vue服务端渲染 项目改造经历
vue ssr 项目改造经历
由于工作项目需求,需要将原有的项目改造,vue ssr 没有用到nuxt,因为vue ssr更利于seo,没办法,一个小白的改造经历,
首先说明一下,小白可以借鉴,高手也可以点评一下,因为,我写的不一定准确,只是针对我的项目。
下面先说一下大致:
原有项目有用到element,在改造ssr过程中,是很坑的。如果可以的话,还是强烈建议你重新改写成nuxt项目。由于我是小白,所以开始时候备份了一下项目,然后开始网上查找相关文章。
1.首先是这位大神的文章https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012440041,笔名 右三。
2.然后是https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/9158675.html,一个小火柴项目的改造过程。
3.https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016637877 ,五步学会基础。
我列举他们三个,是因为,刚开始以为项目直接改改代码就可以,于是按照他们所说改写,发现,处处是坑,总之,他们的说法并不适合我的项目,于是苦思冥想,去看官网,再结合他们文章,开始大刀阔斧改造。
请您备份好:
先上一张原有项目图纸,就是普通的cli2构造出来的,其中theme是element主题,可不用理会。
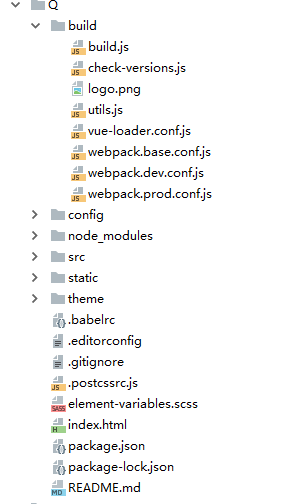
接下来开始改造:
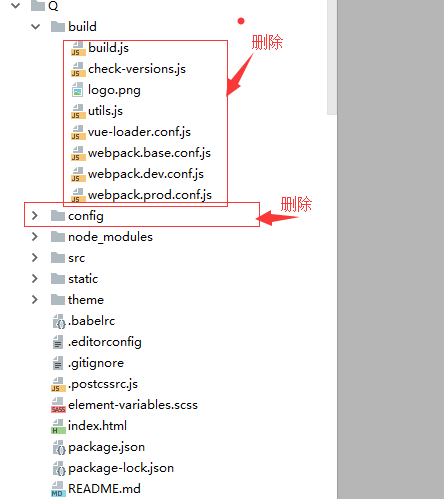
是不是不可思议,不敢整的,可以看文末怎么解决的一些坑。我接着分析
删除完以后,在build里添加四个文件:
1. setup-dev-server.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 | const path = require('path')const webpack = require('webpack')const MFS = require('memory-fs')const clientConfig = require('./webpack.client.config')const serverConfig = require('./webpack.server.config')module.exports = function setupDevServer (app, cb) { let bundle let template // 修改客户端配置添加 热更新中间件 clientConfig.entry.app = ['webpack-hot-middleware/client', clientConfig.entry.app] clientConfig.output.filename = '[name].js' clientConfig.plugins.push( new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(), new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin() ) const clientCompiler = webpack(clientConfig) // 执行webpack const devMiddleware = require('webpack-dev-middleware')(clientCompiler, { publicPath: clientConfig.output.publicPath, stats: { colors: true, chunks: false } }) app.use(devMiddleware) clientCompiler.plugin('done', () => { const fs = devMiddleware.fileSystem // 模板为打包后的html文件 const filePath = path.join(clientConfig.output.path, 'index.html') if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) { template = fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf-8') console.log("执行4") if (bundle) { console.log("执行1") cb(bundle, template) } } }) app.use(require('webpack-hot-middleware')(clientCompiler)) // 监听 server renderer const serverCompiler = webpack(serverConfig) const mfs = new MFS() // 内存文件系统,在JavaScript对象中保存数据。 serverCompiler.outputFileSystem = mfs serverCompiler.watch({}, (err, stats) => { if (err) throw err stats = stats.toJson() stats.errors.forEach(err => console.error(err)) stats.warnings.forEach(err => console.warn(err)) // 读取使用vue-ssr-webpack-plugin生成的bundle(vue-ssr-bundle.json) const bundlePath = path.join(serverConfig.output.path, 'vue-ssr-bundle.json') bundle = JSON.parse(mfs.readFileSync(bundlePath, 'utf-8')) console.log("执行3") if (template) { console.log("执行2") cb(bundle, template) } })} |
2. webpack.base.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 | const path = require('path')const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')const extractCSS = new ExtractTextPlugin('stylesheets/[name]-one.css');// 这样我们在开发过程中仍然可以热重载,CSS 提取应该只用于生产环境const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'module.exports = { devtool: '#source-map', entry: { app: './src/entry-client.js', //app: ["babel-polyfill", "./src/entry-client.js"],///解决ie关键 vendor: [ 'vue', 'vue-router', 'vuex' ] }, output: { path: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'), publicPath: '/dist/', filename: '[name].[chunkhash].js' }, resolve: { alias: { 'static': path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'), // '@': path.resolve('src'), } }, module: { noParse: /es6-promise\.js$/, // avoid webpack shimming process rules: [ { test: /\.vue$/, loader: 'vue-loader', options: { extractCSS: isProduction, preserveWhitespace: false, postcss: [ require('autoprefixer')({ browsers: ['last 3 versions'] }) ] } }, { test: /\.js$/, loader: 'buble-loader', exclude: /node_modules/, options: { objectAssign: 'Object.assign' } }, { test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/, loader: 'url-loader', options: { limit: 10000, name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]' } }, { test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/, loader: 'url-loader', query: { limit: 10000, name: 'fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]' } }, { test: /\.css$/, use: isProduction ? ExtractTextPlugin.extract({ use: 'css-loader', fallback: 'vue-style-loader' }) : ['vue-style-loader', 'css-loader'] } ] }, plugins: isProduction // 确保添加了此插件! ? [new ExtractTextPlugin({ filename: 'common.[chunkhash].css' })] : [], performance: { hints: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warning' : false, maxAssetSize: 30000000, // 整数类型(以字节为单位) maxEntrypointSize: 50000000, // 整数类型(以字节为单位) assetFilter: function(assetFilename) { // 提供资源文件名的断言函数 return assetFilename.endsWith('.css') || assetFilename.endsWith('.js'); } }} |
3. webpack.client.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | const webpack = require('webpack')const merge = require('webpack-merge')const base = require('./webpack.base.config')const HTMLPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')const SWPrecachePlugin = require('sw-precache-webpack-plugin')const config = merge(base, { plugins: [ // 全局变量 new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development'), 'process.env.VUE_ENV': '"client"' }), // 将依赖模块提取到 vendor chunk 以获得更好的缓存,是很常见的做法。 new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'vendor', minChunks: function (module) { return ( // 如果它在 node_modules 中 /node_modules/.test(module.context) && // 如果 request 是一个 CSS 文件,则无需外置化提取 !/\.css$/.test(module.request) ) } }), // 提取 webpack 运行时和 manifest new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'manifest' }), // html模板 new HTMLPlugin({ template: 'index.html' }) ]})if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') { config.plugins.push( // 生产环境下 - 压缩js new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({ compress: { warnings: false } }), // 用于使用service worker来缓存外部项目依赖项。 new SWPrecachePlugin({ cacheId: 'vue-hn', filename: 'service-worker.js', dontCacheBustUrlsMatching: /./, staticFileGlobsIgnorePatterns: [/index\.html$/, /\.map$/] }) )}module.exports = config |
4. webpack.server.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | const webpack = require('webpack')const merge = require('webpack-merge')const base = require('./webpack.base.config')const VueSSRPlugin = require('vue-ssr-webpack-plugin')const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals')module.exports = merge(base, { target: 'node', entry: './src/entry-server.js', devtool: 'source-map', output: { filename: 'server-bundle.js', libraryTarget: 'commonjs2' }, externals: nodeExternals({ // do not externalize CSS files in case we need to import it from a dep whitelist: /\.css$/, "jquery": "$", 'Vue': true, 'VueLazyload': true, '$': true, 'vue-router': 'VueRouter', 'vuex':'Vuex', 'axios': 'axios', // 'element-ui':'ELEMENT', }), plugins: [ new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development'), 'process.env.VUE_ENV': '"server"' }), /* 使用webpack按需代码分割的特性的时候(require.ensure或动态import)结果就是服务端bundle会包含很多分开的文件。 'vue-ssr-webpack-plugin'作用是将其打包为一个单独的JSON文件,这个文件可以传入到bundleRenderer中(server.js),可以极大地简化了工作流。 默认文件名为 `vue-ssr-server-bundle.json`,也可以参数形式传入其他名称 */ new VueSSRPlugin() ]}) |
加完这些,大概是这样子

显然,加如这些不够。
我们还需要在根目录添加
server.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 | const fs = require('fs')const path = require('path')const express = require('express')const compression = require('compression') // 开启gzip压缩const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'const serverInfo = `express/${require('express/package.json').version} ` + `vue-server-renderer/${require('vue-server-renderer/package.json').version}`const app = express()function createRenderer (bundle, template) { return require('vue-server-renderer').createBundleRenderer(bundle, { template, // 缓存 cache: require('lru-cache')({ max: 1000, maxAge: 1000 * 60 * 15 }) })}let rendererif (isProd) { const bundle = require('./dist/vue-ssr-bundle.json') const template = fs.readFileSync(resolve('./dist/index.html'), 'utf-8') renderer = createRenderer(bundle, template)} else { require('./build/setup-dev-server')(app, (bundle, template) => { renderer = createRenderer(bundle, template) })}const serve = (path, cache) => express.static(resolve(path), { maxAge: cache && isProd ? 60 * 60 * 24 * 30 : 0 // 静态资源设置缓存})app.use(compression({ threshold: 0 })) // gzip压缩app.use('/dist', serve('./dist', true)) // 静态资源app.use('/static', serve('./static', true)) // 静态资源 (如:http://localhost:8080/public/logo-120.png)app.use('/manifest.json', serve('./manifest.json', true))app.use('/service-worker.js', serve('./dist/service-worker.js'))app.get('*', (req, res) => { if (!renderer) { return res.end('未渲染成功||wei cheng gong') } const s = Date.now() res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html") res.setHeader("Server", serverInfo) const errorHandler = err => { if (err && err.code === 404) { console.log(404) res.status(404).end('404 | Page Not Found') } else { res.status(500).end('500 | Internal Server Error') console.error(`error during render : ${req.url}`) console.error(err) } } var title = '测试-首页' // 自定义变量(此处用于title) var author ='Anne' // 默认author var keywords ='我是keywords' // 默认keywords var description ='我是description' //默认description renderer.renderToStream({title,author,keywords,description, url: req.url}) .on('error', errorHandler) .on('end', () => console.log(`整体请求: ${Date.now() - s}ms`)) .pipe(res)})const port = process.env.PORT || 3026app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`localhost:${port}`)}) |
在src目录下还有俩:
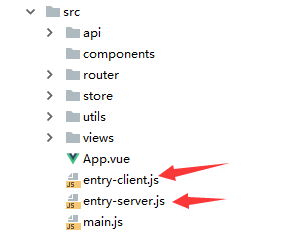
这里注意一下我的入口文件为main.js。
app.js和utils.js文件夹,可不用理会,是项目单分出来的接口文件用axio。我们获取数据接口将在vuex里面写。也就是store文件夹。
entry-client.js:
// entry-client.js 客户端渲染入口文件 import Vue from 'vue' import { app, store, router } from './main' /*Vue-SSR 根据访问的路由会调用当前路由组件中的asyncData方法由服务端调用相关接口,根据数据 生成首屏对应的html,并在返回的html中写入 window.__INITIAL_STATE__ = {服务端请求到的数据} 不需要服务端渲染的数据则在 mounted 中请求接口。*/ /*路由切换时组件的asyncData方法并不会被调用,若该组件存在服务端渲染方法asyncData,可通过下面 三种方式客户端调用,并进行客户端渲染*/ //(1) // 全局mixin,beforeRouteEnter,切换路由时,调用asyncData方法拉取数据进行客户端渲染 // 注意beforeRouteEnter无法直接获取到当前组件this,需使用next((vm)=>{ vm即为this }) 获取 /*Vue.mixin({ beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) { console.log('beforeRouteEnter1') next((vm)=>{ const {asyncData} = vm.$options console.log('beforeRouteEnter1'+ asyncData) if (asyncData) { asyncData(vm.$store, vm.$route).then(next).catch(next) } else { next() } }) } })*/ //(2) // 全局mixin,beforeRouteUpdate,切换路由时,调用asyncData方法拉取数据进行客户端渲染 // beforeRouteUpdate可直接获取到this对象(2.2版本以上) /*Vue.mixin({ beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) { console.log('beforeRouteUpdate2') const { asyncData } = this.$options if (asyncData) { // 传入store与route asyncData(this.$store, this.$route).then(next).catch(next) } else { next() } } })*/ // (3) // 注册全局mixin,所有组件beforeMount时,如果根组件_isMounted为真(即根实例已mounte,该钩子函数是由路由跳转触发的) // 调用asyncData方法拉取数据进行客户端渲染 Vue.mixin({ data(){ //全局mixin一个loading return { //loading:false } }, beforeMount () { const { asyncData } = this.$options; let data=null; //把数据在computed的名称固定为data,防止重复渲染 try{ data=this.data; //通过try/catch包裹取值,防止data为空报错 }catch(e){} if(asyncData&&!data){ //如果拥有asyncData和data为空的时候,进行数据加载 //触发loading加载为true,显示加载器不显示实际内容 //this.loading=true; //为当前组件的dataPromise赋值为这个返回的promise,通过判断这个的运行情况来改变loading状态或者进行数据的处理 (在组件内通过this.dataPromise.then保证数据存在) this.dataPromise=asyncData({store,route:router.currentRoute}) // this.dataPromise.then(()=>{ // //this.loading=false; // }).catch(e=>{ // // this.loading=false; // }) }else if(asyncData){ //如果存在asyncData但是已经有数据了,也就是首屏情况的话返回一个成功函数,防止组件内因为判断then来做的操作因为没有promise报错 this.dataPromise=Promise.resolve(); } } }) // 使用 window.__INITIAL_STATE__ 中的数据替换store中的数据 if (window.__INITIAL_STATE__) { store.replaceState(window.__INITIAL_STATE__) } router.onReady(() => { app.$mount('#app') })
entry-server.js:
// entry-server.js import { app, router, store } from './main' const isDev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' // 开发模式 || 生产模式 export default context => { const s = isDev && Date.now() // 因为有可能会是异步路由钩子函数或组件,所以我们将返回一个 Promise, // 以便服务器能够等待所有的内容在渲染前, // 就已经准备就绪。 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { console.log(context) // push对应访问路径 router.push(context.url) // 等到 router 将可能的异步组件和钩子函数解析完 router.onReady(() => { const matchedComponents = router.getMatchedComponents() // 返回当前路径匹配到的组件 // 匹配不到的路由,reject(),返回 404 if (!matchedComponents.length) { reject({ code: 404 }) } // Promise.all 组件的 asyncData 方法 拿数据 全部数据返回后 为window.__INITIAL_STATE__赋值并 resolve(app) Promise.all(matchedComponents.map(component => { if (component.asyncData) { return component.asyncData({store, route: router.currentRoute}) } })) .then(() => { isDev && console.log(`数据预取: ${Date.now() - s}ms`) context.state = store.state resolve(app) }).catch(reject) }) }) }
同时main.js也需要改:
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import { createRouter } from './router/index' import { createStore } from './store/index' import {sync} from 'vuex-router-sync' //时间过滤器 import './utils/jsontime.js' //title //import titleMixin from './utils/title' //ie //import 'babel-polyfill' require("babel-polyfill"); import axios from 'axios' import VueAxios from 'vue-axios' //import Vuex from'vuex' //import MetaInfo from 'vue-meta-info' Vue.prototype.filterHtml = function (msg) { if (msg) { return msg.replace(/<img/g, "<img style='max-width: 800px;max-height: 500px;margin:10px 30px;'") } return '' }; if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { require('element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'); const ElementUI = require('element-ui'); Vue.use(ElementUI); } // if (process.browser) { // //console.log('浏览器端渲染'); // Vue.use(require('element-ui'),require('element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css')) // } else { // //console.log("非浏览器端渲染"); // } Vue.config.productionTip = false; //Vue.mixin(titleMixin), // Vue.use(Vuex); Vue.use(VueAxios, axios); //Vue.use(MetaInfo); const router = createRouter(); const store = createStore(); sync(store, router); const app = new Vue({ router, store, render: h => h(App) }); export { app, router, store }
这里主要部分还是这几句:其他的一会简单说明,
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import { createRouter } from './router/index' import { createStore } from './store/index' import {sync} from 'vuex-router-sync' Vue.config.productionTip = false; const router = createRouter(); const store = createStore(); sync(store, router); const app = new Vue({ router, store, render: h => h(App) }); export { app, router, store }
还有一个文件:差点忘了那个模板index,html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0"> <title>{{title}}</title> <meta name="keywords" content='{{keywords}}'> <meta name="description" content='{{description}}'> <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" href="/static/favicon.ico"> <style> .Tmain{ margin: 0px; } </style> </head> <body class="Tmain"> <!--vue-ssr-outlet--> </body> </html>
接下来看路由文件:router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' Vue.use(Router) export function createRouter() { return new Router({ mode: 'history', routes: [ { path: '/', name: 'index', component: () =>import('../views/index.vue') }, { path: '/articlex/:id', name: 'articlex', component: resolve => require(['../views/main/article/articlex.vue'], resolve) }, {path: "*", redirect: "/"} ] }) }
这里第一个路由是ssr的异步加载,第二个为懒加载写法,第三个为404,返回到原页面。
还有store/index.js文件,问什么把这个放到最后呢,因为这个文件可以模块化,也可以写到一个里。
在一个里面写:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import axios from 'axios' Vue.use(Vuex) // 数据 let state = { lists: [], // 文章列表 detail: {} // 文章详情 } // 事件 let actions = { // 获取文章列表 fetchLists ({ commit }, data) { return axios.get('https://xxxx/api/v1/topics?page=' + data.page) .then((res) => { if (res.data.success) { commit('setLists', res.data.data) } }) }, // 获取文章详情 fetchDetail ({ commit }, data) { return axios.get('https://xxxx/api/v1/topic/' + data.id) .then((res) => { if (res.data.success) { commit('setDetail', res.data.data) } }) } } // 改变 let mutations = { setLists (state, data) { state.lists = data }, setDetail (state, data) { state.detail = data } } // 获取 let getters = { getLists: state => { return state.lists }, getDetail: state => { return state.detail } } export function createStore () { return new Vuex.Store({ state, actions, mutations, getters }) }
在模块化的话结构这样:

index.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import vuex from 'vuex' import user from './modules/user' import getters from './getters' Vue.use(vuex); export function createStore() { return new vuex.Store({ modules: { user, }, getters }); }
getters.js
const getters = { lists: state => state.user.lists, detail: state => state.detail, }; export default getters
modules/user.js
import axios from 'axios' const user = { state: { lists: [], detail:{}, }, mutations: { SET_LISTS: (state, lists) => { state.lists = lists; }, SET_DETAIL: (state, detail) => { state.detail = detail; }, }, actions: { // 获取文章列表 fetchLists ({ commit }, data) { return axios.get('https://XXX/api/v1/topics?page=' + data.page) .then((res) => { if (res.data.success) { commit('SET_LISTS', res.data.data) } }) }, // 获取文章详情 fetchDetail ({ commit }, data) { return axios.get(XXXX/api/v1/topic/' + data.id) .then((res) => { if (res.data.success) { commit('SET_DETAIL', res.data.data) } }) } } // 前端 登出 FedLogOut({commit}) { return new Promise(resolve => { commit('SET_LISTS', ""); commit('SET_DETAIL', ""); resolve(); }); }, } }; export default user;
写到这也算完成一半多了,继续往下看
一个页面怎么才算是开始渲染,用到了asyncData,
由于项目保密原因我只展示一页内容仅供参考:index.vue
<template> <div> {{lists.id}} </div> </template> <script> import axios from 'axios' export default { /** * [SSR获取所有组件的asyncData并执行获得初始数据] * @param {[Object]} store [Vuex Store] * 此函数会在组件实例化之前调用,所以它无法访问 this。需要将 store 和路由信息作为参数传递进去: */ asyncData (store, route) { return store.dispatch('fetchLists' ) // 服务端渲染触发 }, name: "home", // 数据 data() { return { } }, // 计算属性 computed: { lists () { return this.$store.getters.lists // 文章列表 }, }, mounted() { }, // 方法 methods: { }, // 子组件 components: { } } </script> <!--当前组件的样式 --> <style scoped> </style>
最后启动了,改为
package.json
"scripts": {
"dev": "node server",
"start": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production node server",
"build": "rimraf dist && npm run build:client && npm run build:server",
"build:client": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.client.config.js --progress",
"build:server": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.server.config.js --progress"
},
// 安装依赖包
npm install
// 开发模式
npm run dev
// 生产模式
npm run build
npm run start这样,就算是结束一个简单的渲染了,下面我将介绍我在开发中遇到的问题以及解决方法:
1.当我写完这些后发现一个大的问题,路径问题:之前写的项目有的路径用@/api/sre.js等。
由于重新写完发现@不好使了,没太深究直接../../绝对路径。
2.npm install 安装依赖插件。都安什么呢?
如果少个依赖,看报错信息《Can't find xxxx dependence》。
我这里大致总结了写=些,项目直接码上:
npm install -g npm (更新npm)
npm i vue-server-renderer(一定要和vue版本一致,别问为啥,官方大大)
npm install babel-plugin-component --save-dev(element)
npm i axios buble buble-loader compression cross-env es6-promise express http-proxy-middleware lru-cache serve-favicon sw-precache-webpack-plugin vue-ssr-webpack-plugin vue-style-loader vuex vuex-router-sync webpack-hot-middleware webpack-merge webpack-node-externals
(lru-cache4.0.2,这个插件报错,就换这个版本)
npm install --save babel-polyfill (ie兼容)
3。安装element-ui,这个大坑,趟浑水了。
1. npm i element-ui -S
2. main.js里这样引入就可以了。原因自己猜去吧
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') {
require('element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css');
const ElementUI = require('element-ui');
Vue.use(ElementUI);
}
// if (process.browser) {
// //console.log('浏览器端渲染');
// Vue.use(require('element-ui'),require('element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'))
// } else {
// //console.log("非浏览器端渲染");
// }
3.发现一个问题没有过多探究,好像首页和他的组件不能用懒加载方式。有待研究,因为我用懒加载,报错 error during render : / Error: stream.push() after EOF at readableAddChun
4.ie浏览器不兼容问题。
首页模板index.html 添加
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=7,IE=9"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=7,9"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=Edge,chrome=1"> #以上代码IE=edge告诉IE使用最新的引擎渲染网页,chrome=1则可以激活Chrome Frame.
npm install --save babel-polyfill
main.js里加
require("babel-polyfill");//或者import "babel-polyfill";//注意放的位置
webpack.base.config.js里加
module.exports = {
entry: ["babel-polyfill", "./app/js"]
};
5.假如asyncData 调用多个vuex怎么写,这样就能并发
asyncData ({ store , route }) {
let data1= Promise.all([
store.dispatch('ghnavList'),
store.dispatch('gxnavList'),
store.dispatch('getdonglist',{artdongid:21}),
store.dispatch('getyoulist',{artyouid:22}),
store.dispatch('getzhilist',{artzhiid:23})
])
return data1
},
6.第一次完成项目的时候,发现页面渲染了两次,就是一个页面显示两个一样的版块,很是揪心,于是我将index.html里的文件搞成这样:
<body > <div id="app"> <!--vue-ssr-outlet--> </div> </body>
指标不治本,下次完善。
7.head管理。
新建一个head.js
function getHead (vm) { const { head } = vm.$options; if (head) { return typeof head === 'function' ? head.call(vm) : head; } } const serverHeadMixin = { created () { const head = getHead(this); if (head) { if (head.title) this.$ssrContext.title = `${head.title}`; if (head.author) this.$ssrContext.author = `${head.author}`; if (head.keywords) this.$ssrContext.keywords = head.keywords; if (head.description) this.$ssrContext.description = head.description; } } }; const clientHeadMixin = { mounted () { const head = getHead(this); if (head) { if (head.title) document.title = `${head.title}`; if (head.author) document.querySelector('meta[name="author"]').setAttribute('content', `${head.author}`); if (head.keywords) document.querySelector('meta[name="keywords"]').setAttribute('content', head.keywords); if (head.description) document.querySelector('meta[name="description"]').setAttribute('content', head.description); } } }; export default process.env.VUE_ENV === 'server' ? serverHeadMixin : clientHeadMixin;
在main.js引用
import headMixin from './utils/head'; Vue.mixin(headMixin);
当然index.html也做修改
<head>
<title>{{title}}</title>
<meta name="keywords" content='{{keywords}}'>
<meta name="description" content='{{description}}'>
</head>
在页面引用
export default { name: 'index', head(){ return { 'title': '你好', 'author': '星涑' }; }, }
在server.js里配置默认
var title = '测试-首页' // 自定义变量(此处用于title) var author ='Anne' // 默认author var keywords ='我是keywords' // 默认keywords var description ='我是description' //默认description renderer.renderToStream({title,author,keywords,description, url: req.url})
现在时间24:00整,有很多东西还没有想到,来不及整理了,希望有更多的人看到我文章,对其进行评价补充,我将不胜感激。
还是墨迹那句话,希望有更多的人支持我,点个关注。我会努力发表更好的文章
QQ:1763907618------备注:博客园







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异