ASP.NET Core Web (二)中间件
中间件
中间件类似于装配器,请求处理管道由一系列的中间件组件组成,每个组件在HttpContext上执行操作,按顺序调用管道中的下一个中间件或结束,特定的中间件在通道中装配以后可以获取数据并进行一系列的操作。
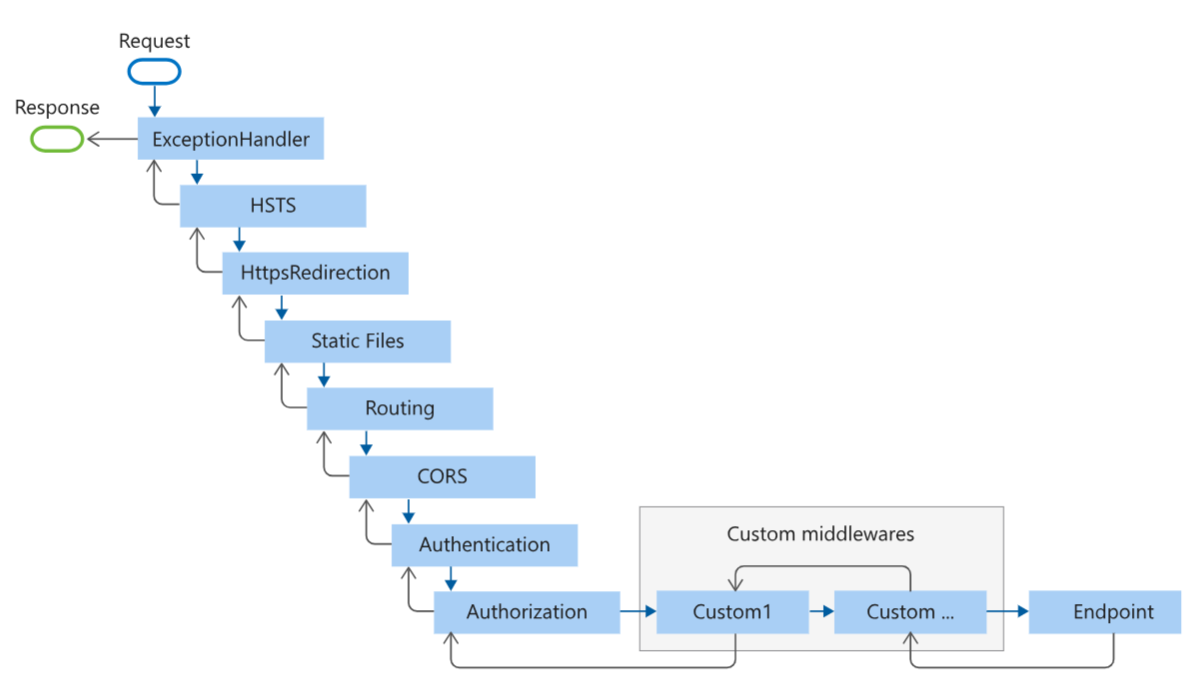
该图表示request到response的相关流程,每个节点的输入输出。
通过调用Use{Feature}扩展方法,向管道添加中间件组件。
设置处理所有请求的单个请求委托:
// 当未找到管道时可执行
app.Run(async context =>
{
// 在特定管道中输出"Hello world!"
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello world!");
});
app.Run();
使用Use方法将多个请求委托链接起来,next表示下一个委托:
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
// 写入响应的工作
// 当不进行Invoke调用时,该管道会短路,短路的主要作用是避免不必要的工作。
await next.Invoke();
// 进行日志记录或其他不写入响应的工作
});
根据请求路径给定的路径开头,执行分支
// 给定路径开头执行HandleMapTest*方法
app.Map("/map1", HandleMapTest1);
app.Map("/map2/seg1", HandleMultiSeg);
app.MapWhen(context => context.Request.Query.ContainsKey("branch"), HandleBranch);
app.Run();
static void HandleMapTest1(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 1");
});
}
static void HandleMultiSeg(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 2");
});
}
static void HandleBranch(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Run(async context =>
{
var branchVer = context.Request.Query["branch"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync($"Branch used = {branchVer}");
});
}
HTTP模块和处理程序迁移到中间件
简单添加中间件
将一个HTTP模块类(IHttpModule)转换为中间件的类,该类采用HttpContext并返回Task的Invoke方法,例如:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyApp.Middleware
{
// 中间件
public class MyMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public MyMiddleware(RequestDelegate next){
_next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
// 请求开始时会调用该方法
// TerminateRequest:如果没有中止求情则进行执行
if(!TerminateRequest()){
await _next.Invoke(context);
}
}
}
// 可引入中间件的方法
public static calss MyMiddlewareExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<MyMiddleware>();
}
}
}
此时MyMiddlewareExtensions帮助类可以轻松的在Program中配置中间件。
使用app.UseMyMiddleware();来作为中间件的引用。
添加中间件处理类
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyApp.Middleware
{
public class MyHandlerMiddleware
{
//必须具有具有此签名的构造函数,否则在运行时发生异常
public MyHandlerMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
string response = GenerateResponse(context);
context.Response.ContentType = GetContentType();
await context.Response.WriteAsync(response);
}
// 获取标题并返回标题信息
private string GenerateResponse(HttpContext context)
{
string title = context.Request.Query["title"];
return string.Format("Title of the report: {0}", title);
}
private string GetContentType()
{
return "text/plain";
}
}
// 可引用的中间件处理程序
public static class MyHandlerExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyHandler(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<MyHandlerMiddleware>();
}
}
}
在Program类中使用MapWhen扩展方法来对管道进行分支操作
app.MapWhen(
context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".report"),
appBranch => {
// 可以选择向该分支添加更多中间件
appBranch.UseMyHandler();
});
MapWhen 采用以下参数:
- 一个 lambda,它采用
HttpContext,并在请求应沿着分支向下前进时返回true。 这意味着不仅可以基于请求扩展名,还可以基于请求标头、查询字符串参数等对请求进行分支。 - 一个 lambda,它采用
IApplicationBuilder并为分支添加所有中间件。 这意味着可以将其他中间件添加到处理程序中间件前面的分支。
分类:
C#
标签:
ASP.NET Core Web




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人