算法总结—深度优先搜索DFS
深度优先搜索(DFS)
往往利用递归函数实现(隐式地使用栈)。
深度优先从最开始的状态出发,遍历所有可以到达的状态。由此可以对所有的状态进行操作,或列举出所有的状态。
1.poj2386 Lake Couting
题意:八连通被认为连接在一起,求总共有多少个水洼?
Sample Input:
10 12 W........WW. .WWW.....WWW ....WW...WW. .........WW. .........W.. ..W......W.. .W.W.....WW. W.W.W.....W. .W.W......W. ..W.......W.
Sample Output
3
思路:从任意W开始,一次DFS把连通的.全部变为W,遍历图直到没有.为止,进行DFS次数即为水洼的个数。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int N, M; 4 char pond[100][100]; //global variable 5 void dfs(int i, int j){ // 注意参数设计,要不要返回值 6 pond[i][j] = '.'; 7 for(int dx = -1; dx <= 1; ++dx){ //八连通遍历方式,四连通往往事先开好数组,见后续题目 8 for(int dy = -1; dy <= 1; ++dy){ 9 int x = i + dx, y = j + dy; 10 if(x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < M && pond[x][y] == 'W'){ 11 dfs(x,y); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 return; 16 } 17 int main(){ 18 cin >> N >> M; 19 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){ 20 for(int j = 0; j < M; ++j){ 21 cin >> pond[i][j]; 22 } 23 } 24 25 int count = 0; 26 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){ 27 for(int j = 0; j < M; ++j){ 28 if(pond[i][j] == 'W'){ 29 dfs(i,j); 30 count ++; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 cout << count << endl; 35 }
2.poj1979 Red and Black
题意:@表示起点,可以上下左右四方向走,"."为黑色,可以走,“#”为红色,不可以走,问可以到达多少个黑色位置?
Sample Input
6 9 ....#. .....# ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... #@...# .#..#. 11 9 .#......... .#.#######. .#.#.....#. .#.#.###.#. .#.#..@#.#. .#.#####.#. .#.......#. .#########. ........... 11 6 ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..### ..#..#..#@. ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..#.. 7 7 ..#.#.. ..#.#.. ###.### ...@... ###.### ..#.#.. ..#.#.. 0 0
Sample Output
45 59 6 13
思路:从起点处DFS遍历即可,当前点为“.”则将其改为“#”,result++,并以该点出发继续遍历。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 char rect[20][20]; 4 int result = 0; //全局的result 5 int dx[4] = {-1,0,0,1}; //四连通处理方法 6 int dy[4] = {0,1,-1,0}; 7 int W = 1, H = 1; 8 void dfs(int sx, int sy){ 9 rect[sx][sy] = '#'; 10 result++; 11 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){ 12 int x = sx + dx[i], y = sy + dy[i]; 13 if(x >= 0 && x < H && y >= 0 && y < W && rect[x][y] == '.'){ 14 dfs(x,y); 15 } 16 } 17 return ; 18 } 19 int main(){ 20 while(W != 0 && H != 0){ 21 cin >> W >> H; 22 if(W == 0 && H == 0){ 23 return 0; 24 } 25 int sx, sy; 26 for(int i = 0; i < H; ++i){ 27 for(int j = 0; j < W; ++j){ 28 cin >> rect[i][j]; 29 if(rect[i][j] == '@'){ 30 sx = i; 31 sy = j; 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 dfs(sx, sy); 36 cout << result << endl; 37 result = 0; 38 } 39 return 0; 40 }
3.aoj0118 Property Distribution
题意: 苹果是@,梨是#, 蜜柑是*。 四连通且相同品种在一个区域。计算每组数据区域的个数。
Sample Input:
10 10 ####*****@ @#@@@@#*#* @##***@@@* #****#*@** ##@*#@@*## *@@@@*@@@# ***#@*@##* *@@@*@@##@ *@*#*@##** @****#@@#@ 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
33
思路:类似第一题的池塘数个数的思路,DFS遍历,将遍历完毕的节点改为不同于上述三种标志的第四种标志,如“X”,
并且在DFS函数中加入标志参数用于判断同类水果区域,一次DFS,result++,当所有标志为X时,遍历结束。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 char garden[100][100]; 4 int H = 1, W = 1; 5 int result = 0; 6 int dx[4] = {-1,0,0,1}; 7 int dy[4] = {0,1,-1,0}; 8 void dfs(int sx, int sy,char c){ //加入char判断是否同一类 9 garden[sx][sy] = 'x'; 10 for(int i = 0; i < 4;++i){ 11 int x = sx + dx[i], y = sy + dy[i]; 12 if(x >= 0 && x < H && y >= 0 && y < W && garden[x][y] == c){ 13 dfs(x,y,c); 14 } 15 } 16 return; 17 } 18 int main(){ 19 while(H != 0 && W != 0){ 20 cin >> H >> W; 21 if(H == 0 && W == 0){ 22 return 0; 23 } 24 for(int i = 0; i < H; ++i){ 25 for(int j = 0; j < W; ++j){ 26 cin >> garden[i][j]; 27 } 28 } 29 for(int i = 0; i < H; ++i){ 30 for(int j = 0; j < W; ++j){ 31 if(garden[i][j] != 'x'){ 32 dfs(i,j,garden[i][j]); 33 result++; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 cout << result << endl; 38 result = 0; 39 } 40 }
4.aoj0033 Ball
题意:A管进球,B,C管出球,给定如球顺序,判断能否移动挡板,使得B,C出球顺序均为从下往上标号递增。
Sample Input
2 3 1 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Output for the Sample Input
YES NO
思路:DFS遍历,一个参数记录当前到第几个球,另外两个记录当前B,C顶端球得数值,以便于比较。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int A[10]; 4 bool dfs(int start, int topB, int topC){ //有返回值的DFS 5 if(start == 9){ //最后一个球啦 6 if(A[start] > topB || A[start] > topC){ 7 return true; 8 } 9 else{ 10 return false; 11 } 12 } 13 bool b1 = false, b2 = false; 14 if(A[start] > topB){ //B可以放,放进去试 15 b1 = dfs(start+1, A[start], topC); 16 } 17 if(A[start] > topC){ //C可以放,放进去试 18 b2 = dfs(start+1,topB,A[start]); 19 } 20 return (b1 || b2 ); //B,C都不可以放的时候,返回false,否则true 21 } 22 int main(){ 23 int N; 24 cin >> N; 25 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){ 26 for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j){ 27 cin >> A[j]; 28 } 29 bool result = dfs(0,0,0); 30 if(result == true){ 31 cout << "YES" << endl; 32 } 33 else{ 34 cout << "NO" <<endl; 35 } 36 } 37 return 0; 38 }
5. poj3009 Curling 2.0
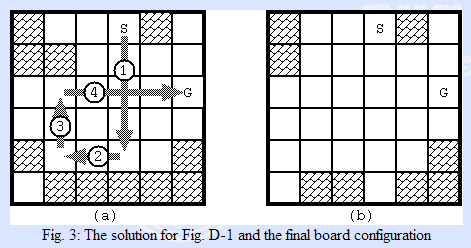
题意:
可以沿上下左右走到障碍物,碰到障碍物后停下,障碍物消失,然后可以继续出发,出界算失败,超过十步算失败,问能否从S到G,
不能输出-1,能输出最少步数。(0路径,1障碍物,2起点,3终点)
Sample Input
2 1 3 2 6 6 1 0 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 6 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 6 1 1 0 2 1 1 3 12 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 13 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 0 0
Sample Output
1 4 -1 4 10 -1
思路:这种走到底的题目也可以用DFS,设计成无返回值,到达3后比较当前值与已有最小值的大小。注意走到底的写法(while)
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<limits.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int board[21][21]; 6 int W = 1, H = 1; 7 int dx[4] = {-1,0,0,1}; 8 int dy[4] = {0,1,-1,0}; 9 int sx, sy,minStep = INT_MAX; 10 void dfs(int sx,int sy,int step){ //设计成无返回值,当board[i][j] == 3时比较当前 step+1 与最小的step并更新 11 if(step >= 10){ //剪枝 12 return; 13 } 14 for(int i = 0; i < 4;++i){ 15 int x = sx + dx[i], y = sy + dy[i]; 16 if(x >= 0 && x < H && y >=0 && y < W && board[x][y] != 1){ 17 while(x >= 0 && x < H && y >=0 && y < W && board[x][y] != 1){ //走到底的判断 18 if(board[x][y] == 3){ 19 if(step + 1 < minStep){ 20 minStep = step + 1; 21 break; 22 } 23 } 24 x += dx[i]; 25 y += dy[i]; 26 if(board[x][y] == 1){ 27 board[x][y] = 0; 28 dfs(x - dx[i], y - dy[i], step + 1); 29 board[x][y] = 1; // 恢复状态 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 return; 35 } 36 37 int main(){ 38 while(W != 0 && H != 0){ 39 cin >> W >> H; 40 if(W == 0 && H == 0){ 41 return 0; 42 } 43 memset(board,0,sizeof(board)); 44 for(int i = 0; i < H; ++i){ 45 for(int j = 0; j < W; ++j){ 46 cin >> board[i][j]; 47 if(board[i][j] == 2){ 48 sx = i; 49 sy = j; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 dfs(sx,sy,0); 54 if(minStep == INT_MAX){ 55 cout << "-1" << endl; 56 } 57 else{ 58 cout << minStep << endl; 59 } 60 minStep = INT_MAX; 61 } 62 return 0; 63 }
6.poj1321 棋盘问题
题意:n*n矩阵形状的棋盘(“#”为可摆放棋盘区域,“.”为不可摆放空白区域),要摆放k个棋子,同行同列不能有两个,共多少种方案?
Sample Input
2 1 #. .# 4 4 ...# ..#. .#.. #... -1 -1
Sample Output
2 1
思路:DFS的思路,一行一行的确定摆放位置,开一个数组place[8]记录哪一列已经有摆放。
注意k如果小于N时,可以有某一行不摆放元素,所以代码24行 DFS(row+1,num) 必须添加。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 int N = 1,K = 1; 5 char chess[8][8]; 6 int result = 0; 7 int placed[8] = {0}; //记录该列是否有摆放 8 void dfs(int row,int num){ 9 if(num == K){ //摆放成功,方案数++ 10 result++; 11 return; 12 } 13 if(row == N){ 14 return; 15 } 16 17 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){ 18 if(chess[row][i] == '#' && placed[i] == 0){ 19 placed[i] = 1; 20 dfs(row + 1, num + 1); 21 placed[i] = 0; 22 } 23 } 24 dfs(row+1,num); //!容易忽略 25 26 } 27 int main(){ 28 while(N != -1 && K != -1){ 29 cin >> N >> K; 30 if(N == -1 && K == -1){ 31 return 0; 32 } 33 memset(chess,0,sizeof(chess)); 34 memset(placed,0,sizeof(placed)); 35 for(int i = 0; i < N;++i){ 36 for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j){ 37 cin >> chess[i][j]; 38 } 39 } 40 dfs(0,0); 41 cout << result << endl; 42 result = 0; 43 } 44 45 }