LeetCode Weekly Contest 6
leetcode现在每周末举办比赛,这是今天上午参加的比赛的题解。
题目难度不算大,两个easy,一个medium,一个hard。hard题之前接触过,所以做得比较顺利。
1. Sum of Left Leaves(Leetcode 404 Easy)
Find the sum of all left leaves in a given binary tree.
Example:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively. Return 24.
分析:比较简单的二叉树问题。二叉树问题大部分用递归就能解决,本题就是traverse的变形,这里加一个flag判断是左子树还是右子树即可。
代码:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 private: 12 int result = 0; 13 void traverse(TreeNode* root, int flag) { 14 if (root == nullptr) { 15 return; 16 } 17 if (root -> left == nullptr && root -> right == nullptr && flag == -1) { 18 result += root -> val; 19 return; 20 } 21 traverse(root -> left, -1); 22 traverse(root -> right, 1); 23 24 } 25 public: 26 int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) { 27 traverse(root, 0); 28 return result; 29 } 30 };
2. Convert a Number to Hexadecimal (Leetcode 405 Easy)
Given an integer, write an algorithm to convert it to hexadecimal. For negative integer, two’s complement method is used.
Note:
- All letters in hexadecimal (
a-f) must be in lowercase. - The hexadecimal string must not contain extra leading
0s. If the number is zero, it is represented by a single zero character'0'; otherwise, the first character in the hexadecimal string will not be the zero character. - The given number is guaranteed to fit within the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
- You must not use any method provided by the library which converts/formats the number to hex directly.
Example 1:
Input: 26 Output: "1a"
Example 2:
Input: -1 Output: "ffffffff"
分析:十六进制的转换,搞清楚负数补码的原理就可以(拿0x100000000 + x即可),注意存的时候用一下long long防止整数溢出。
代码:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 string toHex(int num) { 4 string result; 5 long long num2 = num; 6 char hex[16] = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','a','b','c','d','e','f'}; 7 if (num2 < 0) { 8 num2 = 0x100000000 + num2; 9 } 10 if (num2 == 0) { 11 result += '0'; 12 return result; 13 } 14 while (num2 != 0) { 15 result = hex[num2 % 16] + result; 16 num2 /= 16; 17 } 18 return result; 19 } 20 };
3. Queue Reconstruction by Height (LeetCode406 Medium)
Suppose you have a random list of people standing in a queue. Each person is described by a pair of integers (h, k), where h is the height of the person and k is the number of people in front of this person who have a height greater than or equal to h. Write an algorithm to reconstruct the queue.
Note:
The number of people is less than 1,100.
Example
Input: [[7,0], [4,4], [7,1], [5,0], [6,1], [5,2]] Output: [[5,0], [7,0], [5,2], [6,1], [4,4], [7,1]]
分析:题意是给出人的高度和该高度前面有多少个人,重拍序列满足这一要求。
把序列中的人按照高度从高到低排序,高度一样的前面人越少的越靠前。这样以此处理每一个点,
按照people[i].second中存的有几个比他高来判断他应该在第几个位置插入(比该点高的点已经都进入序列了),处理完毕后即满足要求。
代码:(比较函数用了C++11中的lambda表达式)
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<pair<int, int>> reconstructQueue(vector<pair<int, int>>& people) { 4 vector<pair<int, int>> result; 5 sort(people.begin(), people.end(), [](const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) 6 { 7 if (p1.first == p2.first) { 8 return p1.second < p2.second; 9 } 10 else return p1.first > p2.first; 11 } ); 12 for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); ++i) { 13 result.insert(result.begin() + people[i].second, people[i]); 14 } 15 return result; 16 } 17 };
4. Trapping Rain Water II (Leetcode 407 Hard)
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.
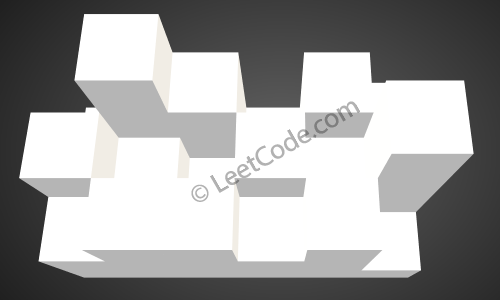
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
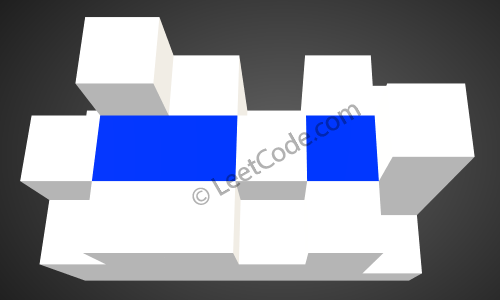
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
分析:
维护一个最小堆和一个记录访问与否的数组flag[m][n], 把图中外层一圈元素存入堆中,flag相应标记。
然后开始如下循环:
拿出其中堆顶元素(temp),BFS的方法查看其四周的四个点,
如果存在高度比temp低的点(heightMap[nx][ny]),则temp.h - heightMap[nx][ny]这段高度肯定可以储水。
然后把nx,ny位置的点加入堆中(但其高度应改为temp.h,多出部分已经储水记录过),并更新flag。
对于高度比temp高的点,直接加入堆中,并更新flag即可。
这样当堆中为空处理完所有点后,结果即为储水的值。
代码:
1 class Solution { 2 private: 3 struct node { 4 int x, y, h; 5 node(int nx, int ny, int nh):x(nx), y(ny), h(nh){} 6 }; 7 int dx[4] = {-1,0,0,1}; 8 int dy[4] = {0,1,-1,0}; 9 struct cmp { 10 bool operator() (const node &n1, const node &n2) { 11 return n1.h > n2.h; 12 } 13 }; 14 public: 15 int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) { 16 if (heightMap.size() == 0) { 17 return 0; 18 } 19 int m = heightMap.size(), n = heightMap[0].size(); 20 int flag[m][n] = {0}; 21 int result = 0; 22 priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp> que; 23 for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { 24 que.push(node(i,0, heightMap[i][0])); 25 flag[i][0] = 1; 26 que.push(node(i,n - 1, heightMap[i][n - 1])); 27 flag[i][n - 1] = 1; 28 } 29 for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; ++i) { 30 que.push(node(0,i,heightMap[0][i])); 31 flag[0][i] = 1; 32 que.push(node(m - 1, i,heightMap[m - 1][i])); 33 flag[m - 1][i] = 1; 34 } 35 while (!que.empty()) { 36 node temp = que.top(); 37 que.pop(); 38 for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { 39 int nx = temp.x + dx[i], ny = temp.y + dy[i]; 40 if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !flag[nx][ny]) { 41 result += max(0, temp.h - heightMap[nx][ny]); 42 que.push(node(nx, ny, max(temp.h, heightMap[nx][ny])) ); 43 flag[nx][ny] = 1; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 return result; 48 } 49 };



