论文笔记: Mutual Learning to Adapt for Joint Human Parsing and Pose Estimation
Mutual Learning to Adapt for Joint Human Parsing and Pose Estimation
2018-11-03 09:58:58
Code: https://github.com/NieXC/pytorch-mula
Related Paper: Deep mutual learning Code: https://github.com/YingZhangDUT/Deep-Mutual-Learning
1. Background and Motivation:
本文提出一种模型 MuLA(Mutual Learning to Adapt)来调整模型,来更好的完成行人解析和姿态估计的问题。之所以会这么做,是因为这两个任务是可以相互协助,互相补充的:Human pose can offer structured information for body part segmentation and lebelling, and on the other hand human parsing can facilitate localizing body joints in difficult scenarios,如图 1 所示:
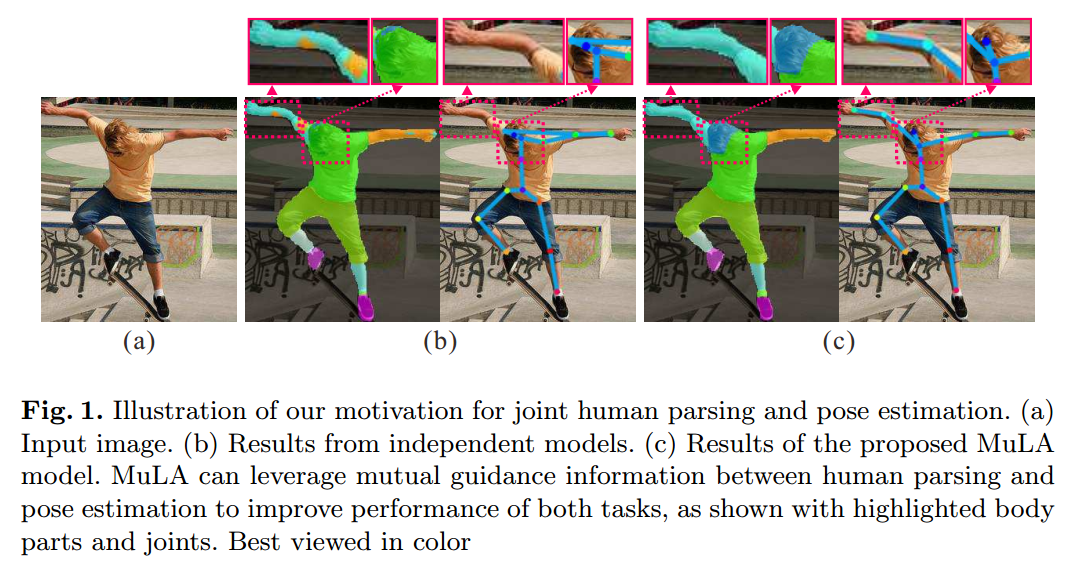

图 1 给出了案例,考虑到这两个任务之间的 mutual guidance information,可以有效的协助改善 parsing 和 localization 的精度。
受到该观察的启发,已经有工作开始借助这种引导信息,来改善这两个任务的性能。但是,现有的方法通常分别训练一个特定的模型,并且用这种引导信息来作为后期处理,从而有如下几个劣势:
1). 严重依赖于手工设计的特征;
2). 仅在 inference procedure 利用该 guidance information,而在 training stage 并没有增强模型的 capacity;
3). 前人工作都是 one-stop solutions,而不能迭代的增强模型,从而改善结果;
4). 这些模型都不是 end-to-end learning。
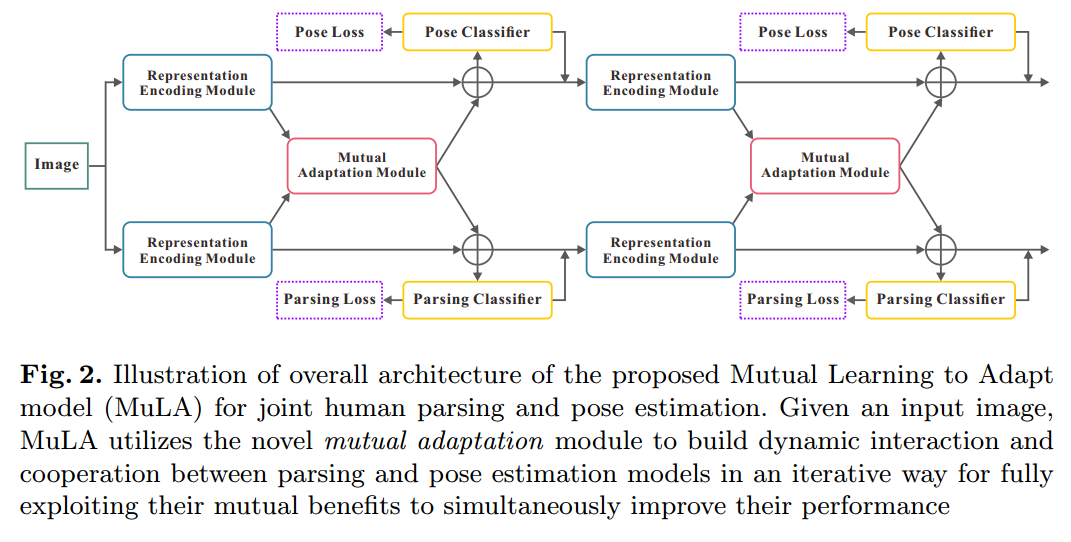
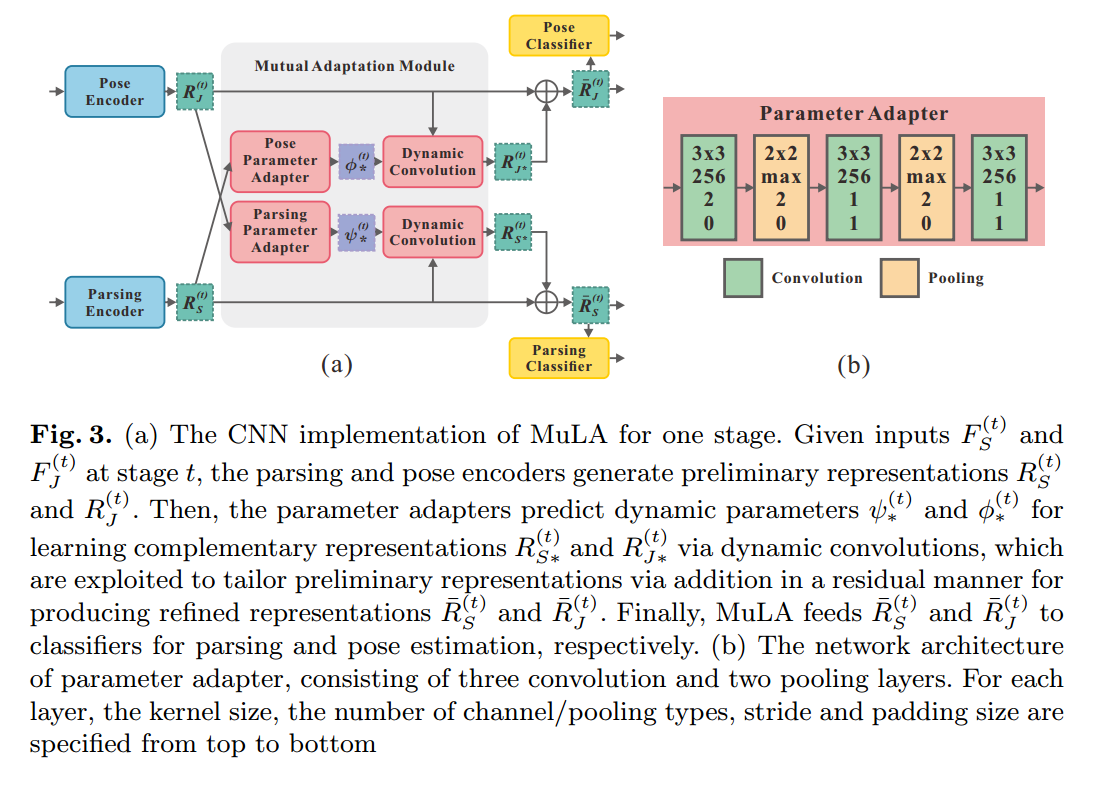
为了解决上述问题,本文提出一种 Mutual Learning to Adapt (MuLA)model 来充分,系统的探索 mutual guidance information。流程图如下所示,该 Mutual Adaptation Module 可以是一个迭代的过程,从而可能会学习到更好的表达。
2. The Details of MuLA:
本文采用 ![]() 来表示 parsing 和 pose models。带有星号 * 的下标表示 the parameters are adaptable to other task。然后本文所提出的 MuLA 模型可以表达成如下迭代学习的形式:
来表示 parsing 和 pose models。带有星号 * 的下标表示 the parameters are adaptable to other task。然后本文所提出的 MuLA 模型可以表达成如下迭代学习的形式:
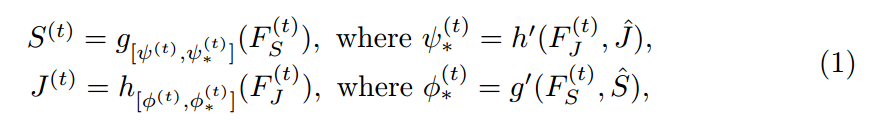
其中,t 表示的迭代次数。$\hat(S)$ 和 $\hat{J}$ 是 parsing 和 pose annotations,F 表示提取出来的特征。如图 2 所示,MuLA 是由三个部分构成的:a representation encoding module, a mutual adaptation module and a classification module。 具体来说,the representation encoding module 是由两个 encoders 对特征进行转换,得到 high-level preliminary representations。the mutual adaptation module 的目标是调整参数,通过两个任务的辅助引导信息,使其增强原始的特征表达。受到 “Learning to Learn” framework 的启发,为了达到快速和高效的 adaptation,在函数 g'(*), h'(*) 的内部,我们设计了两个可学习的 adapters ![]() ,来学习预测这些 adaptive parameters。对于可靠和鲁棒的参数预测,我们从
,来学习预测这些 adaptive parameters。对于可靠和鲁棒的参数预测,我们从 ![]() 中得到最高层的表达,作为 mutual guidance information。也就是说,所设计的两个 adapters
中得到最高层的表达,作为 mutual guidance information。也就是说,所设计的两个 adapters ![]() 将特征作为输入,然后输出调整后的参数,即:
将特征作为输入,然后输出调整后的参数,即:
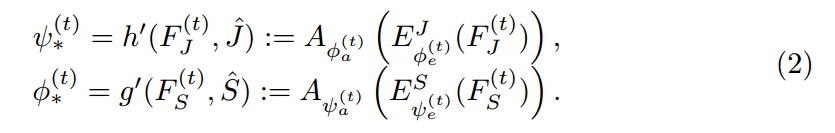
此处,![]() 可以通过结合两个任务之间的互引导信息(mutual guidance information),制作原始的表达,以得到更好的解析和姿态估计的结果,并且用
可以通过结合两个任务之间的互引导信息(mutual guidance information),制作原始的表达,以得到更好的解析和姿态估计的结果,并且用 ![]() 来解码推导出来的 adaptive encoders in MuLA。The mutual adaptation module allows for dynamic interaction and cooperation between two tasks within MuLA for fully exploiting their mutual benefits。
来解码推导出来的 adaptive encoders in MuLA。The mutual adaptation module allows for dynamic interaction and cooperation between two tasks within MuLA for fully exploiting their mutual benefits。
MuLA 利用两个分类器根据 mutual adaptation module 来预测行人解析结果 $S_{(t)}$ 和姿态估计结果 $J_{(t)}$。为了迭代的探索 mutual guidance information,我们设计了两个 mapping modules ![]() 来特征表达以及预测结果映射到下一个阶段的输入,即:
来特征表达以及预测结果映射到下一个阶段的输入,即:
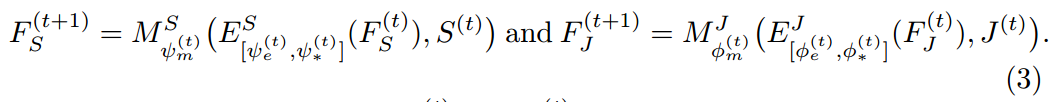
为了训练 MuLA,我们在 human parsing 和 pose estimation 的任务上利用 GT 监督信息,并且定义了如下的损失函数:
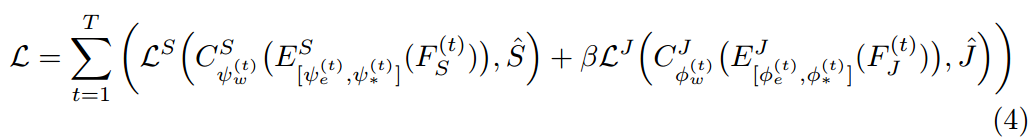
其中,T 是 MuLA 的总迭代次数。第一个和 第二项损失函数,分别是 human parsing 和 pose estimation 的损失函数。
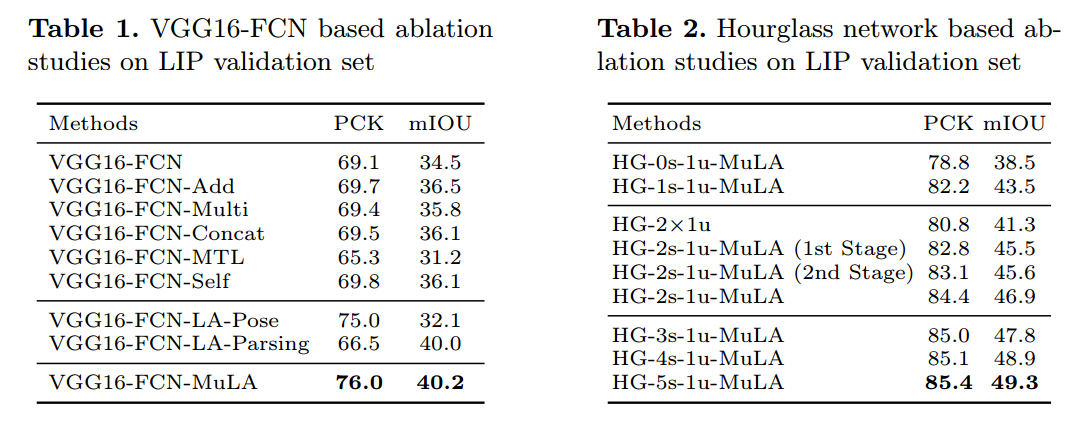
3. Experimental Results:
==



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号