CS231n 2016 通关 第二章-KNN 作业分析
KNN作业要求:
1、掌握KNN算法原理
2、实现具体K值的KNN算法
3、实现对K值的交叉验证
1、KNN原理见上一小节
2、实现KNN
过程分两步:
1、计算测试集与训练集的距离
2、通过比较label出现比例的方式,确定选取的最终label
代码分析:
cell1 - cell5 对数据的预处理
cell6创建KNN类,初始化类的变量,此处是传递测试数据和训练数据
cell7实现包含两个循环的KNN算法:
通过计算单一的向量与矩阵之间的距离(在之前的cell中,已经将图像转换成列:32*32 的图像转换为 1*3072,,
测试集是500张:500*3072,训练集是5000张:5000*3072)
代码基础:使用python 2.7.9 + numpy 1.11.0
技巧:使用help 查看相关函数的用法,或者google
举例:np.square
q 键退出help
可知,np.square() 为了加快运算速度,是用c写的,在这里查不到具体用法。google查看:

例子为计算数组[-1j,1]里边各元素的平方,得到的结果为[-1,1]
代码:实现compute_distances_two_loops(self, X)
1 def compute_distances_two_loops(self, X): 2 """ 3 Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point 4 in self.X_train using a nested loop over both the training data and the 5 test data. 6 7 Inputs: 8 - X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data. 9 10 Returns: 11 - dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j] 12 is the Euclidean distance between the ith test point and the jth training 13 point. 14 """ 15 num_test = X.shape[0] 16 num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] 17 dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) 18 for i in xrange(num_test): 19 for j in xrange(num_train): 20 ##################################################################### 21 # TODO: # 22 # Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth # 23 # training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should # 24 # not use a loop over dimension. # 25 ##################################################################### 26 dists[i,j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i,:]-self.X_train[j,:]))) 27 ##################################################################### 28 # END OF YOUR CODE # 29 ##################################################################### 30 return dists
实现对一张测试图像对应的矩阵与一张训练集图像的矩阵做L2距离。
也可以用numpy.linalg.norm函数实现:
此函数执行的公式: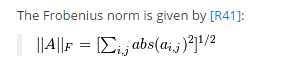
所以核心代码可以写作:
dists[i,j] = np.linalg.norm(self.X_train[j,:]-X[i,:])
cell8 得到的距离可视化,白色表示较大的距离值,黑色是较小距离值
cell9 实现K=1的label预测
代码:实现 classifier.predict_labels()
1 def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1): 2 """ 3 Given a matrix of distances between test points and training points, 4 predict a label for each test point. 5 6 Inputs: 7 - dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j] 8 gives the distance betwen the ith test point and the jth training point. 9 10 Returns: 11 - y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the 12 test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i]. 13 """ 14 num_test = dists.shape[0] 15 y_pred = np.zeros(num_test) 16 for i in xrange(num_test): 17 # A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to 18 # the ith test point. 19 closest_y = [] 20 count = [] 21 ######################################################################### 22 # TODO: # 23 # Use the distance matrix to find the k nearest neighbors of the ith # 24 # testing point, and use self.y_train to find the labels of these # 25 # neighbors. Store these labels in closest_y. # 26 # Hint: Look up the function numpy.argsort. # 27 ######################################################################### 28 buf_labels = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i,:])] 29 closest_y = buf_labels[0:k] 30 ######################################################################### 31 # TODO: # 32 # Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you # 33 # need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. # 34 # Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller # 35 # label. # 36 ######################################################################### 37 #for j in closest_y : 38 # count.append(closest_y.count(j)) 39 #m = max(count) 40 #n = count.index(m) 41 #y_pred[i] = closest_y[n] 42 c = Counter(closest_y) 43 y_pred[i] = c.most_common(1)[0][0] 44 ######################################################################### 45 # END OF YOUR CODE # 46 ######################################################################### 47 48 return y_pred
步骤:
1.使用numpy.argsort对所以距离进行排序,得到排序后的索引。
2.通过索引找到对应的label
3.通过collection包的Counter,对label进行统计表示
4.通过counter的Most common方法得到出现最多的label
cell9 在计算完成后,同时实现了准确率的计算

cell10 实现K =5的KNN
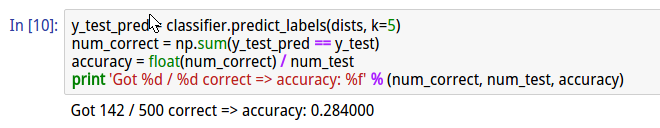
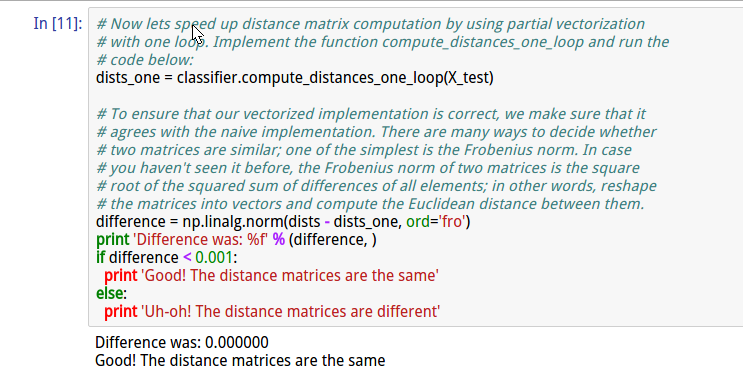
cell11 实现compute_distances_one_loop(X_test)
代码:
1 def compute_distances_one_loop(self, X): 2 """ 3 Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point 4 in self.X_train using a single loop over the test data. 5 6 Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops 7 """ 8 num_test = X.shape[0] 9 num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] 10 dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) 11 for i in xrange(num_test): 12 ####################################################################### 13 # TODO: # 14 # Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training # 15 # points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. # 16 ####################################################################### 17 buf = np.square(self.X_train-X[i,:]) 18 dists[i,:] = np.sqrt(np.sum(buf,axis=1)) 19 ####################################################################### 20 # END OF YOUR CODE # 21 ####################################################################### 22 return dists
并通过计算一个循环与两个循环分别得到的结果的差值平方,来衡量准确性。
cell12 实现完全的数组操作,不使用循环。
1 def compute_distances_no_loops(self, X): 2 """ 3 Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point 4 in self.X_train using no explicit loops. 5 6 Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops 7 """ 8 num_test = X.shape[0] 9 num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] 10 dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) 11 ######################################################################### 12 # TODO: # 13 # Compute the l2 distance between all test points and all training # 14 # points without using any explicit loops, and store the result in # 15 # dists. # 16 # # 17 # You should implement this function using only basic array operations; # 18 # in particular you should not use functions from scipy. # 19 # # 20 # HINT: Try to formulate the l2 distance using matrix multiplication # 21 # and two broadcast sums. # 22 ######################################################################### 23 #buf = np.tile(X,(1,num_train)) 24 buf = np.dot(X, self.X_train.T) 25 buf_test = np.square(X).sum(axis = 1) 26 buf_train = np.square(self.X_train).sum(axis = 1) 27 dists = np.sqrt(-2*buf+buf_train+np.matrix(buf_test).T) 28 ######################################################################### 29 # END OF YOUR CODE # 30 ######################################################################### 31 return dists
使用(a-b)2=a2+b2-2ab 的公式
27行: 此时buf_test 为500*1数组 buf_train为5000*1的数组 需要得到500*5000的数组 此处通过构造矩阵的方式进行broadcast
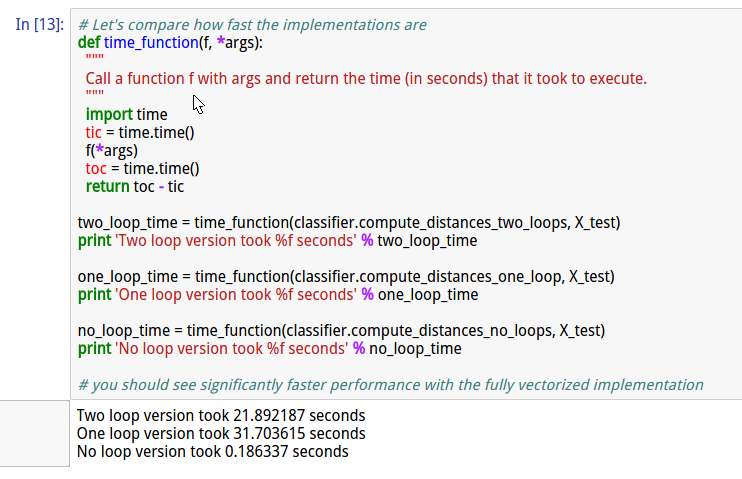
cell13 比较3种方案的执行效率
cell14 交叉验证
交叉验证的思想在上一节有解释过了
代码:(其中带有注释)
1 num_folds = 5 2 k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100] 3 4 X_train_folds = [] 5 y_train_folds = [] 6 ################################################################################ 7 # TODO: # 8 # Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and # 9 # y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where # 10 # y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. # 11 # Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. # 12 ################################################################################ 13 X_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds) 14 y_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds) 15 ################################################################################ 16 # END OF YOUR CODE # 17 ################################################################################ 18 19 # A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find 20 # when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation, 21 # k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different 22 # accuracy values that we found when using that value of k. 23 k_to_accuracies = {} 24 25 26 ################################################################################ 27 # TODO: # 28 # Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each # 29 # possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, # 30 # where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the # 31 # last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all # 32 # values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. # 33 ################################################################################ 34 for k in k_choices: 35 k_to_accuracies[k] = [] 36 37 for k in k_choices: 38 print 'evaluating k=%d' % k 39 for j in range(num_folds): 40 #get validation 41 X_train_cv = np.vstack(X_train_folds[0:j]+X_train_folds[j+1:]) 42 X_test_cv = X_train_folds[j] 43 y_train_cv = np.hstack(y_train_folds[0:j]+y_train_folds[j+1:]) 44 y_test_cv = y_train_folds[j] 45 #train 46 classifier.train(X_train_cv, y_train_cv) 47 dists_cv = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_test_cv) 48 #get accuracy 49 y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists_cv, k) 50 num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test_cv) 51 accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test 52 #add j th accuracy of k to array 53 k_to_accuracies[k].append(accuracy) 54 ################################################################################ 55 # END OF YOUR CODE # 56 ################################################################################ 57 58 # Print out the computed accuracies 59 for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies): 60 for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]: 61 print 'k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy)
cell15 显示k值对应的准确率

上述包含了均值和标准差
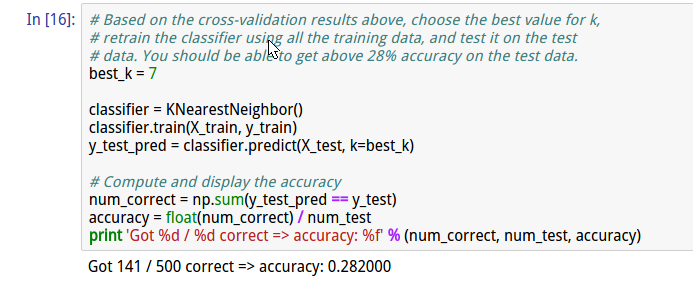
cell16 使用最优值,得到较好的准确率
总结:
整体来说,第一个作业难度较大,主要难度不是在算法部分,而是在熟悉python相关函数与相应的用法方面。对于python大神而言,难度低。
但是经过扎实的第一次作业后,后边的作业相对简单了。之后的作业细节方面讲解的少些。
附:通关CS231n企鹅群:578975100 validation:DL-CS231n




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号