java-实现哈希表 跳表
一,哈希表,将关键字与储存位置通过某种函数关联起来,拿到要查找的对象后,通过关键字得出对象的储存位置,
使得查询时间复杂度为O(1),而不用遍历集合去比较,哈希函数是函数,
存在输入不同key得到相同解的情况,即发生哈希碰撞。理论上只要储存空间有限,必定会发生哈希碰撞。

哈希表的关键:设计哈希函数,和哈希碰撞处理。
实例:用除留余数法哈希函数,和拉链法解决哈希碰撞
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxiongcanguan/p/10190861.html
除留余数:表数组的长度L有限,关键字对L求余,即储存地址都落在0-(L-1)上,
拉链法:当发生哈希碰撞,落在相同储存位置的对象储存再同一个链表上,表头在数组里,这样查找时
先求出,储存地址,在按该地址上的对象链表上找即可。
代码:

import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Map; /** * 拉链发, * 负载因子-0.75 自动扩容 * */ public class HashTable { //节点类 class Node{ private int Key; private Object Value; private Node next=null; public Node(int key,Object value){ this.Key=key; this.Value=value; } } //数组大小 private int size; //负载因子 private float loadFactory; //数组 private Node[] nodes; //默认哈希表容量 private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY=16; //扩容翻倍数 private final static int REHASH_BASE=2; //默认负责因子 private final static float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR=0.75f; //构造方法 public HashTable(){ this.size=0; this.loadFactory=DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; nodes=new Node[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; } public HashTable(int capacity){ this.size=0; this.loadFactory=DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; this.nodes=new Node[capacity]; } public HashTable(int capacity,float loadFactor){ this.size=0; this.loadFactory=loadFactor; this.nodes=new Node[capacity]; } //通过hash值缺定对应下标 private int getIndex(int key,Node[] n){ int hash=key^(key>>>16); return (n.length-1)&hash; } //遍历链表 //返回目标的前驱节点,没有则返回最后一个节点 private Node getPreNodeInNodes(Node node,int key){ Node nextNode=node.next; while(nextNode!=null){ if(nextNode.Key==key){ return node; }else{ node=nextNode; nextNode=nextNode.next; } } return node; } //增删改查 //增改 public Object put(int key,Object value){ if(needReHash()){ rehash(); } int index=getIndex(key,this.nodes); Node root=this.nodes[index]; if(root==null){ this.nodes[index]=new Node(key,value); this.size++; return null; } if(root.Key==key){ Object oldvalue=root.Value; root.Value=value; return oldvalue; }else{ Node preNode=getPreNodeInNodes(root,key); Node targetNode=preNode.next; if(targetNode!=null){ Object oldvalue=root.Value; targetNode.Value=value; return oldvalue; }else{//不在链表中返回链表最后一个 preNode.next=new Node(key,value); this.size++; return null; } } } //删 public Object remove(int key){ int index=getIndex(key,this.nodes); Node root=this.nodes[index]; if(root==null) return null; if(root.Key==key){ this.nodes[index]=root.next; this.size--; return root.Value; }else{ Node preNode=getPreNodeInNodes(root,key); //System.out.println("preNode: "+preNode.Key); Node targetNode=preNode.next; if(targetNode!=null){ preNode.next=targetNode.next; this.size--; return targetNode.Value; }else{ return null; } } } //查 public Object get(int key){ int index=getIndex(key,this.nodes); Node root=this.nodes[index]; if(root==null) return null; if(root.Key==key) return root.Value; else{ Node preNode=getPreNodeInNodes(root,key); Node targetNode=preNode.next; if(targetNode!=null) return targetNode.Value; else return null; } } //是否需要扩容 private boolean needReHash(){ if(this.size>this.nodes.length*this.loadFactory) return true; return false; } //扩容 private void rehash(){ Node[] newNodes=new Node[this.nodes.length*REHASH_BASE]; for (int i=0;i<this.nodes.length;i++){ //System.out.println("rehash-"+i); Node curNode=this.nodes[i]; if(curNode!=null){ Node pnext=curNode.next; int index=getIndex(curNode.Key,newNodes); Node root=newNodes[index]; if(root==null){ newNodes[index]=new Node(curNode.Key,curNode.Value); } else{ while(root.next!=null){ root=root.next; } root.next=new Node(curNode.Key,curNode.Value); } while(pnext!=null){ int index1=getIndex(pnext.Key,newNodes); Node root1=newNodes[index1]; //System.out.println(index1); if(root1==null){ newNodes[index1]=new Node(pnext.Key,pnext.Value); } else{ while(root1.next!=null){ root1=root1.next; } root1.next=new Node(pnext.Key,pnext.Value); } pnext=pnext.next; } } } this.nodes=newNodes; } //打印 private void printTable(){ System.out.println("哈希表:"); for(int i=0;i<this.nodes.length;i++){ System.out.print(i+": "); Node root=this.nodes[i]; if(root!=null){ Node nextNode=root.next; System.out.print(root.Key+"["+root.Value+"]"+"->"); while(nextNode!=null){ System.out.print(nextNode.Key+"["+nextNode.Value+"]"+"->"); nextNode=nextNode.next; } System.out.print("null"); }else System.out.print("null"); System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String args[]) { HashTable table=new HashTable(8); table.put(45,"qwe"); table.put(23,"qwe"); table.put(18,"qwe"); table.put(6,"qwe"); table.put(27,"qwe"); table.put(34,"qwe"); // table.put(3,"qwe"); // table.put(7,"qwe"); // table.put(22,"qwe"); // table.put(49,"qwe"); // table.put(57,"qwe"); // table.put(38,"qwe"); // table.put(33,"qwe"); // table.put(29,"qwe"); // table.put(28,"qwe"); System.out.println(table.get(88)); table.printTable(); //Hashtable h=new Hashtable(); } }
二,跳表
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/pcwl1206/article/details/83512600 这边文章分析的很透彻,关于跳表的,性质,原理。
https://www.cnblogs.com/acfox/p/3688607.html
跳表:在单链表的基础上,再维持几条索引,类似二叉树或红黑树那样,从上层往下层找,层层缩小查找范围
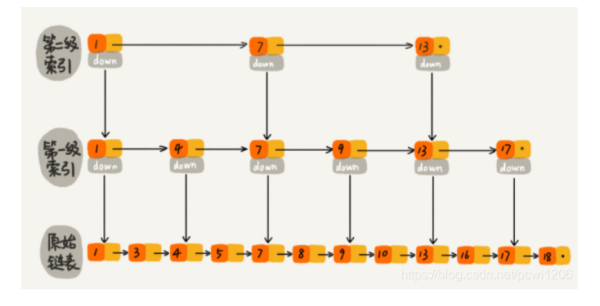
但想再插入删除后维持完美的上层索引,同AVL树,RB树一样麻烦。要实现基于单链表实现简单的维护操作(类似维护平衡的操作)
跳表的维护原理是:通过随机函数来维护上层索引。

插入节点时通过随机数给出一个层级N,这个层级即表示把向上N层也插入索引,N的概率:2n分之一。
删除节点时,如果节点出现在索引中,从索引中删除。
代码:
https://blog.csdn.net/pcwl1206/article/details/83512600
搬运的代码,解释一下我理解的
Node 类,有一个数组,该数组的长度为,随机函数产生高度如图:
忘记了,level3包括level2,2333下面图中level2的节点画的太多了,233自行脑补把
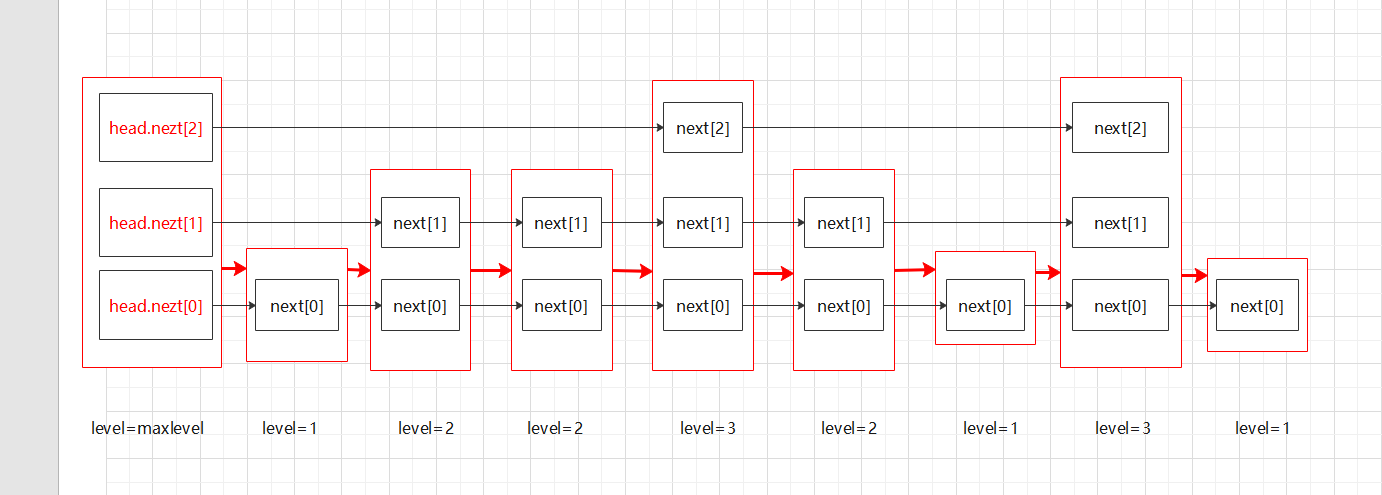
红色框表示一个节点,节点高多少既有一个容量为即的数组,直接用数组的好处是省掉了只用单个节点时的child节点,这样维护起来更简单。
即:
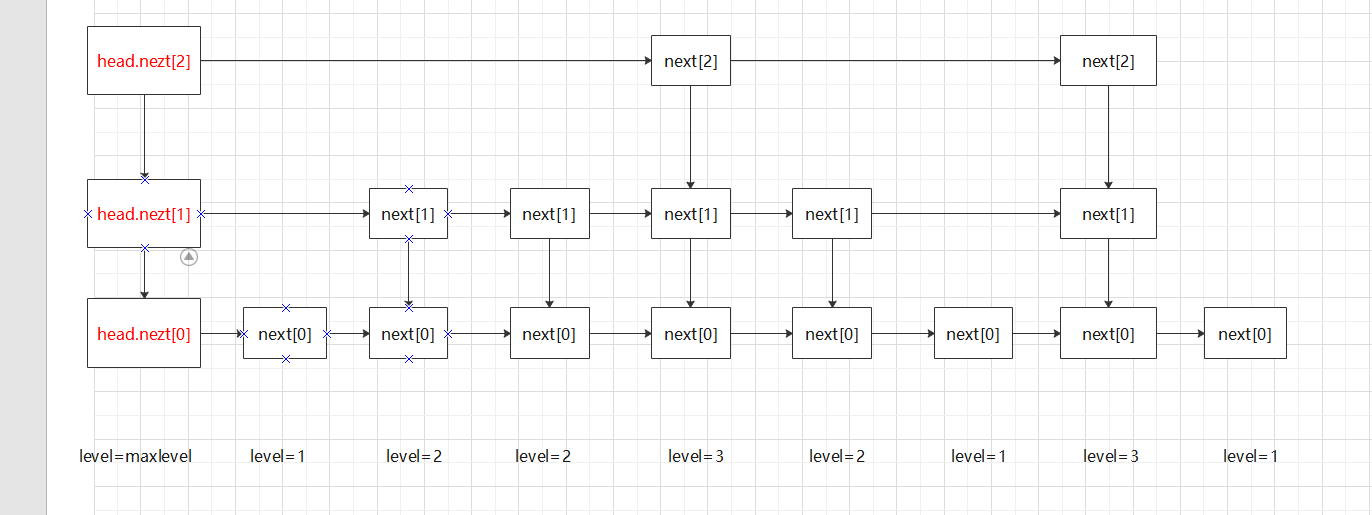
代码:

import java.util.Random; /**参考: * https://www.cnblogs.com/acfox/p/3688607.html * https://blog.csdn.net/pcwl1206/article/details/83512600 * * 查找 * 插入 * 删除 */ public class SkipList { private static final int MAX_LEVEL=16; private int levelCount=1; private Node head=new Node(); //内部类 public class Node{ private int data=-1; private Node next[]=new Node[MAX_LEVEL]; private int maxLevel=0; } //查找 public Node find(int data){ Node p=head; for(int i=levelCount-1;i>=0;--i){ while(p.next[i]!=null&&p.next[i].data<data){ p=p.next[i]; } } if(p.next[0]!=null&&p.next[0].data==data){ return p.next[0]; }else return null; } // public void insert(int value) { int level = randomLevel(); if (levelCount < level){ levelCount = levelCount+1; level=levelCount; } Node newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = value; newNode.maxLevel = level; Node update[]=new Node[level]; for(int i=0;i<level;i++) update[i]=head; Node p = head; //找到新节点再所有所在层(level)的前驱节点, for(int i=level-1;i>=0;i--){ while(p.next[i]!=null&&p.next[i].data<value){ p=p.next[i]; } update[i]=p; } //再所有所在层插入节点 for(int i=0;i<level;i++){ newNode.next[i]=update[i].next[i]; update[i].next[i]=newNode; } } //删除操作 public void delete(int data){ Node[] update=new Node[levelCount]; Node p=head; for(int i=levelCount-1;i>=0;i--){ while(p.next[i]!=null&&p.next[i].data<data){ p=p.next[i]; } update[i]=p; } if(p.next[0]!=null&&p.next[0].data==data){ for(int i=levelCount-1;i>=0;i--){ if(update[i].next!=null&&update[i].next[i].data==data){ update[i].next[i]=update[i].next[i].next[i]; } } } } //随机函数-保证第n层的节点数是总结的数的2的n-1次方分子一 //抛硬币,抛最大层数次,连续出现几次正面,就几层 private int randomLevel(){ Random rand=new Random(); int level=1; for(int i=0;i<MAX_LEVEL;i++){ int a=rand.nextInt(2);//产生0或者1 //System.out.println("a="+a); if(a==0){ level++; }else break; } System.out.println("l="+level); return level; } //打印跳表 private void printlist(){ Node p=head; System.out.println("跳表:"); for(int i=levelCount-1;i>=0;i--){ p=head; while (p.next[i]!=null){ System.out.print(p.next[i].data+"->"); p=p.next[i]; } if(p.next[i]==null) System.out.print("null"); System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String args[]) { SkipList l=new SkipList(); //l.randomLevel(); l.insert(3); l.insert(5); l.insert(7); l.insert(2); l.insert(9); l.insert(4); l.insert(17); //System.out.println("跳表层数:"+l.levelCount); l.printlist(); System.out.println(l.find(3).maxLevel); l.delete(5); l.printlist(); } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号