| 名称 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 博客班级 | 班级链接 |
| 作业要求 | 作业链接 |
| 学号 | 3180701126 |
一.实验目的
1.理解感知器算法原理,能实现感知器算法;
2.掌握机器学习算法的度量指标;
3.掌握最小二乘法进行参数估计基本原理;
4.针对特定应用场景及数据,能构建感知器模型并进行预测。
二.实验内容
1.安装Pycharm,注册学生版。
2.安装常见的机器学习库,如Scipy、Numpy、Pandas、Matplotlib,sklearn等。
3.编程实现感知器算法。
4.熟悉iris数据集,并能使用感知器算法对该数据集构建模型并应用
三.实验过程及结果
实验代码及注释
1、
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
2、
# load data
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)//将列名设置为特征
df['label'] = iris.target//增加一列为类别标签
3、
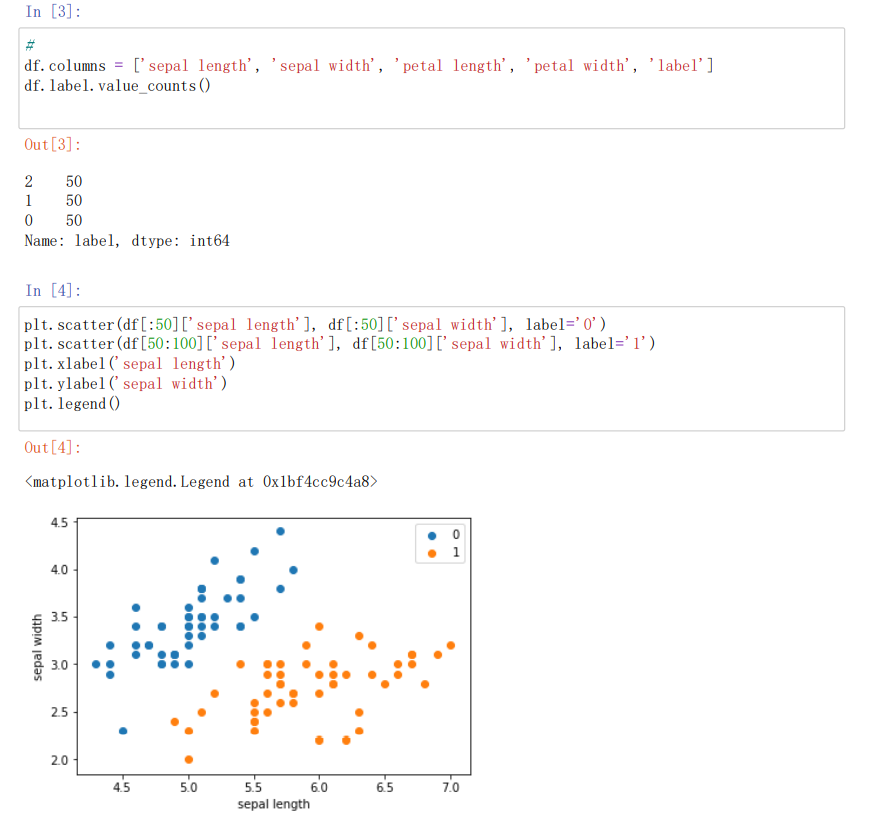
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']//将各个列重命名
df.label.value_counts()value_counts//确认数据出现的频率
4、
plt.scatter(df[:50]['sepal length'], df[:50]['sepal width'], label='0')//绘制散点图
plt.scatter(df[50:100]['sepal length'], df[50:100]['sepal width'], label='1')
plt.xlabel('sepal length')//给图加上图例
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
5、
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])//按行索引,取出第0,1,-1列
6、
X, y = data[:,:-1], data[:,-1]//X为sepal length,sepal width y为标签
7、
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])//将两个类别设重新设置为+1 —1
8、
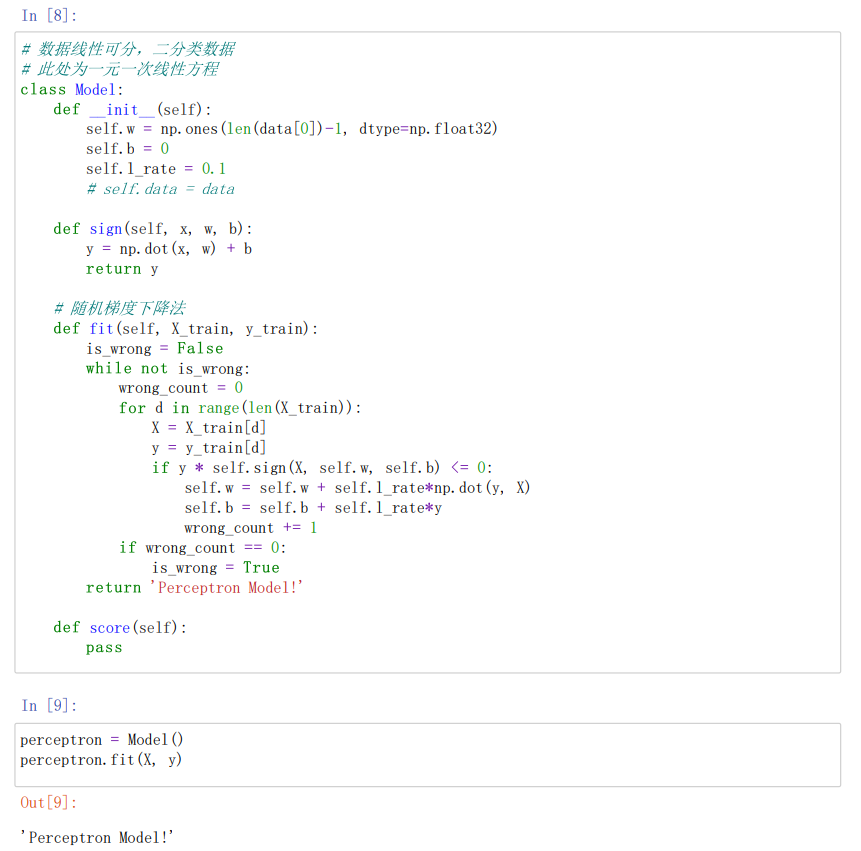
#数据线性可分,二分类数据
#此处为一元一次线性方程
class Model:
def init(self)://将参数w1,w2置为1 b置为0 学习率为0.1
self.w = np.ones(len(data[0])-1, dtype=np.float32) //data[0]为第一行的数据len(data[0]=3)这里取两个w权重参数
self.b = 0
self.l_rate = 0.1
%# self.data = data
def sign(self, x, w, b):
y = np.dot(x, w) + b
return y
# 随机梯度下降法
def fit(self, X_train, y_train)://拟合训练数据求w和b
is_wrong = False//判断是否误分类
while not is_wrong:
wrong_count = 0
for d in range(len(X_train))://取出样例,不断的迭代
X = X_train[d]
y = y_train[d]
if y * self.sign(X, self.w, self.b) <= 0://根据错误的样本点不断的更新和迭代w和b的值(根据相乘结果是否为负来判断是否出错,本题将0也归为错误)
self.w = self.w + self.l_ratenp.dot(y, X)
self.b = self.b + self.l_ratey
wrong_count += 1
if wrong_count == 0://直到误分类点为0 跳出循环
is_wrong = True
return 'Perceptron Model!'
def score(self):
pass
9、
#拟合
perceptron = Model()#生成一个算法对象
perceptron.fit(X, y)#将测试数据代入算法中
10、
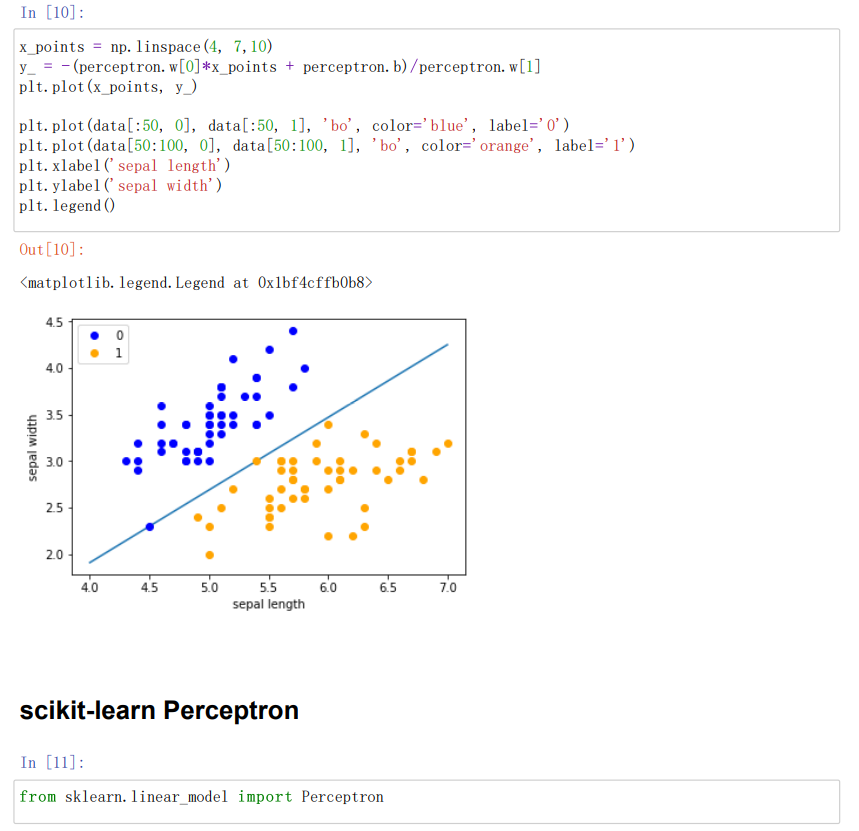
#画出超平面
x_points = np.linspace(4, 7,10)//x轴的划分
y_ = -(perceptron.w[0]*x_points + perceptron.b)/perceptron.w[1]
plt.plot(x_points, y_)//绘制模型图像(数据、颜色、图例等信息)
plt.plot(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], 'bo', color='blue', label='0')
plt.plot(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], 'bo', color='orange', label='1')
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
11、
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron//定义感知机(下面将使用感知机)
12、
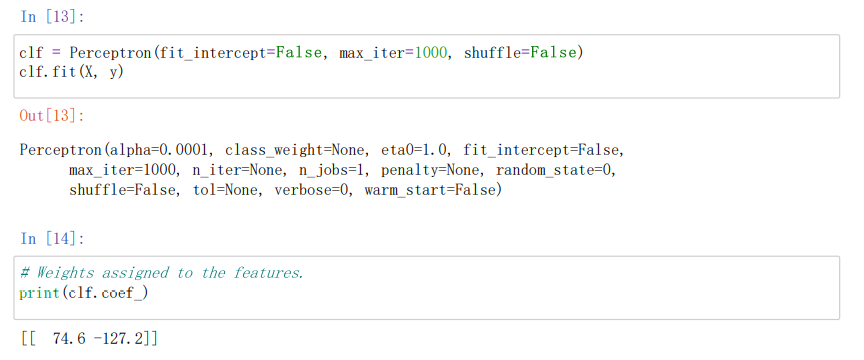
clf = Perceptron(fit_intercept=False, max_iter=1000, shuffle=False)
clf.fit(X, y)//使用训练数据拟合
13、
%# Weights assigned to the features.
print(clf.coef_)//输出感知机模型参数
14、
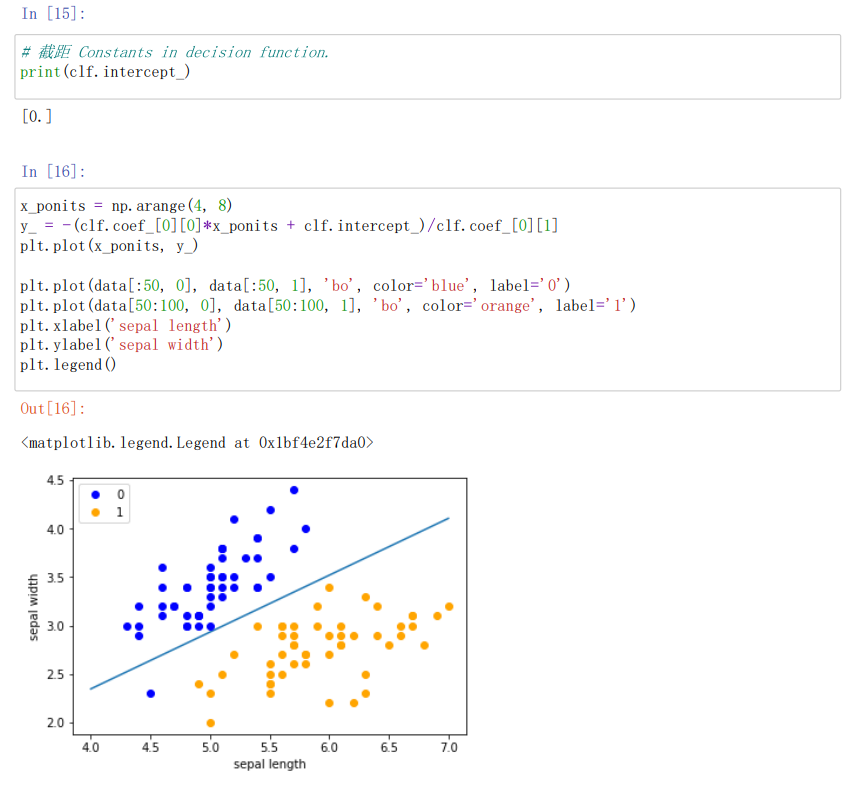
%# 截距 Constants in decision function.
print(clf.intercept_)//输出感知机模型参数
15、
#画出sklearn结果的散点图
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)#x,为4,5,6,7,默认步长为1,起始为4,终止为8,不取8
y_ = -(clf.coef_[0][0]*x_ponits + clf.intercept_)/clf.coef_[0][1]#绘制超平面
plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)
plt.plot(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], 'bo', color='blue', label='0')#将数据的前50个数据绘制散点图
plt.plot(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], 'bo', color='orange', label='1')#将数据的50-100之间的数据绘制成散点图
plt.xlabel('sepal length')#x坐标命名
plt.ylabel('sepal width')#y坐标命名
plt.legend()
实验结果截图


psp表格
| psp2.1 | 任务内容 | 计划完成需要的时间(min) | 实际完成需要的时间(min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 110 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 110 | 150 |
| Analysis | 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 10 | 10 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 30 | 40 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 5 | 10 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 5 | 5 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 10 | 12 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 30 | 20 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 5 | 7 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 8 | 16 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 9 | 6 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 5 | 5 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 3 | 1 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 3 | 3 |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号