c语言学习笔记
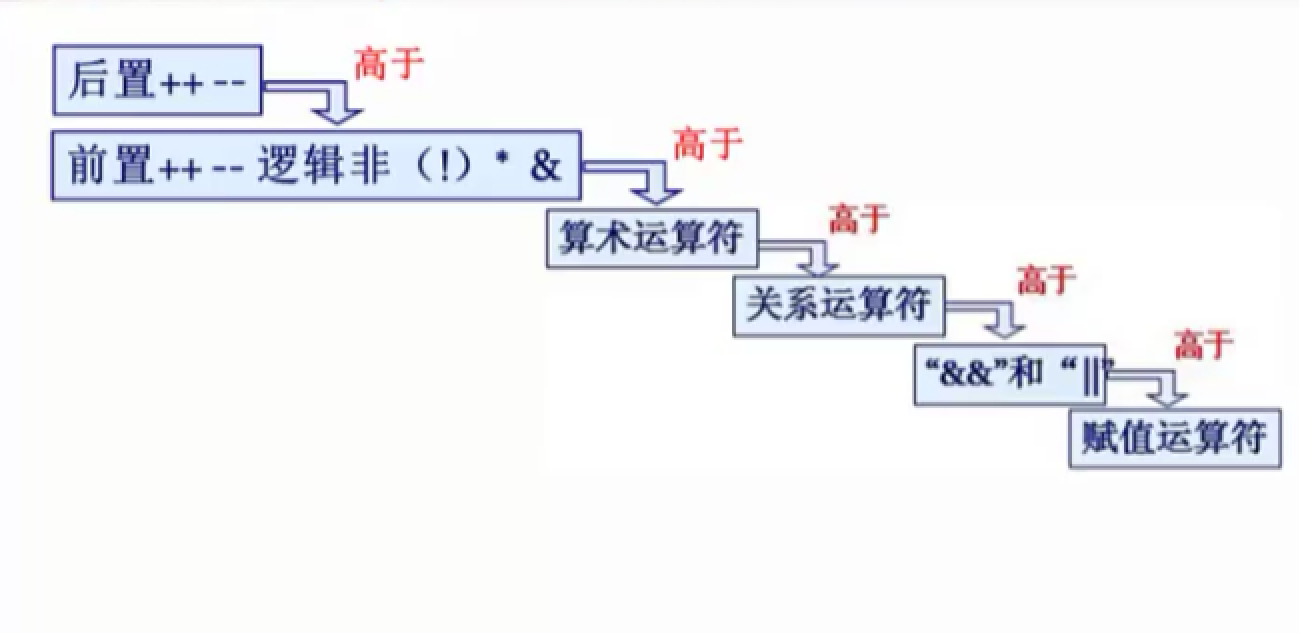
运算符优先级:
1.100以内素数筛选法:
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() { int sum = 0, a[100] = { 0 }; for (int i = 2; i < sqrt(100.0); i++) { sum = i; if (a[sum] == 0) { while (sum < 100) { sum += i; if (sum < 100)a[sum] = 1; } } } for (int i = 2; i < 100; i++) { if (a[i] == 0)cout << i << " "; } return 0; }
2.cin && cin.get &&getchar && cin.getline
cin.get(c, 10, '\n') 每次读最多9个字符,如果提前碰到结束标识符,则小于9
cin不能读空格/回车,cin.get可以;getchar不跳过任何字符
cin/cin.get 缓冲区指针停在终止字符前;
cin.getline 缓冲区指针停在终止字符后;
3.引入文件 :#include “xxx.h”
4.m个苹果放进n个盘子有多少种情况:
int count(int m, int n) { if (m <= 1 || n <= 1)return 1;//一个苹果或者1个盘子的情况 if (m < n) return count(m, m);//苹果数小于盘子数,多余的盘子可以不要 else //苹果数大于盘子数,分解成盘子空和盘子不空的情况 return count(m, n - 1) + count(m - n, n); }
5.逆波兰表达式计算
double notation(){ char str[10]; cin >> str; switch (str[0]) { case '+':return notation() + notation(); case '-':return notation()- notation(); case '*':return notation() * notation(); case '/':return notation() / notation(); default:return atof(str); } }
6.汉诺塔问题
void move(int m, char x, char y, char z) { if (m == 1) { cout << "把一个盘子从" << x << "移动到" << z << endl; } else { move(m - 1, x, z, y); cout << "把一个盘子从" << x << "移动到" << z << endl; move(m - 1, y, x, z); } }
7.二进制打印
int binary(int n) { if (n / 2 != 0) binary(n / 2); if (n!=0) cout << n % 2 ; return 0; }
8.
先计算后置++
9.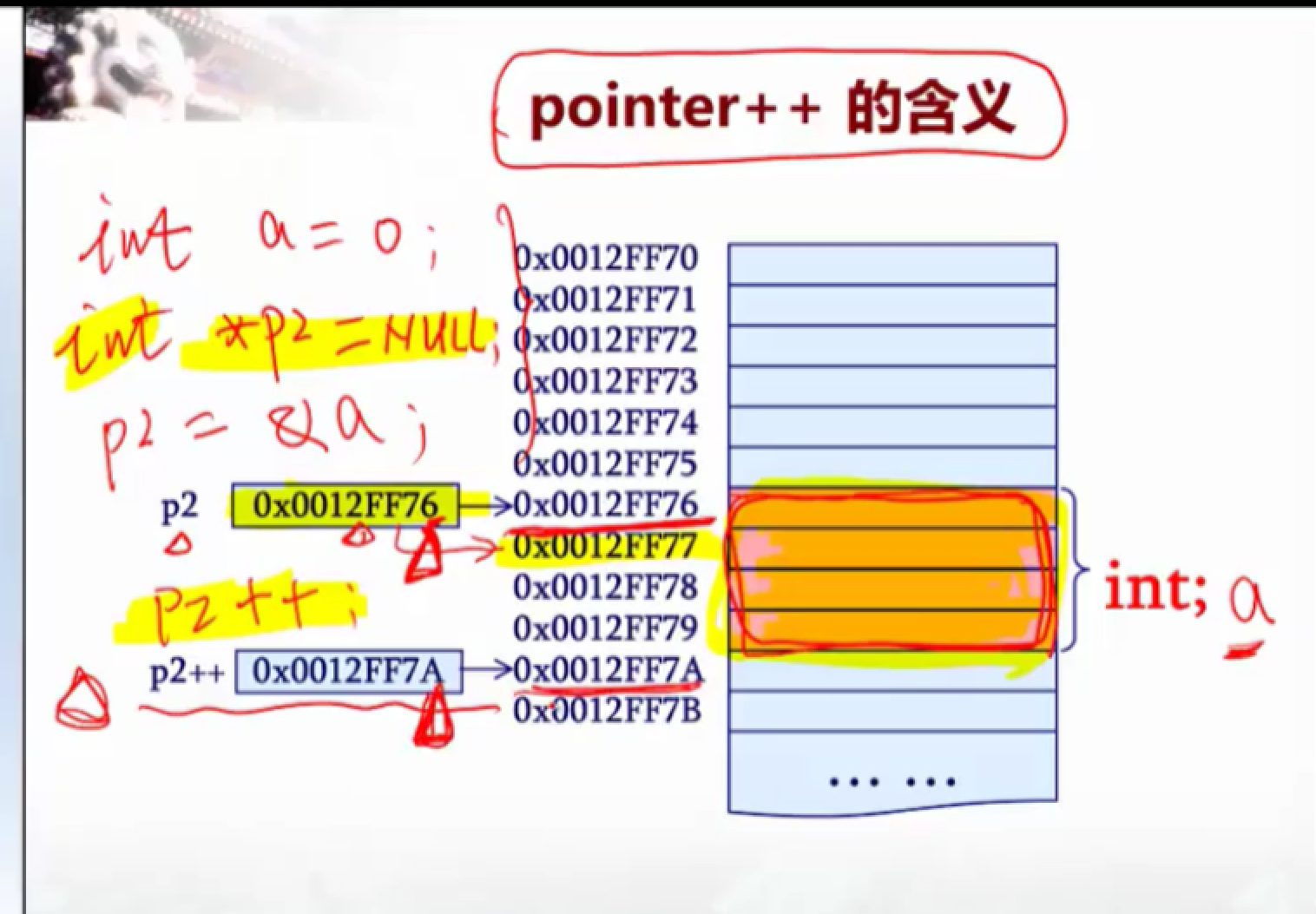
原因:p2的基类型是int类型,占4个字节,不可分割,因此系统会跨过4个字节


10.指针与数组
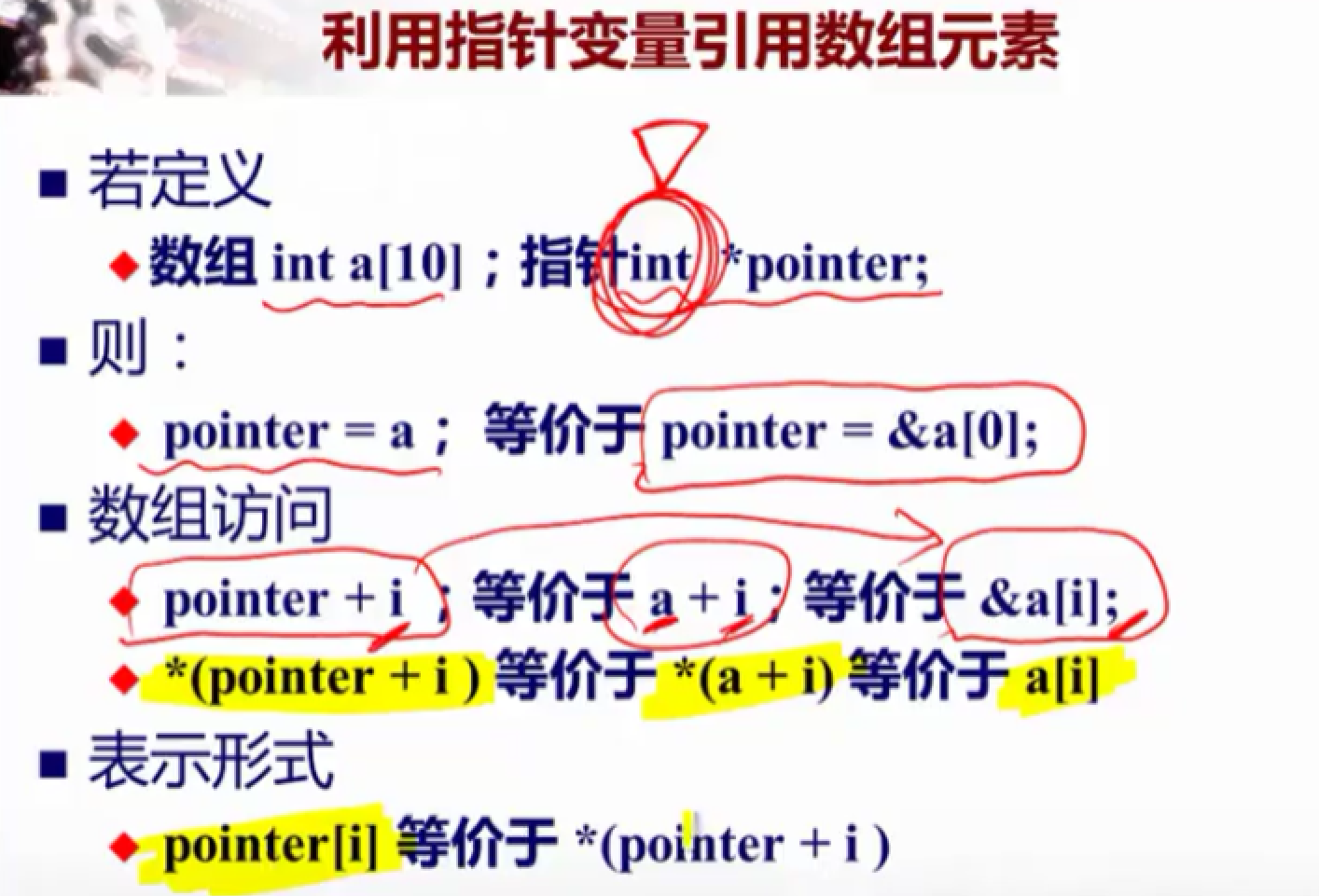
11.
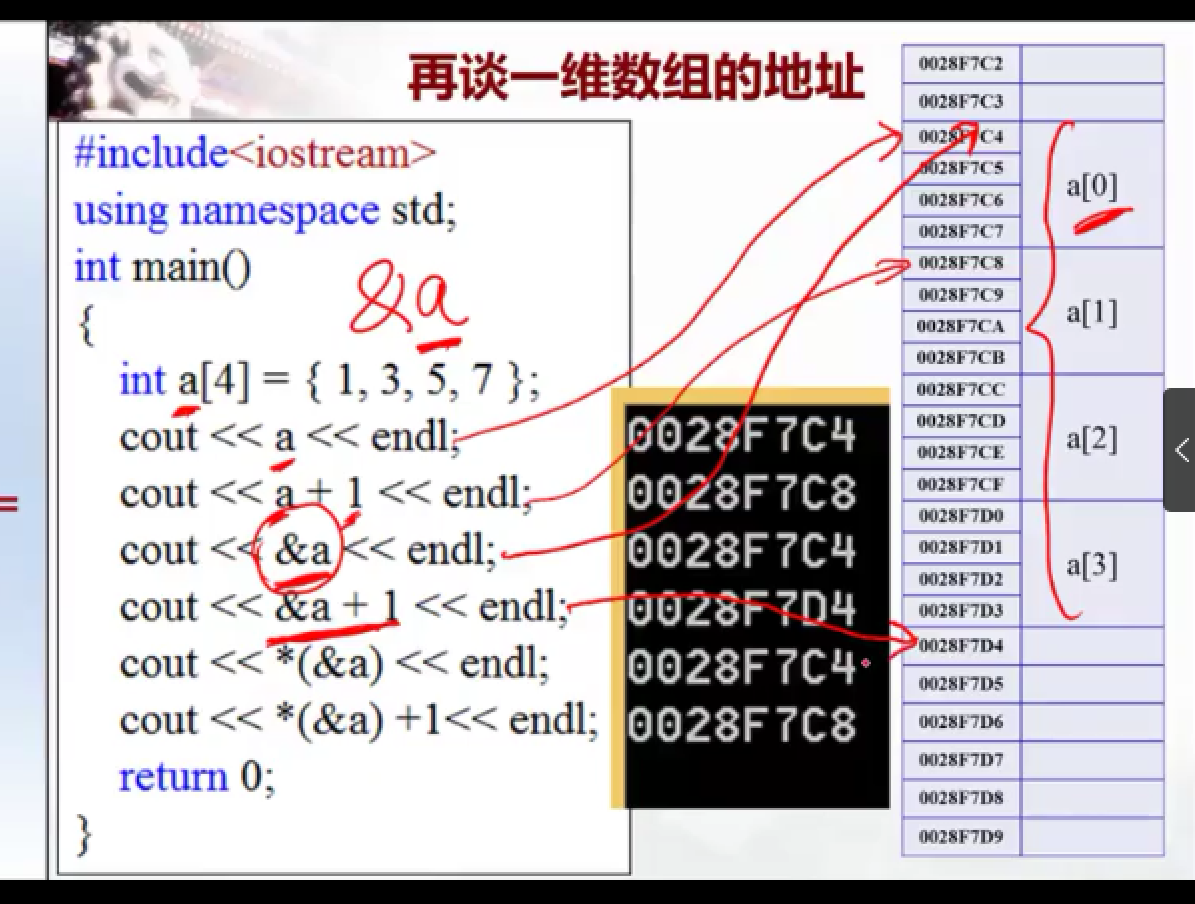
数组名前加&,扩大a的管辖范围,由数组第一个元素扩大到整个数组
* (&a),缩小&a的管辖范围,由整个数组地址缩小为数组第一个元素地址;
*a,缩小a的管辖范围,由数组第一个元素地址缩小为数组第一个元素的值;
12.二维数组
级别排序:&a>a>a[0]>a[0][0]
&a:指向整个二维数组的指针
a:指向数组a[0]的指针
a[0]:指向 a[0][0]的指针
a[0][0]:数组第一个元素的值

13.
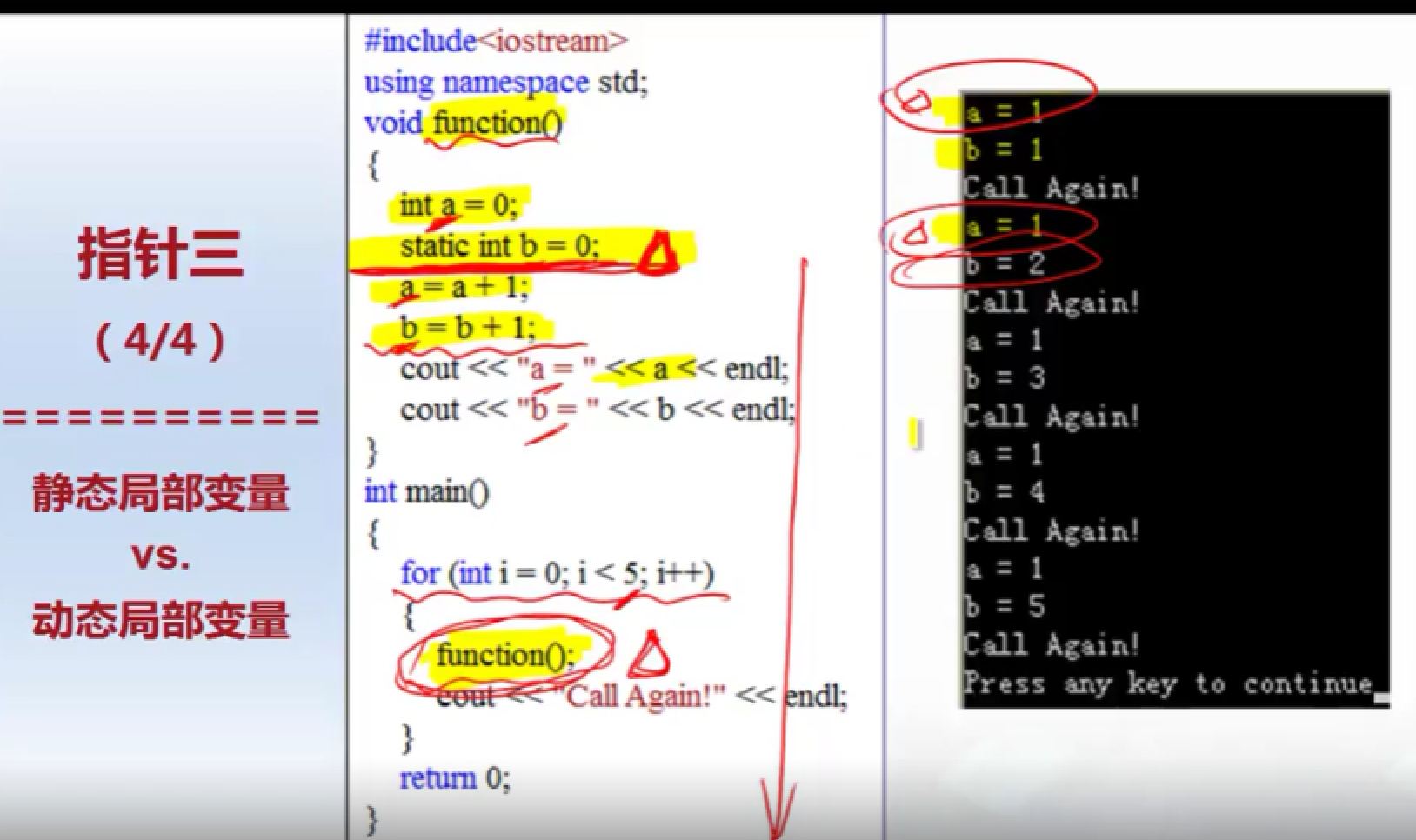
static int b=0; 仅在第一次调用函数的时候执行,下次直接跳过;
14.结构体应用
统计n个学生里生日相同的学生学号,并按日期顺序输出

注:count 数组用于记录生日是当前日期是第几个学生;j用于记录生日是当前日期的学生数量
count[k] 拿出结构体里面生日是当前日期的学生序号


