python实训day2
作业:
'''
1.让用户输入用户名与密码
2.校验用户名是否存在
3.用户名存在后检验密码是否正确,若正确打印“登陆成功”
否则打印“用户名或密码错误”,并让用户重新输入
4.用户密码输入错误超过三次则退出循环。
'''
def login():
i = 1
while i <= 3:
user = input('请输入用户名:').strip()
pwd = input('请输入密码:').strip()
with open('user.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
old_info = f.read().split(',')
for index in range(len(old_info)):
if old_info[index] == user:
if old_info[index+1] == pwd:
print("登录成功")
i = 4
break
else:
print("用户名或密码错误")
i += 1
break
login()
结果:
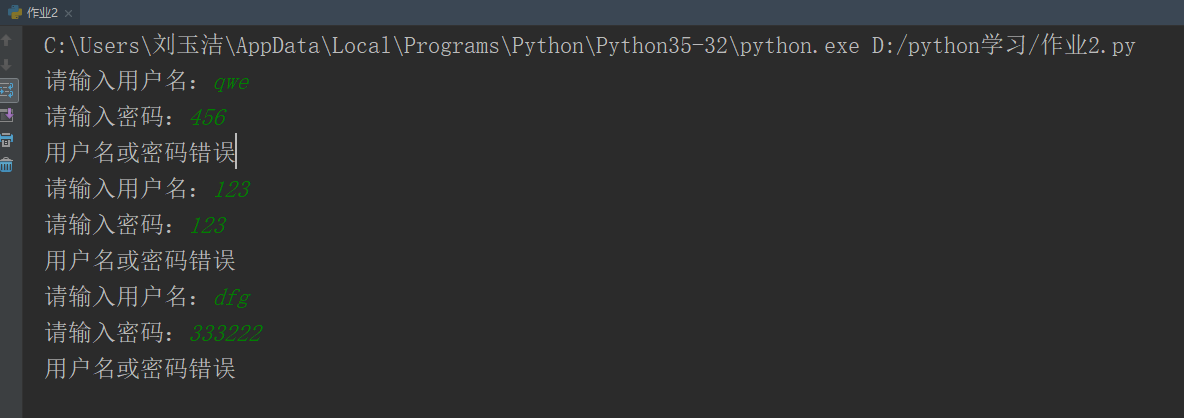

总结:
1.列表类型主要方法、深拷贝与浅拷贝:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
# 列表内置方法list1=['hao',20,'male',2.0,3,'广东']print(list1[4])print(list1[-2])list1.append('张伟')print(list1)list1.insert(1,'li')print(list1)list2=list1.copy()print(list2,'添加值前')list3=list1print(list3,'添加值前')list1.append('jie')print(list2,'后')print(list3,'后')from copy import deepcopylist4=['hao',20,'male',2.0,3,'广东',[12,3]]list6=deepcopy(list4)list5=list4.copy()list4[6].append(4)print(list4,'前')print(list5,'后')print(list6,'后')<br><br> |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
extend() # 合并list1 = [1, 2, 3]list2 = [4, 5, 6]list1.extend(list2)print(list1)# 9.reverse() # 反转list1.reverse()print(list1)# 10.sort() # 排序list3 = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 2, 4, 6]# 升序# list3.sort()# print(list3)# 降序list3.sort(reverse=True)print(list3) |
2.两种快捷建用法:
# tab : 往右空四个空格
# shift + tab : 往左减四个空格
3.字典及常用方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#字典常用方法--无序#按照key取值dict1={'name':'hao','age':20,'sex':'male','school':'ahpu'}print(dict1['school'])print(dict1.get('px'))print(dict1.get('school','hnlg'))print(dict1.get('san','1500'))#删除# del dict1['name']# print(dict1)dict2={"position":"student"}dict1.update(dict2)print(dict1)#遍历for k,v in dict1.items(): print((k,v))<br><br> |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#长度lenprint(len(dict1)) #成员运算in和not inprint('name' in dict1) print('sal' in dict1)print('sal' not in dict1)#随机取出字典中的某个值dict1.popitem()print(dict1)#keys、values、itemsprint(dict1.keys())print(dict1.values())print(dict1.items())#循环# 循环字典中所有的keyfor key in dict1: print(key)# update()print(dict1)dict2 = {"work": "student"}# 把dict2加到dict1字典中dict1.update(dict2)print(dict1) |
4.集合--一般用于去重
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
# 在{}以逗号隔开,可存放多个值,但集合会自带默认去重功能。set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1, 3, 4}print(set1)# 集合是无序的set1 = set()set2 = {}print(set1)print(set2)set2['name'] = 'tank'print(type(set2)) |
5.元组tuple
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
# 二 元组类型(在小括号内,以逗号隔开存放多个值)# 注意: 元组与列表的区别,元组是不可变类型,列表是可变类型。tuple1 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)print(tuple1)# 1.按索引取值print(tuple1[2])# 2.切片(顾头不顾尾)print(tuple1[0:6]) # (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)# 步长print(tuple1[0:6:2]) # (1, 3, 5)# 3.长度print(len(tuple1)) # 6# 4.成员运算 in 和 not inprint(1 in tuple1) # Trueprint(1 not in tuple1) # False# 5.循环for line in tuple1: print(line) |
6.文件操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
# 文件读写基本使用# 对文本进行操作# open(参数1: 文件的绝对路径/文件的名字,参数2:操作模式, 参数3: 指定字符编码)# f: 称之为 句柄# r: 避免转义符# 打开文件会产生两种资源,一种是python解释器与python文件的资源,程序结束python会自动回收。# 另一种是操作系统打开文件的资源,文件打开后,操作系统并不会帮我们自动收回,所以需要手动回收资源。# 写文件f=open(r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\ya.txt',mode="wt",encoding="utf-8") #默认模式rtf.write("hello!")f.close()#读文件f=open(r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\ya.txt',mode="r",encoding="utf-8")res=f.read()print(res)f.close()#追加模式f=open(file=r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\ya.txt',mode="a",encoding="utf-8")f.write("\nhigh")f.close()#with open方式# 文件处理之上下文管理: with# with会自带close()功能,# 会在文件处理完以后自动调用close()关闭文件with open(r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\yh.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write("life is long")with open(r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\yh.txt',mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as f: res=f.read() print(res)with open(r'E:\\pycharm2018\\PyCharm-Pro\\yh.txt',mode="a",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(' baidu') |
|
1
|
<br> |
7.图片与视频读写操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
import requestsres=requests.get('https://timgsa.baidu.com/timg?image&quality=80&size=b9999_10000&sec=1560323359733&di=3e9865f9690a76e8db8279cb68834263&imgtype=0&src=http%3A%2F%2Fpic.rmb.bdstatic.com%2Fcd2476300bbad8dfcfff1d277b79401a.jpeg')print(res.content)#写入图片with open('风景.jpeg','wb') as f: f.write(res.content)#读取图片with open('风景.jpeg','rb') as f: res=f.read() print(res)#文件拷贝操作with open('风景.jpeg','rb') as f,open('风景2.jpeg','wb') as w: res=f.read() w.write(res)#视频,一次打开# with open('Eddy Kim - When A Long Night Comes (긴 밤이 오면).mkv.mkv','rb') as f,open('copy.mkv','wb') as w:# res=f.read()# print(res)# w.write(res)#一行一行打开,防溢出with open('Eddy Kim - When A Long Night Comes (긴 밤이 오면).mkv.mkv','rb') as f,open('copy.mkv','wb') as w: f.read() for line in f: w.write(line) |



