C++类设计1(Class without pointer members)
一、Class without pointer members (class complex)
1.防卫式声明
#ifndef _COMPLEX_ #define _COMPLEX_ ...... #endif
2.inline function
函数若在class体内完成定义,则自动成为内联函数候选人; 若在class外,需添加inline关键字;同时真正是否inline由编译器决定。
class complex{ public: complex (double r = 0, double i = 0):re(r), im(i){} //inline complex& operator += {const complex&}; double real() const{return re;} //inline double imag() const{return im;} //inline private: double re,im; friend complex& _doap1 (complex*, const complex); }; inline double imag(const complex& x){ //inline return x.imag(); }
3.访问级别
private: 数据部分,封装,不被外界(class外)访问。
public: 可以被外界访问(class外)的。
定义时不一定集中在两段,可以根据实际情况交替使用两个关键字。
4 构造函数(ctor)
创建对象是调用构造函数,函数名与类名相同,无返回值类型。
下述三种创建对象方式均调用构造函数
class complex{ public: complex (double r = 0, double i = 0):re(r), im(i) {} //可以带参数,参数可以有默认值,即未指明时使用默认值 //初始化列表 : re(r),im(i) 能使用初始化列表时尽量使用 complex& operator += {const complex&}; double real() const{return re;} double imag() const{return im;} private: double re,im; friend complex& _doap1 (complex*, const complex); }; { complex c1(2,1); //三种方式均调用构造函数 complex c2; complex *p = new complex(4); ... }
4.2 构造函数在private 区域
不能被外界调动,例如在单例模式中使用
class A{ public: static A& getInstance(); //静态类型变量 setup(){} private: A(); //构造函数在private区域 A(const A& ths); ... }; A& A::getInstance(){ static A a; return a; } A::getInstance().setup(); //使用时利用类的getInstace()函数
5 重载(overloading)
同名函数可以存在,判断是否可以重载即判定编译器是否能区分两种函数使用。
double real() const {return re;} void real(double r) {re = r;} //正确重载 complex(double r= 0, double i = 0): re(r),im(i) {}; complex() : re(r), im(i){}; // 错误,编译器无法判断, 如: complex c1; 不知道调用哪个。
6 const member functions
注意const functions中 const 的位置: 函数名之后,函数体之前
double real() const{return re;} double imag() const{return im;} //不改变数据内容,则一定要加const,否则可能引起错误,如: //外界调用该函数时 使用:const complex c1(1,2); //声明常对象,常对象不可调用非常成员函数,出现错误
7 pass by value or pass by reference (to const)
传值会造成开销较大(基本类型可以传值),能传引用时尽量传递引用(开销仅4bytes)。
如果不想给予对方修改权限,则使用const关键字 如 const complex& 为常见形式。
class complex{ public: complex (double r = 0, double i = 0):re(r), im(i){} //pass by value complex& operator += {const complex&}; //pass by reference double real() const{return re;} double imag() const{return im;} private: double re,im; friend complex& _doap1 (complex*, const complex&); //pass by reference };
8 return by value or return by reference
尽量传递引用,不可以情况参考后 8.1 和临时变量章节
complex& operator += {const complex&}; friend complex& __doapl (complex*, const complex&);
8.1 什么时候可以return by reference
函数运算返回结果
1)必须在函数内新创建对象,不能返回reference,因为函数结束时,对象消亡,引用指向的本体已经不在。
2)当返回结果是已经存在的对象,可以返回引用,常见情况this指针
inline complex& __doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r) { ths->re += r.re; ths->im += r.im; return *ths; } inline complex& complex::operator += (const complex& r) { return __doapl (this, r); }
8.2 pass/ return by reference 语法分析
传递者无需知道接收端以何种形式进行接收;
如下例,返回传递仅需传递原值,接收者自己决定接收引用或接受值(调用拷贝构造)。
inline complex& __doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r) { ths->re += r.re; ths->im += r.im; return *ths; }
9. 友元(friend)
friend complex& __doapl (complex*, const complex&); inline complex& _doap1 (complex* ths, const complex& r){ ths->re += r.re; //自由取得friend的private变量,但破坏封装 ths->im +=r.im; return *ths; }
9.1 相同类(class)的各个对象(objects)之间互为友元
class complex{ public: complex (double r = 0, double i = 0):re(r),im(i){ } int func(const complex& param){ return param.re + param.im; } //直接拿param私有变量,可以用相同类的各个对象之间互为友元解释 private: double re, im; };
10. 运算符重载1 ,成员函数(operator overloading)
二元操作符被编译器看待的形式:(注意是看待形式,this存在可以使用,但参数列表中this不可写出)this指向调用者
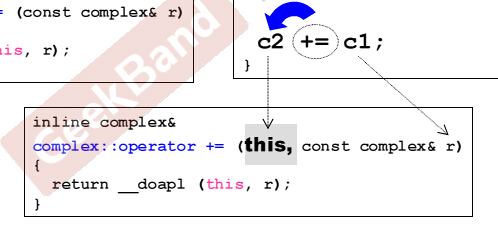
实际代码如下:
inline complex& __doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r) { ths->re += r.re; ths->im += r.im; return *ths; } inline complex& complex::operator += (const complex& r) //operator += 在程序员使用时可能采用c1 += c2 += c3形式 // 故需要返回complex&类型,不能是void, 类似还有重载cout返回类型 { return __doapl (this, r) }
11. 运算符重载2 非成员函数(无this指针)
全局函数,无this指针.
例如此复数类,重载加减等符号时,存在复数加减实数情况,故不宜使用成员函数。
inline complex operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y) { return complex (real (x) + real (y), imag (x) + imag (y)); //返回的是函数内临时变量(local object),函数结束后消亡,故不可使用return by reference } inline complex operator + (const complex& x, double y) { return complex (real (x) + y, imag (x)); } inline complex operator + (double x, const complex& y) { return complex (x + real (y), imag (y)); }
#include ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const complex&){ //两个参数为 << 左边和右边,如 cout << c1; cout类型为ostream, return os << '(' << real(x) << ',' << imag(x) << ')'; }
12 complex 类完整代码 与测试代码

1 complex.h 2 #ifndef __MYCOMPLEX__ 3 #define __MYCOMPLEX__ 4 5 class complex; 6 complex& 7 __doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r); 8 complex& 9 __doami (complex* ths, const complex& r); 10 complex& 11 __doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r); 12 13 14 class complex 15 { 16 public: 17 complex (double r = 0, double i = 0): re (r), im (i) { } 18 complex& operator += (const complex&); 19 complex& operator -= (const complex&); 20 complex& operator *= (const complex&); 21 complex& operator /= (const complex&); 22 double real () const { return re; } 23 double imag () const { return im; } 24 private: 25 double re, im; 26 27 friend complex& __doapl (complex *, const complex&); 28 friend complex& __doami (complex *, const complex&); 29 friend complex& __doaml (complex *, const complex&); 30 }; 31 32 33 inline complex& 34 __doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r) 35 { 36 ths->re += r.re; 37 ths->im += r.im; 38 return *ths; 39 } 40 41 inline complex& 42 complex::operator += (const complex& r) 43 { 44 return __doapl (this, r); 45 } 46 47 inline complex& 48 __doami (complex* ths, const complex& r) 49 { 50 ths->re -= r.re; 51 ths->im -= r.im; 52 return *ths; 53 } 54 55 inline complex& 56 complex::operator -= (const complex& r) 57 { 58 return __doami (this, r); 59 } 60 61 inline complex& 62 __doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r) 63 { 64 double f = ths->re * r.re - ths->im * r.im; 65 ths->im = ths->re * r.im + ths->im * r.re; 66 ths->re = f; 67 return *ths; 68 } 69 70 inline complex& 71 complex::operator *= (const complex& r) 72 { 73 return __doaml (this, r); 74 } 75 76 inline double 77 imag (const complex& x) 78 { 79 return x.imag (); 80 } 81 82 inline double 83 real (const complex& x) 84 { 85 return x.real (); 86 } 87 88 inline complex 89 operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y) 90 { 91 return complex (real (x) + real (y), imag (x) + imag (y)); 92 } 93 94 inline complex 95 operator + (const complex& x, double y) 96 { 97 return complex (real (x) + y, imag (x)); 98 } 99 100 inline complex 101 operator + (double x, const complex& y) 102 { 103 return complex (x + real (y), imag (y)); 104 } 105 106 inline complex 107 operator - (const complex& x, const complex& y) 108 { 109 return complex (real (x) - real (y), imag (x) - imag (y)); 110 } 111 112 inline complex 113 operator - (const complex& x, double y) 114 { 115 return complex (real (x) - y, imag (x)); 116 } 117 118 inline complex 119 operator - (double x, const complex& y) 120 { 121 return complex (x - real (y), - imag (y)); 122 } 123 124 inline complex 125 operator * (const complex& x, const complex& y) 126 { 127 return complex (real (x) * real (y) - imag (x) * imag (y), 128 real (x) * imag (y) + imag (x) * real (y)); 129 } 130 131 inline complex 132 operator * (const complex& x, double y) 133 { 134 return complex (real (x) * y, imag (x) * y); 135 } 136 137 inline complex 138 operator * (double x, const complex& y) 139 { 140 return complex (x * real (y), x * imag (y)); 141 } 142 143 complex 144 operator / (const complex& x, double y) 145 { 146 return complex (real (x) / y, imag (x) / y); 147 } 148 149 inline complex 150 operator + (const complex& x) 151 { 152 return x; 153 } 154 155 inline complex 156 operator - (const complex& x) 157 { 158 return complex (-real (x), -imag (x)); 159 } 160 161 inline bool 162 operator == (const complex& x, const complex& y) 163 { 164 return real (x) == real (y) && imag (x) == imag (y); 165 } 166 167 inline bool 168 operator == (const complex& x, double y) 169 { 170 return real (x) == y && imag (x) == 0; 171 } 172 173 inline bool 174 operator == (double x, const complex& y) 175 { 176 return x == real (y) && imag (y) == 0; 177 } 178 179 inline bool 180 operator != (const complex& x, const complex& y) 181 { 182 return real (x) != real (y) || imag (x) != imag (y); 183 } 184 185 inline bool 186 operator != (const complex& x, double y) 187 { 188 return real (x) != y || imag (x) != 0; 189 } 190 191 inline bool 192 operator != (double x, const complex& y) 193 { 194 return x != real (y) || imag (y) != 0; 195 } 196 197 #include 198 199 inline complex 200 polar (double r, double t) 201 { 202 return complex (r * cos (t), r * sin (t)); 203 } 204 205 inline complex 206 conj (const complex& x) 207 { 208 return complex (real (x), -imag (x)); 209 } 210 211 inline double 212 norm (const complex& x) 213 { 214 return real (x) * real (x) + imag (x) * imag (x); 215 } 216 217 #endif //__MYCOMPLEX__

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "complex.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 ostream& 7 operator << (ostream& os, const complex& x) 8 { 9 return os << '(' << real (x) << ',' << imag (x) << ')'; 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 complex c1(2, 1); 15 complex c2(4, 0); 16 17 cout << c1 << endl; 18 cout << c2 << endl; 19 20 cout << c1+c2 << endl; 21 cout << c1-c2 << endl; 22 cout << c1*c2 << endl; 23 cout << c1 / 2 << endl; 24 25 cout << conj(c1) << endl; 26 cout << norm(c1) << endl; 27 cout << polar(10,4) << endl; 28 29 cout << (c1 += c2) << endl; 30 31 cout << (c1 == c2) << endl; 32 cout << (c1 != c2) << endl; 33 cout << +c2 << endl; 34 cout << -c2 << endl; 35 36 cout << (c2 - 2) << endl; 37 cout << (5 + c2) << endl; 38 39 return 0; 40 }




