/ >>> os.path.normpath('c://windows\\System32\\../Temp/') 'c:\\windows\\Temp' >>> a='/Users/jieli/test1/\\\a1/\\\\aa.py/../..' >>> print(os.path.normpath(a)) /Users/jieli/test1
os路径处理 #方式一:推荐使用 import os #具体应用 import os,sys possible_topdir = os.path.normpath(os.path.join( os.path.abspath(__file__), os.pardir, #上一级 os.pardir, os.pardir )) sys.path.insert(0,possible_topdir) #方式二:不推荐使用 os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
2.4 sys模块
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
sys.maxint 最大的Int值
sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称

#=========知识储备========== #进度条的效果 [# ] [## ] [### ] [#### ] #指定宽度 print('[%-15s]' %'#') print('[%-15s]' %'##') print('[%-15s]' %'###') print('[%-15s]' %'####') #打印% print('%s%%' %(100)) #第二个%号代表取消第一个%的特殊意义 #可传参来控制宽度 print('[%%-%ds]' %50) #[%-50s] print(('[%%-%ds]' %50) %'#') print(('[%%-%ds]' %50) %'##') print(('[%%-%ds]' %50) %'###') #=========实现打印进度条函数========== import sys import time def progress(percent,width=50): if percent >= 1: percent=1 show_str=('[%%-%ds]' %width) %(int(width*percent)*'#') print('\r%s %d%%' %(show_str,int(100*percent)),file=sys.stdout,flush=True,end='') #=========应用========== data_size=1025 recv_size=0 while recv_size < data_size: time.sleep(0.1) #模拟数据的传输延迟 recv_size+=1024 #每次收1024 percent=recv_size/data_size #接收的比例 progress(percent,width=70) #进度条的宽度70 打印进度条
2.5 subprocess模块
import subprocess ''' sh-3.2# ls /Users/egon/Desktop |grep txt$ mysql.txt tt.txt 事物.txt ''' res1=subprocess.Popen('ls /Users/jieli/Desktop',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE) res=subprocess.Popen('grep txt$',shell=True,stdin=res1.stdout, stdout=subprocess.PIPE) print(res.stdout.read().decode('utf-8')) #等同于上面,但是上面的优势在于,一个数据流可以和另外一个数据流交互,可以通过爬虫得到结果然后交给grep res1=subprocess.Popen('ls /Users/jieli/Desktop |grep txt$',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE) print(res1.stdout.read().decode('utf-8')) #windows下: # dir | findstr 'test*' # dir | findstr 'txt$' import subprocess res1=subprocess.Popen(r'dir C:\Users\Administrator\PycharmProjects\test\函数备课',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE) res=subprocess.Popen('findstr test*',shell=True,stdin=res1.stdout, stdout=subprocess.PIPE) print(res.stdout.read().decode('gbk')) #subprocess使用当前系统默认编码,得到结果为bytes类型,在windows下需要用gbk解码 #subprocess.call作用是创建一个新进程,并返回运行状态,shell=True,运行字符串,shell=False运行数组,成功运行状态0; import subprocess subprocess.call('ls /Users/momo/Desktop | grep .txt$', shell = True)
2.6 re模块
就其本质而言,正则表达式(或 RE)是一种小型的、高度专业化的编程语言,(在Python中)它内嵌在Python中,并通过 re 模块实现。正则表达式模式被编译成一系列的字节码,然后由用 C 编写的匹配引擎执行。
字符匹配(普通字符,元字符):
1 普通字符:大多数字符和字母都会和自身匹配
>>> re.findall('alvin','yuanaleSxalexwupeiqi')
['alvin']
2 元字符:. ^ $ * + ? { } [ ] | ( ) \
元字符之. ^ $ * + ? { }
import re ret=re.findall('a..in','helloalvin') print(ret)#['alvin'] ret=re.findall('^a...n','alvinhelloawwwn') print(ret)#['alvin'] ret=re.findall('a...n$','alvinhelloawwwn') print(ret)#['awwwn'] ret=re.findall('a...n$','alvinhelloawwwn') print(ret)#['awwwn'] ret=re.findall('abc*','abcccc')#贪婪匹配[0,+oo] print(ret)#['abcccc'] ret=re.findall('abc+','abccc')#[1,+oo] print(ret)#['abccc'] ret=re.findall('abc?','abccc')#[0,1] print(ret)#['abc'] ret=re.findall('abc{1,4}','abccc') print(ret)#['abccc'] 贪婪匹配
注意:前面的*,+,?等都是贪婪匹配,也就是尽可能匹配,后面加?号使其变成惰性匹配
ret=re.findall('abc*?','abcccccc') print(ret)#['ab']
元字符之字符集[]:
#--------------------------------------------字符集[] ret=re.findall('a[bc]d','acd') print(ret)#['acd'] ret=re.findall('[a-z]','acd') print(ret)#['a', 'c', 'd'] ret=re.findall('[.*+]','a.cd+') print(ret)#['.', '+'] #在字符集里有功能的符号: - ^ \ ret=re.findall('[1-9]','45dha3') print(ret)#['4', '5', '3'] ret=re.findall('[^ab]','45bdha3') print(ret)#['4', '5', 'd', 'h', '3'] ret=re.findall('[\d]','45bdha3') print(ret)#['4', '5', '3']
元字符之转义符\
反斜杠后边跟元字符去除特殊功能,比如\.
反斜杠后边跟普通字符实现特殊功能,比如\d
\d 匹配任何十进制数;它相当于类 [0-9]。
\D 匹配任何非数字字符;它相当于类 [^0-9]。
\s 匹配任何空白字符;它相当于类 [ \t\n\r\f\v]。
\S 匹配任何非空白字符;它相当于类 [^ \t\n\r\f\v]。
\w 匹配任何字母数字字符;它相当于类 [a-zA-Z0-9_]。
\W 匹配任何非字母数字字符;它相当于类 [^a-zA-Z0-9_]
\b 匹配一个特殊字符边界,比如空格 ,&,#等
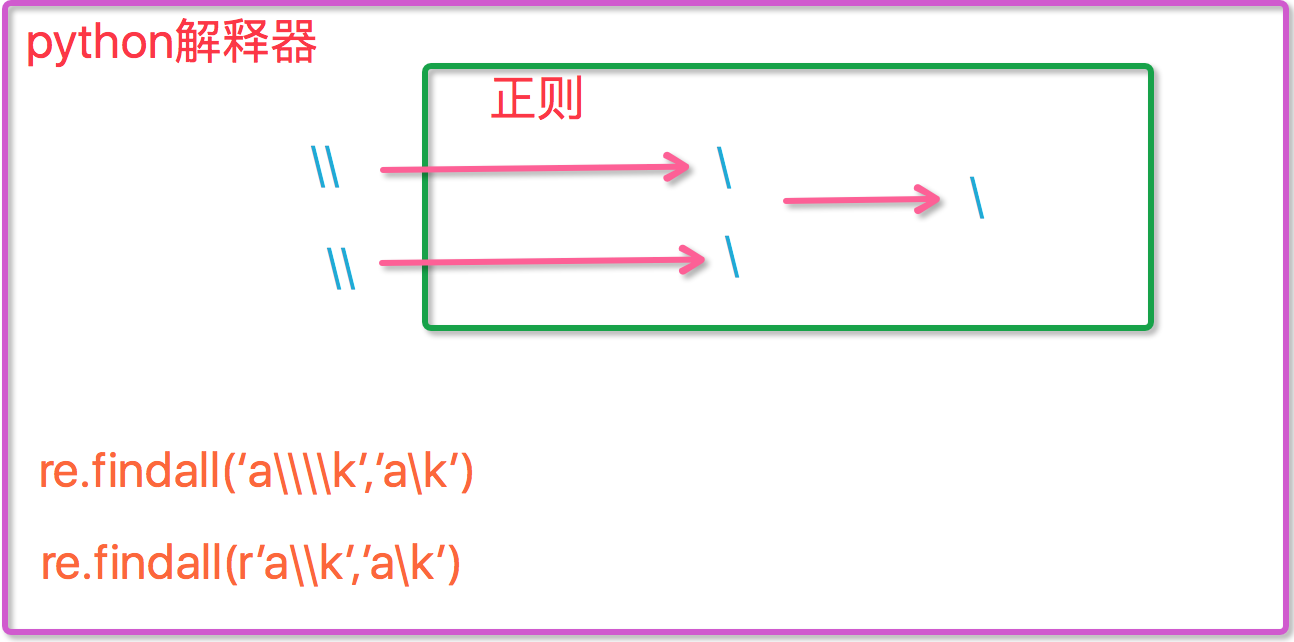
ret=re.findall('I\b','I am LIST') print(ret)#[] ret=re.findall(r'I\b','I am LIST') print(ret)#['I'] #-----------------------------eg1: import re ret=re.findall('c\l','abc\le') print(ret)#[] ret=re.findall('c\\l','abc\le') print(ret)#[] ret=re.findall('c\\\\l','abc\le') print(ret)#['c\\l'] ret=re.findall(r'c\\l','abc\le') print(ret)#['c\\l'] #-----------------------------eg2: #之所以选择\b是因为\b在ASCII表中是有意义的 m = re.findall('\bblow', 'blow') print(m) m = re.findall(r'\bblow', 'blow') print(m)
元字符之分组()
m = re.findall(r'(ad)+', 'add') print(m) ret=re.search('(?P<id>\d{2})/(?P<name>\w{3})','23/com') print(ret.group())#23/com print(ret.group('id'))#23
元字符之 |
ret=re.search('(ab)|\d','rabhdg8sd') print(ret.group())#ab
re模块下的常用方法
import re #1 re.findall('a','alvin yuan') #返回所有满足匹配条件的结果,放在列表里 #2 re.search('a','alvin yuan').group() #函数会在字符串内查找模式匹配,只到找到第一个匹配然后返回一个包含匹配信息的对象,该对象可以 # 通过调用group()方法得到匹配的字符串,如果字符串没有匹配,则返回None。 #3 re.match('a','abc').group() #同search,不过尽在字符串开始处进行匹配 #4 ret=re.split('[ab]','abcd') #先按'a'分割得到''和'bcd',在对''和'bcd'分别按'b'分割 print(ret)#['', '', 'cd'] #5 ret=re.sub('\d','abc','alvin5yuan6',1) print(ret)#alvinabcyuan6 ret=re.subn('\d','abc','alvin5yuan6') print(ret)#('alvinabcyuanabc', 2) #6 obj=re.compile('\d{3}') ret=obj.search('abc123eeee') print(ret.group())#123 1 2 3 4 5 6 import re ret=re.finditer('\d','ds3sy4784a') print(ret) #<callable_iterator object at 0x10195f940> print(next(ret).group()) print(next(ret).group())
import re ret=re.findall('www.(baidu|oldboy).com','www.oldboy.com') print(ret)#['oldboy'] 这是因为findall会优先把匹配结果组里内容返回,如果想要匹配结果,取消权限即可 ret=re.findall('www.(?:baidu|oldboy).com','www.oldboy.com') print(ret)#['www.oldboy.com']
import re print(re.findall("<(?P<tag_name>\w+)>\w+</(?P=tag_name)>","<h1>hello</h1>")) print(re.search("<(?P<tag_name>\w+)>\w+</(?P=tag_name)>","<h1>hello</h1>")) print(re.search(r"<(\w+)>\w+</\1>","<h1>hello</h1>")) #匹配出所有的整数 import re #ret=re.findall(r"\d+{0}]","1-2*(60+(-40.35/5)-(-4*3))") ret=re.findall(r"-?\d+\.\d*|(-?\d+)","1-2*(60+(-40.35/5)-(-4*3))") ret.remove("") print(ret)
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5732581.html






