Siam R-CNN: Visual Tracking by Re-Detection
Siam R-CNN: Visual Tracking by Re-Detection
2019-12-02 22:21:48
Paper:https://128.84.21.199/abs/1911.12836
Code: 静候佳音
1. Background and Motivation:
本文尝试从 Tracking by Re-Detection 的角度来处理跟踪问题,提出一种新颖的 re-detector,即将 Faster-RCNN 结合到 Siamese architecture 中,通过在一个图像中任何位置进行重新检测 template object,判断给定的 region proposal 是否是同一个物体,然后对该物体进行 BBox 的回归。本文所提出的 two-stage re-detection architecture 对物体的外观和长宽比有较好的鲁棒性。Tracking by Re-detection 已经有较长的历史,但是这种方法仍然有局限性是因为 distractor objects 和 template object 非常相似的时候,很难确定物体的位置。对于相似物体的挑战,前人的方法或者利用较强的空间先验(Spatial Priors)或者 在线更新(Online Adaptation)的方式来解决,但是这些方法都可能会导致 model drift。
本文在 Siam R-CNN re-detector 的基础之上,提出两个改进点来解决 distractor 的问题:
1). 本文提出一种新颖的 hard example mining 方法,对困难的 distractors 进行特殊的训练;
2). 提出一种新颖的 Tracklet Dynamic Programming Algorithm (TDPA),该方法可以同时跟踪所有潜在的目标物体,包括:distractor objects, 通过从前一帧进行 re-detect 所有的物体候选 BBox,并将这些 BBox 划分为 tracklets(short object tracks)。然后利用动态规划的思想,选择当前时刻最优的 object。通过显示建模 motion 和 interaction of all potential objects,然后从检测中得到的相似物体进行 pooling, 得到 tracklets,Siam R-CNN 可以有效的进行 long-term tracking,对 tracker drift 有较好的抑制,在物体消失后,可以有效地进行重检测。
效率方面,该方法可以在 ResNet-101 上达到 4.7 FPS,在 ResNet-50 上取得 15 FPS 的速度。
2. The Proposed Method:
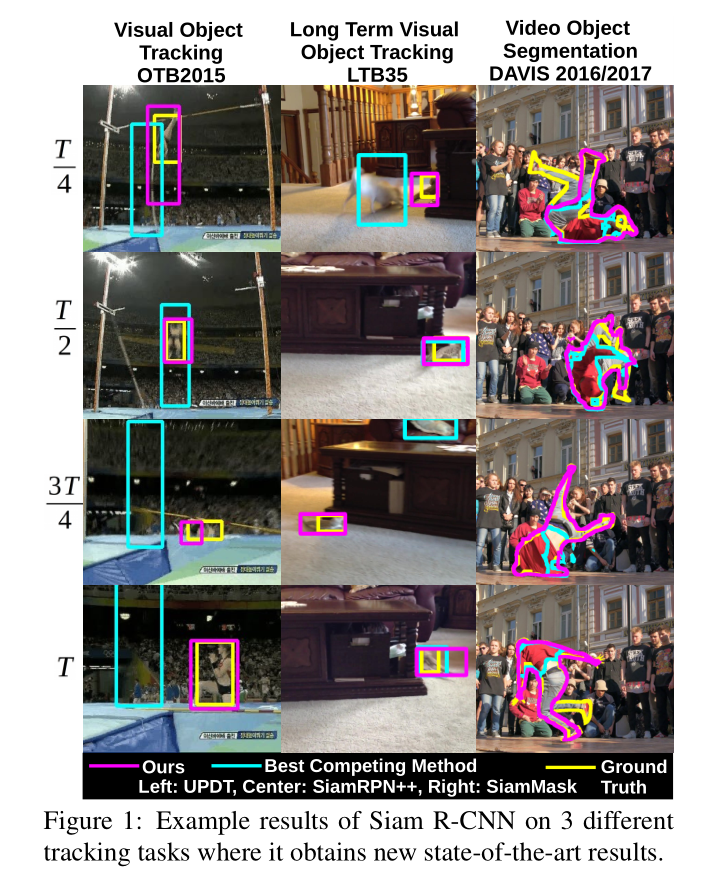
本文所提出的 Siam R-CNN 方法示意图如下图所示:
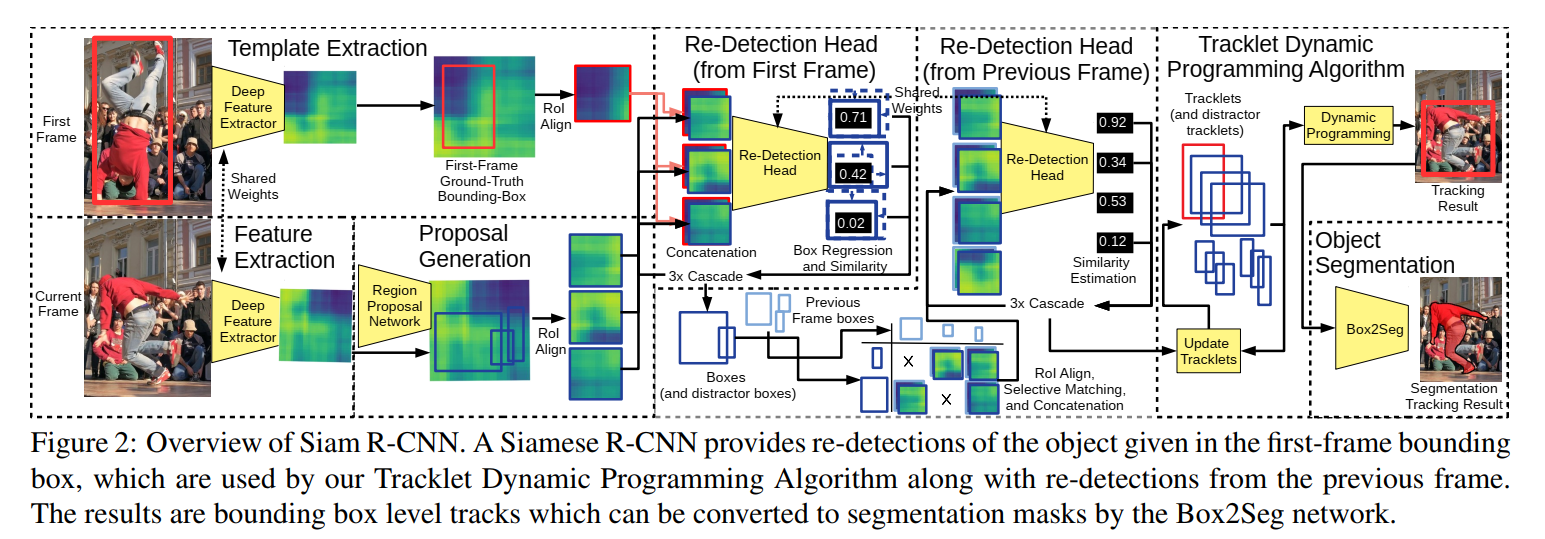
可以看到,本文方法是由多个模块构成的: CNN+RPN 生成 proposal,然后作者还把第一帧的物体也抠出来和提取的 proposal 组合到一起;输入到 Re-detection 模块中。
2.1. Siam R-CNN:
本小节主要是讲了如何将 Faster RCNN 的那一套用于 Proposal 生成,来得到多个候选。
2.2 Video Hard Example Mining:
在传统 Faster RCNN 训练阶段,negative examples 是从 target image 上用 RPN 来采样得到的。但是,在许多图像中,仅有少量的 negative examples。为了最大化 re-detection head 的判别能力,作者认为需要在 hard negative samples 上进行训练。类似的思路在物体检测和跟踪上也都被广泛的应用。
Embedding Network.
一种直观的方法选择相关的 videos 以得到 hard negative examples 的是:寻找与当前物体属于同一个类比的物体。然而,物体的类别标签并不总是可靠,一些同类的物体很容易区分,不同类别的物体反而可能是理想的 hard negative。所以,本文受到 person re-identification 的影响,提出利用 embedding network 的方法,将 Ground truth BBox 中的物体映射为 embedding vector 来表示目标物体。本文利用 PReMVOS 提出的网络,该网络是在 COCO 数据集上用 batch-hard triplet loss 来训练得到的:two distinct persons should be far away in the embedding space, while two crops of the same person iin different frames shoule be close.
Index Structure:
我们接下来构建一个有效的索引结构来估计紧邻 queries,然后用于寻找所需要跟踪的物体在 embedding space 中的最近邻。图 3 展示了一些检索得到的 negative examples。

Training Procedure.
本文对训练数据的每一个 Ground truth BBox 都提取其 RoI-aligned features。在每一个时刻,随机的选择一个 video 和 object,然后随机的选择一个 reference 和 target frame。在此之后,作者用上一节提到的 indexing structure 来检索 10000 个紧邻 reference box,从中选择出 100 个 negative training examples。
2.3 Tracklet Dynamic Programming Algorithm:
本文所提出的 片段动态规划算法(Tracklet Dynamic Programming Algorithm)显示对感兴趣目标物体和潜在的 distrators 都进行跟踪,所以 distractor objects 可以得到抑制。为了达到这个目的,TDPA 保持了一组 tracklets,即:short sequences of detections。然后用基于 scoring algorithm 的方法来进行 dynamic programming 方式来选择最优的结果。每一个 detection 都定义为:a bounding box, a re-dection score, and its RoI-aligned features。此外,each detection 是 tracklet 的组成部分。每一个 tracklet 都有一个 start 和 end time,并且由 a set of detections 来定义。
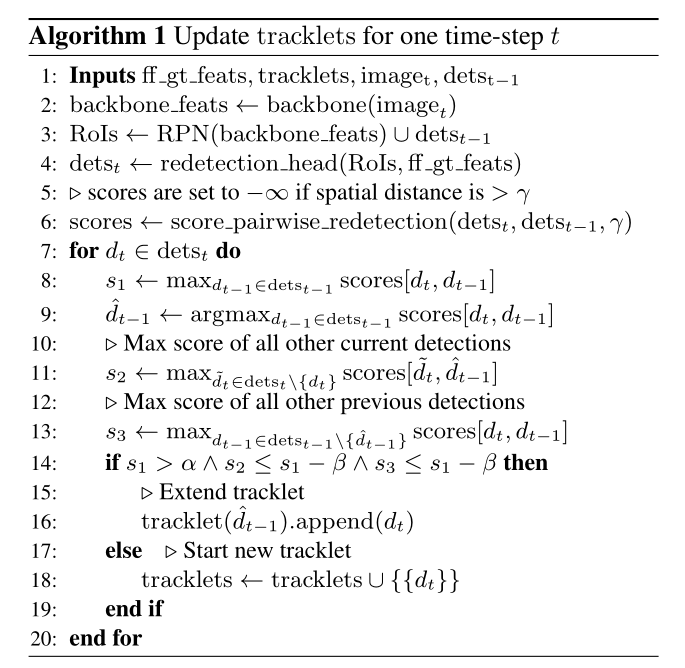
Tracklet Building.
首先提取第一帧 ground truth BBox 的 features,并且用于初始化 tracklet。对于每一个新的视频帧来说,我们采用如下的方式来更新 tracklets(如算法1 所示):
1. 我们提取当前帧的 backbone features,然后用 RPN 来评价当前的 feature。
==


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号