ContentProvider的启动
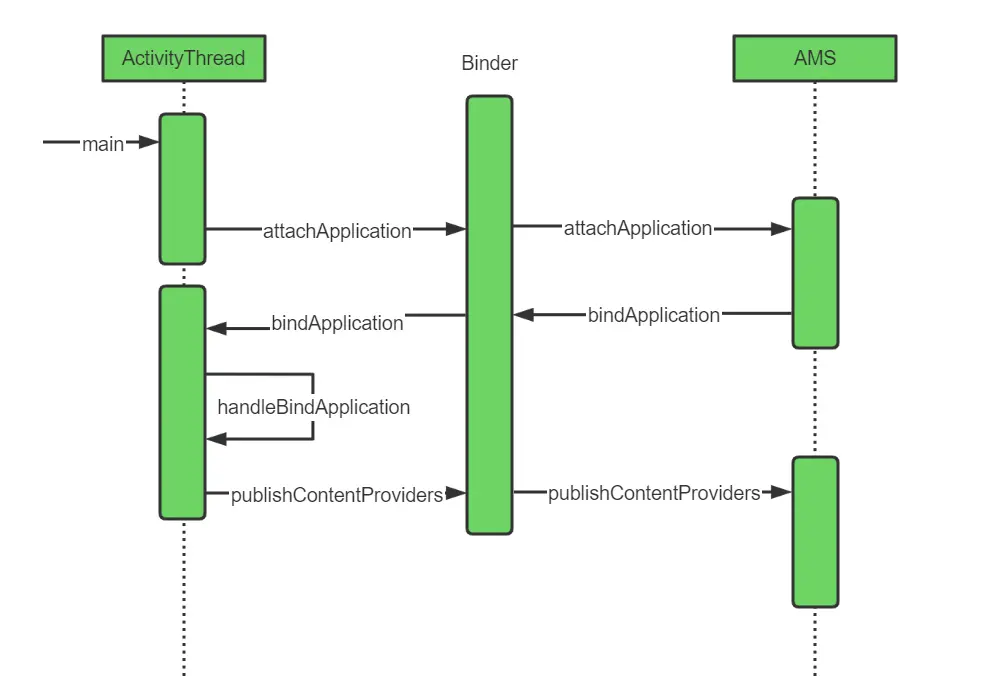
ContentProvider是在应用进程被创建的时候被创建的,所以这个流程也是进程创建的流程。进程间的通信是通过Binder机制实现的。
在Activity中我是使用如下代码调用Content Provider的:
public class ContentProviderActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final static String TAG = "ContentProviderActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_content_provider); Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovide.GameProvider"); ContentValues mContentValues = new ContentValues(); mContentValues.put("_id", 2); mContentValues.put("name", "大航海时代ol"); mContentValues.put("describe", "最好玩的航海网游"); getContentResolver().insert(uri, mContentValues);//1 Cursor gameCursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, new String[]{"name", "describe"}, null, null, null); ... } }
要想调用Content Provider,首先需要使用注释1处的getContentResolver方法,如下所示。
frameworks/base/core/Java/android/content/ContextWrapper.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
Context mBase;
@Override public ContentResolver getContentResolver() { return mBase.getContentResolver(); }
这里mBase指的是ContextImpl,ContextImpl的getContentResolver方法如下所示。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private final ApplicationContentResolver mContentResolver;
@Override public ContentResolver getContentResolver() { return mContentResolver; }
上面的代码return了ApplicationContentResolver类型的mContentResolver对象,ApplicationContentResolver是ContextImpl中的静态内部类,继承自ContentResolver,它在ContextImpl的构造方法中被创建。
private ContextImpl(@Nullable ContextImpl container, @NonNull ActivityThread mainThread, @NonNull LoadedApk packageInfo, @NonNull ContextParams params, @Nullable String attributionTag, @Nullable AttributionSource nextAttributionSource, @Nullable String splitName, @Nullable IBinder token, @Nullable UserHandle user, int flags, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader, @Nullable String overrideOpPackageName) { mOuterContext = this; // If creator didn't specify which storage to use, use the default // location for application. if ((flags & (Context.CONTEXT_CREDENTIAL_PROTECTED_STORAGE | Context.CONTEXT_DEVICE_PROTECTED_STORAGE)) == 0) { final File dataDir = packageInfo.getDataDirFile(); if (Objects.equals(dataDir, packageInfo.getCredentialProtectedDataDirFile())) { flags |= Context.CONTEXT_CREDENTIAL_PROTECTED_STORAGE; } else if (Objects.equals(dataDir, packageInfo.getDeviceProtectedDataDirFile())) { flags |= Context.CONTEXT_DEVICE_PROTECTED_STORAGE; } } mMainThread = mainThread; mToken = token; mFlags = flags; if (user == null) { user = Process.myUserHandle(); } mUser = user; mPackageInfo = packageInfo; mSplitName = splitName; mClassLoader = classLoader; mResourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance(); String opPackageName; if (container != null) { mBasePackageName = container.mBasePackageName; opPackageName = container.mOpPackageName; setResources(container.mResources); mDisplay = container.mDisplay; mForceDisplayOverrideInResources = container.mForceDisplayOverrideInResources; mIsConfigurationBasedContext = container.mIsConfigurationBasedContext; mContextType = container.mContextType; mContentCaptureOptions = container.mContentCaptureOptions; } else { mBasePackageName = packageInfo.mPackageName; ApplicationInfo ainfo = packageInfo.getApplicationInfo(); if (ainfo.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID && ainfo.uid != Process.myUid()) { // Special case: system components allow themselves to be loaded in to other // processes. For purposes of app ops, we must then consider the context as // belonging to the package of this process, not the system itself, otherwise // the package+uid verifications in app ops will fail. opPackageName = ActivityThread.currentPackageName(); } else { opPackageName = mBasePackageName; } } mOpPackageName = overrideOpPackageName != null ? overrideOpPackageName : opPackageName; mParams = Objects.requireNonNull(params); mAttributionSource = createAttributionSource(attributionTag, nextAttributionSource, params.getRenouncedPermissions()); mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread); }
当我们调用ContentResolver的insert、query、update等方法时就会启动Content Provider,这里拿query方法来进行举例。
query方法的实现在ApplicationContentResolver的父类ContentResolver中,代码如下所示。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/ContentResolver.java
@Override public final @Nullable Cursor query(final @RequiresPermission.Read @NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable String[] projection, @Nullable Bundle queryArgs, @Nullable CancellationSignal cancellationSignal) { Objects.requireNonNull(uri, "uri"); try { if (mWrapped != null) { return mWrapped.query(uri, projection, queryArgs, cancellationSignal); } } catch (RemoteException e) { return null; } //返回IContentProvider类型的unstableProvider对象 IContentProvider unstableProvider = acquireUnstableProvider(uri); if (unstableProvider == null) { return null; } IContentProvider stableProvider = null; Cursor qCursor = null; try { long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); ICancellationSignal remoteCancellationSignal = null; if (cancellationSignal != null) { cancellationSignal.throwIfCanceled(); remoteCancellationSignal = unstableProvider.createCancellationSignal(); cancellationSignal.setRemote(remoteCancellationSignal); } try {
//调用query方法 qCursor = unstableProvider.query(mContext.getAttributionSource(), uri, projection, queryArgs, remoteCancellationSignal); } catch (DeadObjectException e) { // The remote process has died... but we only hold an unstable // reference though, so we might recover!!! Let's try!!!! // This is exciting!!1!!1!!!!1 unstableProviderDied(unstableProvider); stableProvider = acquireProvider(uri); if (stableProvider == null) { return null; } qCursor = stableProvider.query(mContext.getAttributionSource(), uri, projection, queryArgs, remoteCancellationSignal); } if (qCursor == null) { return null; } // Force query execution. Might fail and throw a runtime exception here. qCursor.getCount(); long durationMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime; maybeLogQueryToEventLog(durationMillis, uri, projection, queryArgs); // Wrap the cursor object into CursorWrapperInner object. final IContentProvider provider = (stableProvider != null) ? stableProvider : acquireProvider(uri); final CursorWrapperInner wrapper = new CursorWrapperInner(qCursor, provider); stableProvider = null; qCursor = null; return wrapper; } catch (RemoteException e) { // Arbitrary and not worth documenting, as Activity // Manager will kill this process shortly anyway. return null; } finally { if (qCursor != null) { qCursor.close(); } if (cancellationSignal != null) { cancellationSignal.setRemote(null); } if (unstableProvider != null) { releaseUnstableProvider(unstableProvider); } if (stableProvider != null) { releaseProvider(stableProvider); } } }
我们查看acquireUnstableProvider方法做了什么,如下所示。
/** * Returns the content provider for the given content URI. * * @param uri The URI to a content provider * @return The ContentProvider for the given URI, or null if no content provider is found. * @hide */ public final IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Uri uri) { if (!SCHEME_CONTENT.equals(uri.getScheme())) {//1 return null; } String auth = uri.getAuthority(); if (auth != null) { return acquireUnstableProvider(mContext, uri.getAuthority());//2 } return null; }
注释1处用来检查Uri的scheme是否等于”content”,如果不是则返回null。注释2处调用了acquireUnstableProvider方法,这是个抽象方法,它的实现在ContentResolver的子类ApplicationContentResolver中:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final @NonNull ActivityThread mMainThread;
@Override protected IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Context c, String auth) { return mMainThread.acquireProvider(c, ContentProvider.getAuthorityWithoutUserId(auth), resolveUserIdFromAuthority(auth), false); }
return了ActivityThread类型的mMainThread对象的acquireProvider方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage public final IContentProvider acquireProvider( Context c, String auth, int userId, boolean stable) { final IContentProvider provider = acquireExistingProvider(c, auth, userId, stable);//1 if (provider != null) { return provider; } // There is a possible race here. Another thread may try to acquire // the same provider at the same time. When this happens, we want to ensure // that the first one wins. // Note that we cannot hold the lock while acquiring and installing the // provider since it might take a long time to run and it could also potentially // be re-entrant in the case where the provider is in the same process. ContentProviderHolder holder = null; final ProviderKey key = getGetProviderKey(auth, userId); try { synchronized (key) { holder = ActivityManager.getService().getContentProvider( getApplicationThread(), c.getOpPackageName(), auth, userId, stable);//2 // If the returned holder is non-null but its provider is null and it's not // local, we'll need to wait for the publishing of the provider. if (holder != null && holder.provider == null && !holder.mLocal) { synchronized (key.mLock) { key.mLock.wait(ContentResolver.CONTENT_PROVIDER_READY_TIMEOUT_MILLIS); holder = key.mHolder; } if (holder != null && holder.provider == null) { // probably timed out holder = null; } } } } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { holder = null; } finally { // Clear the holder from the key since the key itself is never cleared. synchronized (key.mLock) { key.mHolder = null; } } if (holder == null) { if (UserManager.get(c).isUserUnlocked(userId)) { Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to find provider info for " + auth); } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to find provider info for " + auth + " (user not unlocked)"); } return null; } // Install provider will increment the reference count for us, and break // any ties in the race. holder = installProvider(c, holder, holder.info, true /*noisy*/, holder.noReleaseNeeded, stable); return holder.provider; }
注释1处检查ActivityThread中的ArrayMap类型的mProviderMap中是否有目标ContentProvider存在,有则返回,没有就会在注释2处调用AMS的getContentProvider方法。注释3处的installProvider方法用来将注释2处返回的ContentProvider相关的数据存储在mProviderMap中,起到缓存的作用,这样使用相同的Content Provider时,就不需要每次都要调用AMS的getContentProvider方法。使用我们接着查看AMS的getContentProvider方法,代码如下所示。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
final ContentProviderHelper mCpHelper;
@Override public final ContentProviderHolder getContentProvider( IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, String name, int userId, boolean stable) { traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "getContentProvider: ", name); try { return mCpHelper.getContentProvider(caller, callingPackage, name, userId, stable); } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); } }
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ContentProviderHelper.java
ContentProviderHolder getContentProvider(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, String name, int userId, boolean stable) { mService.enforceNotIsolatedCaller("getContentProvider"); if (caller == null) { String msg = "null IApplicationThread when getting content provider " + name; Slog.w(TAG, msg); throw new SecurityException(msg); } // The incoming user check is now handled in checkContentProviderPermissionLocked() to deal // with cross-user grant. final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); if (callingPackage != null && mService.mAppOpsService.checkPackage( callingUid, callingPackage) != AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED) { throw new SecurityException("Given calling package " + callingPackage + " does not match caller's uid " + callingUid); } return getContentProviderImpl(caller, name, null, callingUid, callingPackage, null, stable, userId); }
private ContentProviderHolder getContentProviderImpl(IApplicationThread caller, String name, IBinder token, boolean stable, int userId) { ... ProcessRecord proc = getProcessRecordLocked( cpi.processName, cpr.appInfo.uid, false);//1 if (proc != null && proc.thread != null && !proc.killed) { ... if (!proc.pubProviders.containsKey(cpi.name)) { checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: scheduling install"); proc.pubProviders.put(cpi.name, cpr); try { proc.thread.scheduleInstallProvider(cpi);//2 } catch (RemoteException e) { } } } else { checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: before start process"); proc = startProcessLocked(cpi.processName, cpr.appInfo, false, 0, "content provider", new ComponentName(cpi.applicationInfo.packageName, cpi.name), false, false, false);//3 checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: after start process"); ... } ... }
getContentProviderImpl方法的代码很多,这里截取了关键的部分。注释1处通过getProcessRecordLocked方法来获取目标ContentProvider的应用程序进程信息,这些信息用ProcessRecord类型的proc来表示,如果该应用进程已经启动就会调用注释2处的代码,否则就会调用注释3的startProcessLocked方法来启动进程。这里我们假设ContentProvider的应用进程还没有启动,最终会调用ActivityThread的main方法,代码如下所示。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args) { ... Looper.prepareMainLooper();//1 ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();//2 thread.attach(false); if (sMainThreadHandler == null) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } if (false) { Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread")); } // End of event ActivityThreadMain. Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); Looper.loop();//3 throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
注释1处通过prepareMainLooper方法在ThreadLocal中获取Looper,并在注释3处开启消息循环。在注释2处创建了ActivityThread并调用了它的attach方法:
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) { sCurrentActivityThread = this; mConfigurationController = new ConfigurationController(this); mSystemThread = system; if (!system) { android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>", UserHandle.myUserId()); RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder()); final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService(); //1 try { mgr.attachApplication(
, startSeq); //2 } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } // Watch for getting close to heap limit. BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) { return; } Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime(); long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory(); long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory(); if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) { if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024) + " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024) + " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024)); mSomeActivitiesChanged = false; try { ActivityTaskManager.getService().releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } } }); } else { // Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes, // we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die. android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process", UserHandle.myUserId()); try { mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation(); mInstrumentation.basicInit(this); ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext( this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo); mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null); mInitialApplication.onCreate(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e); } } ViewRootImpl.ConfigChangedCallback configChangedCallback = (Configuration globalConfig) -> { synchronized (mResourcesManager) { // TODO (b/135719017): Temporary log for debugging IME service. if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE && mHasImeComponent) { Log.d(TAG, "ViewRootImpl.ConfigChangedCallback for IME, " + "config=" + globalConfig); } // We need to apply this change to the resources immediately, because upon returning // the view hierarchy will be informed about it. if (mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResources(globalConfig, null /* compat */, mInitialApplication.getResources().getDisplayAdjustments())) { mConfigurationController.updateLocaleListFromAppContext( mInitialApplication.getApplicationContext()); // This actually changed the resources! Tell everyone about it. final Configuration updatedConfig = mConfigurationController.updatePendingConfiguration(globalConfig); if (updatedConfig != null) { sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, globalConfig); mPendingConfiguration = updatedConfig; } } } }; ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(configChangedCallback); }
注释1处最终会得到AMS,在注释2处调用AMS的attachApplication方法,并将ApplicationThread类型的mAppThread对象传进去。
query方法到AMS的调用过程,如下面时序图所示(省略应用程序进程启动过程)
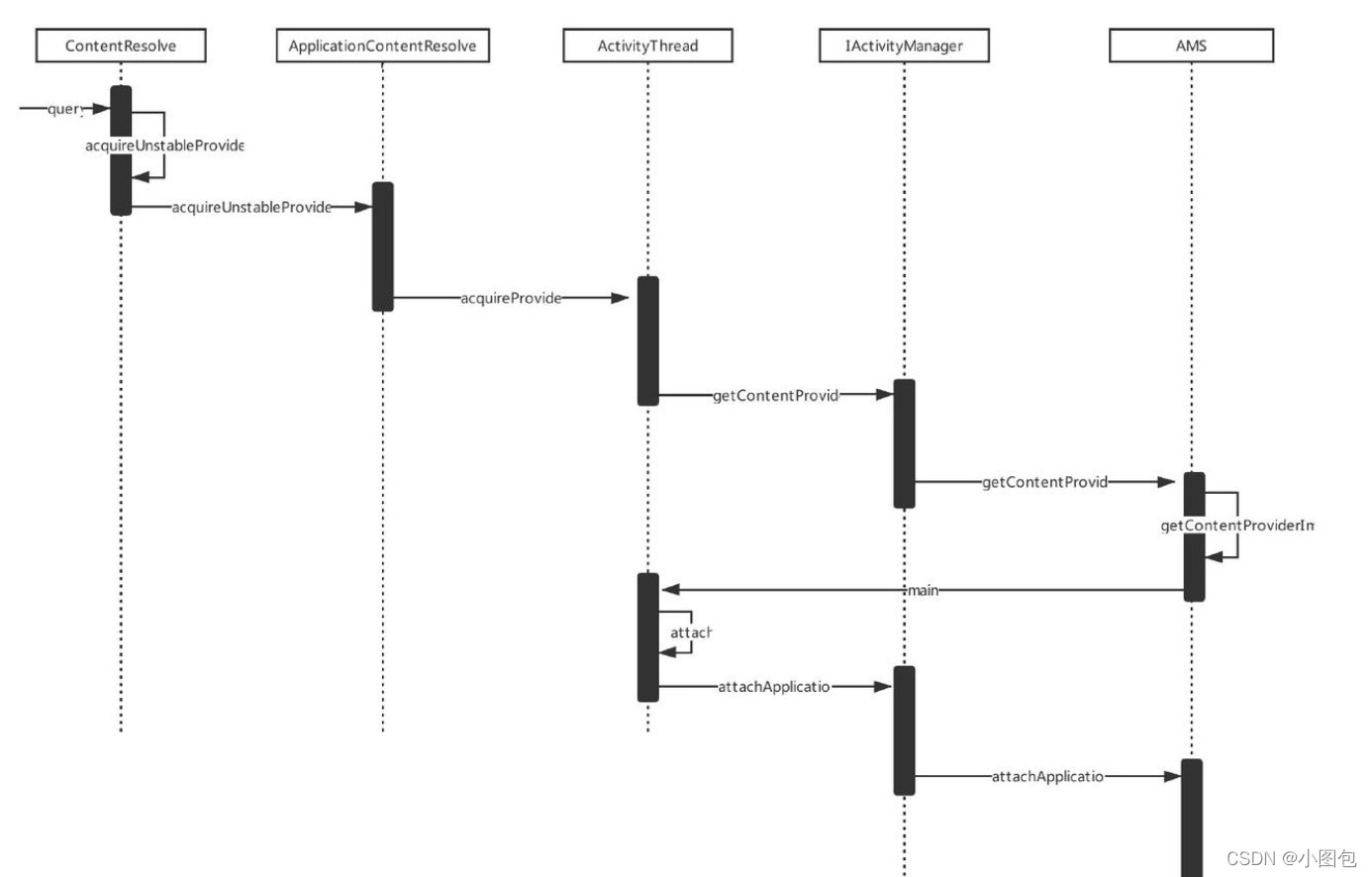
2.AMS启动Content Provider的过程
我们接着来查看AMS的attachApplication方法,如下所示。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
@Override public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) { if (thread == null) { throw new SecurityException("Invalid application interface"); } synchronized (this) { int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid(); final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq); Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); } }
attachApplication方法中又调用了attachApplicationLocked方法:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread, int pid) { ... thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass, profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher, app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode, mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation, isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent, new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated), mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked()); ... }
attachApplicationLocked方法中调用了thread的bindApplication方法,thread是IApplicationThread类型的,从类型名字就可以看出来是用于进程间通信,在 attachApplicationLocked 函数中调用了 thread.bindApplication 方法,thread 是 IApplicationThread ,这里和 IActivityManager 一样采用了 aidl 进行进程间传输数据,我们回到 ActivityThread 内部类 ApplicationThread 的 bindApplication 方法
//ActivityThread.java public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo, List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs, IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode, boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings, String buildSerial) { if (services != null) { // Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services); } setCoreSettings(coreSettings); AppBindData data = new AppBindData(); data.processName = processName; data.appInfo = appInfo; data.providers = providers; data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName; data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs; data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher; data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection; data.debugMode = debugMode; data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking; data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation; data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode; data.persistent = persistent; data.config = config; data.compatInfo = compatInfo; data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo; data.buildSerial = buildSerial; //发送消息给 H 类 sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data); }
ActivityThread 内部类 H 收到消息,开始处理 BIND_APPLICSTION消息,代码如下:
case BIND_APPLICATION: Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication"); AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj; handleBindApplication(data); Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); break;
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// Register the UI Thread as a sensitive thread to the runtime.
VMRuntime.registerSensitiveThread();
// In the case the stack depth property exists, pass it down to the runtime.
String property = SystemProperties.get("debug.allocTracker.stackDepth");
if (property.length() != 0) {
VMDebug.setAllocTrackerStackDepth(Integer.parseInt(property));
}
if (data.trackAllocation) {
DdmVmInternal.setRecentAllocationsTrackingEnabled(true);
}
// Note when this process has started.
Process.setStartTimes(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(), SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
AppCompatCallbacks.install(data.disabledCompatChanges);
// Let libcore handle any compat changes after installing the list of compat changes.
AppSpecializationHooks.handleCompatChangesBeforeBindingApplication();
mBoundApplication = data;
mConfigurationController.setConfiguration(data.config);
mConfigurationController.setCompatConfiguration(data.config);
mConfiguration = mConfigurationController.getConfiguration();
mProfiler = new Profiler();
String agent = null;
if (data.initProfilerInfo != null) {
mProfiler.profileFile = data.initProfilerInfo.profileFile;
mProfiler.profileFd = data.initProfilerInfo.profileFd;
mProfiler.samplingInterval = data.initProfilerInfo.samplingInterval;
mProfiler.autoStopProfiler = data.initProfilerInfo.autoStopProfiler;
mProfiler.streamingOutput = data.initProfilerInfo.streamingOutput;
if (data.initProfilerInfo.attachAgentDuringBind) {
agent = data.initProfilerInfo.agent;
}
}
// send up app name; do this *before* waiting for debugger
Process.setArgV0(data.processName);
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName(data.processName,
data.appInfo.packageName,
UserHandle.myUserId());
VMRuntime.setProcessPackageName(data.appInfo.packageName);
// Pass data directory path to ART. This is used for caching information and
// should be set before any application code is loaded.
VMRuntime.setProcessDataDirectory(data.appInfo.dataDir);
if (mProfiler.profileFd != null) {
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
// If the app is Honeycomb MR1 or earlier, switch its AsyncTask
// implementation to use the pool executor. Normally, we use the
// serialized executor as the default. This has to happen in the
// main thread so the main looper is set right.
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB_MR1) {
AsyncTask.setDefaultExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR);
}
// Let the util.*Array classes maintain "undefined" for apps targeting Pie or earlier.
UtilConfig.setThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds(
data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.Q);
Message.updateCheckRecycle(data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion);
// Supply the targetSdkVersion to the UI rendering module, which may
// need it in cases where it does not have access to the appInfo.
android.graphics.Compatibility.setTargetSdkVersion(data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion);
/*
* Before spawning a new process, reset the time zone to be the system time zone.
* This needs to be done because the system time zone could have changed after the
* the spawning of this process. Without doing this this process would have the incorrect
* system time zone.
*/
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
/*
* Set the LocaleList. This may change once we create the App Context.
*/
LocaleList.setDefault(data.config.getLocales());
if (Typeface.ENABLE_LAZY_TYPEFACE_INITIALIZATION) {
try {
Typeface.setSystemFontMap(data.mSerializedSystemFontMap);
} catch (IOException | ErrnoException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to parse serialized system font map");
Typeface.loadPreinstalledSystemFontMap();
}
}
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
/*
* Update the system configuration since its preloaded and might not
* reflect configuration changes. The configuration object passed
* in AppBindData can be safely assumed to be up to date
*/
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResources(data.config, data.compatInfo);
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = data.config.densityDpi;
// This calls mResourcesManager so keep it within the synchronized block.
mConfigurationController.applyCompatConfiguration();
}
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);
if (agent != null) {
handleAttachAgent(agent, data.info);
}
/**
* Switch this process to density compatibility mode if needed.
*/
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SCREEN_DENSITIES)
== 0) {
mDensityCompatMode = true;
Bitmap.setDefaultDensity(DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT);
}
mConfigurationController.updateDefaultDensity(data.config.densityDpi);
// mCoreSettings is only updated from the main thread, while this function is only called
// from main thread as well, so no need to lock here.
final String use24HourSetting = mCoreSettings.getString(Settings.System.TIME_12_24);
Boolean is24Hr = null;
if (use24HourSetting != null) {
is24Hr = "24".equals(use24HourSetting) ? Boolean.TRUE : Boolean.FALSE;
}
// null : use locale default for 12/24 hour formatting,
// false : use 12 hour format,
// true : use 24 hour format.
DateFormat.set24HourTimePref(is24Hr);
updateDebugViewAttributeState();
StrictMode.initThreadDefaults(data.appInfo);
StrictMode.initVmDefaults(data.appInfo);
if (data.debugMode != ApplicationThreadConstants.DEBUG_OFF) {
// XXX should have option to change the port.
Debug.changeDebugPort(8100);
if (data.debugMode == ApplicationThreadConstants.DEBUG_WAIT) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application " + data.info.getPackageName()
+ " is waiting for the debugger on port 8100...");
IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.showWaitingForDebugger(mAppThread, true);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
Debug.waitForDebugger();
try {
mgr.showWaitingForDebugger(mAppThread, false);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application " + data.info.getPackageName()
+ " can be debugged on port 8100...");
}
}
// Allow binder tracing, and application-generated systrace messages if we're profileable.
boolean isAppDebuggable = (data.appInfo.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0;
boolean isAppProfileable = isAppDebuggable || data.appInfo.isProfileable();
Trace.setAppTracingAllowed(isAppProfileable);
if ((isAppProfileable || Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE) && data.enableBinderTracking) {
Binder.enableTracing();
}
// Initialize heap profiling.
if (isAppProfileable || Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE) {
nInitZygoteChildHeapProfiling();
}
// Allow renderer debugging features if we're debuggable.
HardwareRenderer.setDebuggingEnabled(isAppDebuggable || Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE);
HardwareRenderer.setPackageName(data.appInfo.packageName);
// Pass the current context to HardwareRenderer
HardwareRenderer.setContextForInit(getSystemContext());
// Instrumentation info affects the class loader, so load it before
// setting up the app context.
final InstrumentationInfo ii;
if (data.instrumentationName != null) {
ii = prepareInstrumentation(data);
} else {
ii = null;
}
1. 创建 ContentImpl
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
mConfigurationController.updateLocaleListFromAppContext(appContext);
// Initialize the default http proxy in this process.
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Setup proxies");
try {
// In pre-boot mode (doing initial launch to collect password), not all system is up.
// This includes the connectivity service, so trying to obtain ConnectivityManager at
// that point would return null. Check whether the ConnectivityService is available, and
// avoid crashing with a NullPointerException if it is not.
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (b != null) {
final ConnectivityManager cm =
appContext.getSystemService(ConnectivityManager.class);
Proxy.setHttpProxyConfiguration(cm.getDefaultProxy());
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
if (!Process.isIsolated()) {
final int oldMask = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWritesMask();
try {
setupGraphicsSupport(appContext);
} finally {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicyMask(oldMask);
}
} else {
HardwareRenderer.setIsolatedProcess(true);
}
// Install the Network Security Config Provider. This must happen before the application
// code is loaded to prevent issues with instances of TLS objects being created before
// the provider is installed.
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install");
NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install(appContext);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
创建 Instrumentation
// Continue loading instrumentation.
if (ii != null) {
initInstrumentation(ii, data, appContext);
} else {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
mInstrumentation.basicInit(this);
}
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_LARGE_HEAP) != 0) {
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
} else {
// Small heap, clamp to the current growth limit and let the heap release
// pages after the growth limit to the non growth limit capacity. b/18387825
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clampGrowthLimit();
}
// Allow disk access during application and provider setup. This could
// block processing ordered broadcasts, but later processing would
// probably end up doing the same disk access.
Application app;
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy writesAllowedPolicy = StrictMode.getThreadPolicy();
try {
创建 Application
// If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment with the base application class.
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
// Propagate autofill compat state
app.setAutofillOptions(data.autofillOptions);
// Propagate Content Capture options
app.setContentCaptureOptions(data.contentCaptureOptions);
sendMessage(H.SET_CONTENT_CAPTURE_OPTIONS_CALLBACK, data.appInfo.packageName);
mInitialApplication = app;
final boolean updateHttpProxy;
synchronized (this) {
updateHttpProxy = mUpdateHttpProxyOnBind;
// This synchronized block ensures that any subsequent call to updateHttpProxy()
// will see a non-null mInitialApplication.
}
if (updateHttpProxy) {
ActivityThread.updateHttpProxy(app);
}
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
ContentProvider 启动的
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
}
}
// Do this after providers, since instrumentation tests generally start their
// test thread at this point, and we don't want that racing.
try {
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Exception thrown in onCreate() of "
+ data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
try {
调用 Application onCreate 生命周期方法
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
} finally {
// If the app targets < O-MR1, or doesn't change the thread policy
// during startup, clobber the policy to maintain behavior of b/36951662
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.O_MR1
|| StrictMode.getThreadPolicy().equals(writesAllowedPolicy)) {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy);
}
}
// Preload fonts resources
FontsContract.setApplicationContextForResources(appContext);
if (!Process.isIsolated()) {
try {
final ApplicationInfo info =
getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
data.appInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.GET_META_DATA /*flags*/,
UserHandle.myUserId());
if (info.metaData != null) {
final int preloadedFontsResource = info.metaData.getInt(
ApplicationInfo.METADATA_PRELOADED_FONTS, 0);
if (preloadedFontsResource != 0) {
data.info.getResources().preloadFonts(preloadedFontsResource);
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
看 ContentProvider 是如何启动的,代码如下:
@UnsupportedAppUsage private void installContentProviders( Context context, List<ProviderInfo> providers) { final ArrayList<ContentProviderHolder> results = new ArrayList<>(); 遍历当前应用程序进程的 ProviderInfo 列表,得到每个 ContentProvicer 的存储信息 for (ProviderInfo cpi : providers) { if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) { StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(128); buf.append("Pub "); buf.append(cpi.authority); buf.append(": "); buf.append(cpi.name); Log.i(TAG, buf.toString()); }
调用 installProvider 方法来启动这些 ContentProvider ContentProviderHolder cph = installProvider(context, null, cpi, false /*noisy*/, true /*noReleaseNeeded*/, true /*stable*/); if (cph != null) { cph.noReleaseNeeded = true; results.add(cph); } }
将启动了的 ContentProvider 存入 AMS 的 mProviderMap 中 就是用来缓存启动过的 ContentProvider try { ActivityManager.getService().publishContentProviders( getApplicationThread(), results); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } }
现在来看调用 installProvider 方法来启动这些 ContentProvider
/** * Installs the provider. * * Providers that are local to the process or that come from the system server * may be installed permanently which is indicated by setting noReleaseNeeded to true. * Other remote providers are reference counted. The initial reference count * for all reference counted providers is one. Providers that are not reference * counted do not have a reference count (at all). * * This method detects when a provider has already been installed. When this happens, * it increments the reference count of the existing provider (if appropriate) * and returns the existing provider. This can happen due to concurrent * attempts to acquire the same provider. */ @UnsupportedAppUsage private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context, ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info, boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) { ContentProvider localProvider = null; IContentProvider provider; if (holder == null || holder.provider == null) { if (DEBUG_PROVIDER || noisy) { Slog.d(TAG, "Loading provider " + info.authority + ": " + info.name); } Context c = null; ApplicationInfo ai = info.applicationInfo; if (context.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) { c = context; } else if (mInitialApplication != null && mInitialApplication.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) { c = mInitialApplication; } else { try { c = context.createPackageContext(ai.packageName, Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE); } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) { // Ignore } } if (c == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to get context for package " + ai.packageName + " while loading content provider " + info.name); return null; } if (info.splitName != null) { try { c = c.createContextForSplit(info.splitName); } catch (NameNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if (info.attributionTags != null && info.attributionTags.length > 0) { final String attributionTag = info.attributionTags[0]; c = c.createAttributionContext(attributionTag); } try { final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = c.getClassLoader(); LoadedApk packageInfo = peekPackageInfo(ai.packageName, true); if (packageInfo == null) { // System startup case. packageInfo = getSystemContext().mPackageInfo; }
实例化 ContentProvider 对象 localProvider = packageInfo.getAppFactory() .instantiateProvider(cl, info.name); provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider(); if (provider == null) { Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to instantiate class " + info.name + " from sourceDir " + info.applicationInfo.sourceDir); return null; } if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v( TAG, "Instantiating local provider " + info.name); // XXX Need to create the correct context for this provider.
调用它的 attachInfo 方法
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info); } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(null, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to get provider " + info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } return null; } } else { provider = holder.provider; if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Installing external provider " + info.authority + ": " + info.name); } ContentProviderHolder retHolder; synchronized (mProviderMap) { if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Checking to add " + provider + " / " + info.name); IBinder jBinder = provider.asBinder(); if (localProvider != null) { ComponentName cname = new ComponentName(info.packageName, info.name); ProviderClientRecord pr = mLocalProvidersByName.get(cname); if (pr != null) { if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) { Slog.v(TAG, "installProvider: lost the race, " + "using existing local provider"); } provider = pr.mProvider; } else { holder = new ContentProviderHolder(info); holder.provider = provider; holder.noReleaseNeeded = true; pr = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked(provider, localProvider, holder); mLocalProviders.put(jBinder, pr); mLocalProvidersByName.put(cname, pr); } retHolder = pr.mHolder; } else { ProviderRefCount prc = mProviderRefCountMap.get(jBinder); if (prc != null) { if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) { Slog.v(TAG, "installProvider: lost the race, updating ref count"); } // We need to transfer our new reference to the existing // ref count, releasing the old one... but only if // release is needed (that is, it is not running in the // system process). if (!noReleaseNeeded) { incProviderRefLocked(prc, stable); try { ActivityManager.getService().removeContentProvider( holder.connection, stable); } catch (RemoteException e) { //do nothing content provider object is dead any way } } } else { ProviderClientRecord client = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked( provider, localProvider, holder); if (noReleaseNeeded) { prc = new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1000, 1000); } else { prc = stable ? new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1, 0) : new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 0, 1); } mProviderRefCountMap.put(jBinder, prc); } retHolder = prc.holder; } } return retHolder; }
//ContentProvider.java public void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info) { attachInfo(context, info, false); } private void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info, boolean testing) { mNoPerms = testing; if (mContext == null) { mContext = context; if (context != null) { mTransport.mAppOpsManager = (AppOpsManager) context.getSystemService( Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE); } mMyUid = Process.myUid(); if (info != null) { setReadPermission(info.readPermission); setWritePermission(info.writePermission); setPathPermissions(info.pathPermissions); mExported = info.exported; mSingleUser = (info.flags & ProviderInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER) != 0; setAuthorities(info.authority); } /** * 安装成功,调用生命周期函数 onCreate */ ContentProvider.this.onCreate(); } } public abstract boolean onCreate();
可以看到最后在 ContentProvider 的 attachInfo 函数中进行调用了抽象方法 onCreate, 那么它的子类就会进行实现 onCreate 达到启动成功的通知。
(296条消息) Android 源码分析 (十一) ContentProvider 启动_android contentprovider 启动_小图包的博客-CSDN博客



