windows服务是如何被调用的?
1、服务介绍
操作系统在启动的时候,会启动一些不需要用户交互的进程。这些进程被称为服务。当操作系统启动后它就自动被运行。
2、组成
服务程序、服务控制程序(SCP,service control program)和服务控制管理器(SCM,service control manager)组成了Windows服务。我们可以通过SCP操纵SCM启动、暂停、停止服务程序。其中服务程序和SCP由我们自己编写。
SCM
servics.exe是操作系统内置的一个部件。建立数据库、启动服务(自启动),分配服务进程。
SCP
服务控制程序,例如windows自带的服务工具:
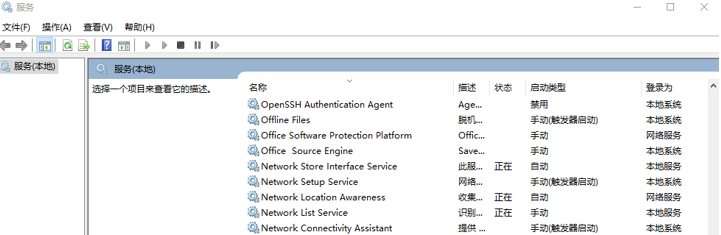
当然也可以自己写一个服务管理工具。
服务程序
我们需要执行的任务
3、执行原理
首先看看服务入口:
static void Main() { ServiceBase[] ServicesToRun; ServicesToRun = new ServiceBase[] { new MainService() }; ServiceBase.Run(ServicesToRun); }
从入口看,这和控制台程序一样,因为绝大部分的服务都不需要交互,所以没有用户界面。 那么ServiceBase.Run到底做了什么事情呢?平常情况下,我们并不关心,只是windows服务听起来有点神秘。于是就搜索关于windows service原理的文章,理解一下。如下图:
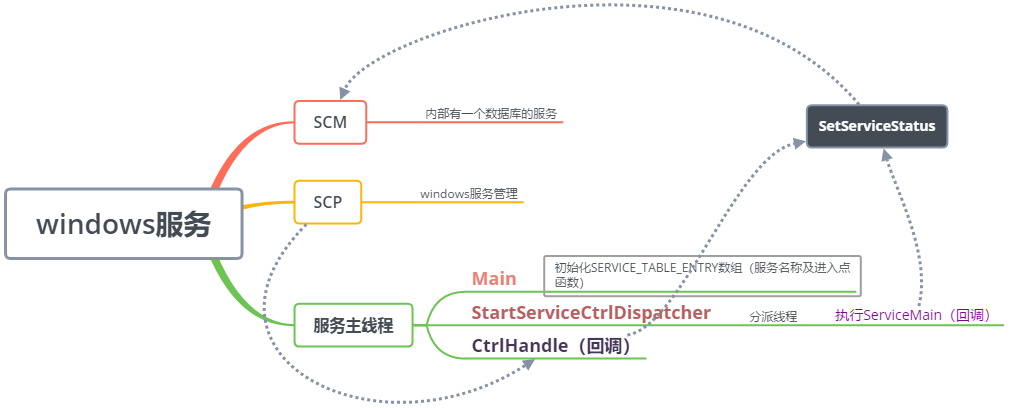
大致原理:服务主线程调用StartServiceCtrlDispatcher,最终执行了ServiceMain回调,调用了我们自己写的服务代码。SCP通过CtrlHandle回调了我们对服务的一些操作,比如暂停,启动等等。它们都通过SetServiceStatus方法与SCM通信,把服务的状态等信息及时地告诉SCM。我结合代码主要介绍下,我们的服务代码是如何被调用的。
Main方法中的ServiceBase是一个什么样的类呢?


从继承关系上看,它是可以跨应用程序域调用(MarshalByRefObject——Enables access to objects across application domain boundaries in applications that support remoting)以及需要释放资源(IDisposable)。这说明,可以远程调用服务以及服务占用了非托管资源。
我们看Run方法:
1 public static void Run(ServiceBase[] services) 2 { 3 if ((services == null) || (services.Length == 0)) 4 { 5 throw new ArgumentException(Res.GetString("NoServices")); 6 } 7 if (Environment.OSVersion.Platform != PlatformID.Win32NT) 8 { 9 string message = Res.GetString("CantRunOnWin9x"); 10 string title = Res.GetString("CantRunOnWin9xTitle"); 11 LateBoundMessageBoxShow(message, title); 12 } 13 else 14 { 15 IntPtr entry = Marshal.AllocHGlobal((IntPtr) ((services.Length + 1) * Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY)))); 16 System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY[] service_table_entryArray = new System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY[services.Length]; 17 bool multipleServices = services.Length > 1; 18 IntPtr zero = IntPtr.Zero; 19 for (int i = 0; i < services.Length; i++) 20 { 21 services[i].Initialize(multipleServices); 22 service_table_entryArray[i] = services[i].GetEntry(); 23 zero = (IntPtr) (((long) entry) + (Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY)) * i)); 24 Marshal.StructureToPtr(service_table_entryArray[i], zero, true); 25 } 26 System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY structure = new System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY { 27 callback = null, 28 name = IntPtr.Zero 29 }; 30 zero = (IntPtr) (((long) entry) + (Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY)) * services.Length)); 31 Marshal.StructureToPtr(structure, zero, true); 32 bool flag2 = System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.StartServiceCtrlDispatcher(entry); 33 foreach (ServiceBase base2 in services) 34 { 35 if (base2.startFailedException != null) 36 { 37 base2.startFailedException.Throw(); 38 } 39 } 40 string str = ""; 41 if (!flag2) 42 { 43 str = new Win32Exception().Message; 44 string str4 = Res.GetString("CantStartFromCommandLine"); 45 if (Environment.UserInteractive) 46 { 47 string str5 = Res.GetString("CantStartFromCommandLineTitle"); 48 LateBoundMessageBoxShow(str4, str5); 49 } 50 else 51 { 52 Console.WriteLine(str4); 53 } 54 } 55 foreach (ServiceBase base3 in services) 56 { 57 base3.Dispose(); 58 if (!flag2 && (base3.EventLog.Source.Length != 0)) 59 { 60 object[] args = new object[] { str }; 61 base3.WriteEventLogEntry(Res.GetString("StartFailed", args), EventLogEntryType.Error); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 }
第32行 System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.StartServiceCtrlDispatcher(entry),这是一个平台调用,它非常关键,看看原型:

它接收一个参数 entry,这是一个指针或者句柄类型( A platform-specific type that is used to represent a pointer or a handle)。那么它应该指向服务的入口地址。我们看看entry是什么结构?
第15行 IntPtr entry = Marshal.AllocHGlobal((IntPtr) ((services.Length + 1) * Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY)))); 这句一看就是分配内存的。如果我们都学过c语言的话,也不会陌生。虽然c#自动分配内存,我们不用管,其实这件事情还是存在的。SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY,这个结构如下:
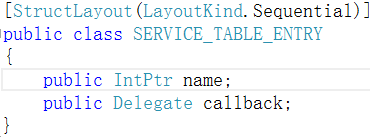
callback是委托类型。这个类什么时候实例化的?第22行 service_table_entryArray[i] = services[i].GetEntry(); GetEntry方法如下:
1 private System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY GetEntry() 2 { 3 System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY service_table_entry = new System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY(); 4 this.nameFrozen = true; 5 service_table_entry.callback = this.mainCallback; 6 service_table_entry.name = this.handleName; 7 return service_table_entry; 8 }
第5行,callback的实例是this.mainCallback,定义 private System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.ServiceMainCallback mainCallback; 它的类型: public delegate void ServiceMainCallback(int argCount, IntPtr argPointer);在什么时候实例化呢?
private void Initialize(bool multipleServices) { if (!this.initialized) { ...this.status.currentState = 2; this.status.controlsAccepted = 0; this.status.win32ExitCode = 0; this.status.serviceSpecificExitCode = 0; this.status.checkPoint = 0; this.status.waitHint = 0; this.mainCallback = new System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.ServiceMainCallback(this.ServiceMainCallback); ... } }
在服务初始化的方法中实例化的。在Run方法的第21行中调用了初始化方法 :services[i].Initialize(multipleServices); 所以现在重心转移到 this.ServiceMainCallback:
public unsafe void ServiceMainCallback(int argCount, IntPtr argPointer) { fixed (System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SERVICE_STATUS* service_statusRef = &this.status) { string[] state = null; ...this.startCompletedSignal = new ManualResetEvent(false); this.startFailedException = null; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(this.ServiceQueuedMainCallback), state); this.startCompletedSignal.WaitOne(); if ((this.startFailedException != null) && (this.status.win32ExitCode == 0)) { this.status.win32ExitCode = 0x428; } if (!System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SetServiceStatus(this.statusHandle, service_statusRef)) { object[] objArray2 = new object[] { new Win32Exception().Message }; this.WriteEventLogEntry(Res.GetString("StartFailed", objArray2), EventLogEntryType.Error); this.status.currentState = 1; System.ServiceProcess.NativeMethods.SetServiceStatus(this.statusHandle, service_statusRef); } } }
在这段代码中,它开启了一个新的线程 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem,回调了ServiceQueuedMainCallback,除此之外,定义了ManualResetEvent,用于主线程和子线程之间的同步。this.startCompletedSignal.WaitOne() 开启子线程后,先阻塞主线程运行,等待子线程的结果。ServiceQueuedMainCallback干了些什么事情?
1 private void ServiceQueuedMainCallback(object state) 2 { 3 string[] args = (string[]) state; 4 try 5 { 6 this.OnStart(args); 7 this.WriteEventLogEntry(Res.GetString("StartSuccessful")); 8 this.status.checkPoint = 0; 9 this.status.waitHint = 0; 10 this.status.currentState = 4; 11 } 12 catch (Exception exception) 13 { 14 object[] objArray1 = new object[] { exception.ToString() }; 15 this.WriteEventLogEntry(Res.GetString("StartFailed", objArray1), EventLogEntryType.Error); 16 this.status.currentState = 1; 17 if (!System.LocalAppContextSwitches.DontThrowExceptionsOnStart) 18 { 19 this.startFailedException = ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(exception); 20 } 21 } 22 this.startCompletedSignal.Set(); 23 }
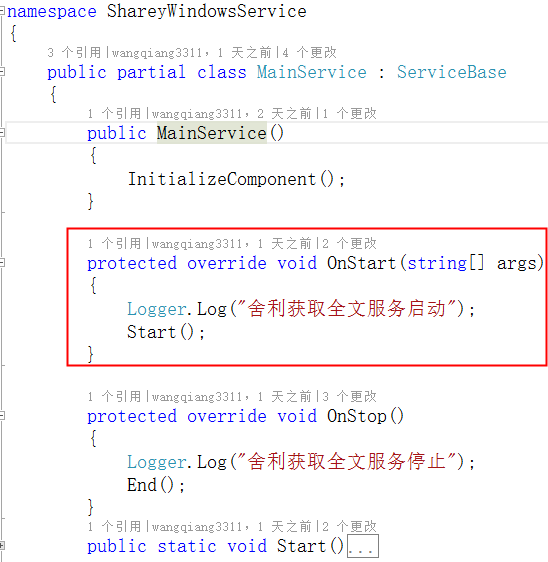
第6行,this.OnStart,这是一个服务开始运行的地方。
protected virtual void OnStart(string[] args) { }
相应还有OnStop方法,微软暴露出这些虚方法,我们在子类中,刚好重写,这样我们写的服务代码就被执行了。
感兴趣的同学,可以写个服务,安装个反编译工具,按F12,就可以跟进到代码里面去看了。




