对 Flask 运行机制的理解
(一) 概述
Flask 是 Python 中有名的同步的轻量级 web 框架,主要提供最基本的 api 接口功能,表现形式主要是服务端被动接收客户端的请求后做出响应,然后客户端根据响应结果做出业务操作。
(二) 对 Flask 运行机制的源码的初步理解
以下所有 Flask 的源码基于 Flask==1.1.2 版本
1. app.run()
既然要理解 Flask 运行的机制,不可避免的要看 Flask 的源码,咱们以 app.run() 为入口去探索
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello world'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
2. run() 函数的源码
run() 函数是 flask/app.py 中的 Flask 类的一个方法,核心代码如下:
def run(self, host=None, port=None, debug=None, load_dotenv=True, **options):
'''省略部分代码'''
_host = "127.0.0.1"
_port = 5000
server_name = self.config.get("SERVER_NAME")
sn_host, sn_port = None, None
if server_name:
sn_host, _, sn_port = server_name.partition(":")
host = host or sn_host or _host
# pick the first value that's not None (0 is allowed)
port = int(next((p for p in (port, sn_port) if p is not None), _port))
options.setdefault("use_reloader", self.debug)
options.setdefault("use_debugger", self.debug)
options.setdefault("threaded", True)
cli.show_server_banner(self.env, self.debug, self.name, False)
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
try:
run_simple(host, port, self, **options)
finally:
# reset the first request information if the development server
# reset normally. This makes it possible to restart the server
# without reloader and that stuff from an interactive shell.
self._got_first_request = False
在 run 函数内,函数设置了服务器启动的 address、port 等信息,最后引入了一个 werkzeug 库的 run_simple 方法,另外还传入了一个 options 参数。
- 请注意:
options.setdefault("threaded", True)这行代码是用来启动多线程的,也就相当于,在 Flask==1.1.2 版本中,Flask 的基本运行是基于单进程多线程的(下面会进行具体的说明)
3. run() 函数源码以前版本的解释
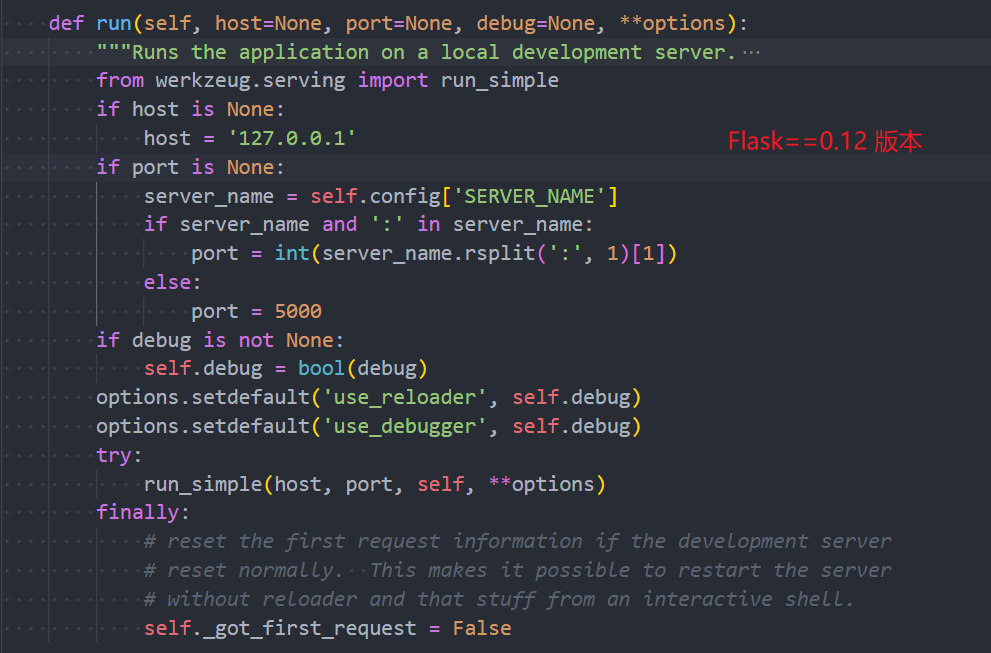
在以前的 Flask 版本中,threaded 这个参数是没有的,在 werkzeug 库的 run_simple 方法中,threaded 的默认值是 False,因此在最早的 Flask 版本中,Flask 的运行时基于单进程单线程的。
在后续增加了 threaded 后,就可以在使用 app.run() 启动的时候,添加 threaded 参数,可以手动的设置是使用单进程单线程还是使用单进程多线程的方式来跑 Flask。
- 单进程单线程
当设置app.run(threaded=False)的方式,将会使得 Flask 以单进程单线程的阻塞方式运行;这样当一个请求过来,当前请求未处理完,其它后续过来的请求都会排队等待,也就是处于阻塞的状态。 - 单进程多线程
如果以app.run()的方式运行,那么 threaded 被设置的默认值为 True,options.setdefault("threaded", True),这时 Flask 以单进程多线程的非阻塞方式运行;每过来一个请求,Flask 都会开启一个线程去处理这个请求,这时候就不存在请求排队等待的过程了;这时多线程就由操作系统来调度,操作系统来决定哪个线程先执行,执行多长时间,什么时候切换到另一个线程去执行,我们相信操作系统的调度能力。
4. werkzeug 库的 run_simple 方法
run_simple() 函数在 werkzeug/serving.py 中,核心代码如下:
def run_simple(
hostname,
port,
application,
use_reloader=False,
use_debugger=False,
use_evalex=True,
extra_files=None,
reloader_interval=1,
reloader_type="auto",
threaded=False,
processes=1,
request_handler=None,
static_files=None,
passthrough_errors=False,
ssl_context=None,
):
'''省略部分代码'''
def inner():
try:
fd = int(os.environ["WERKZEUG_SERVER_FD"])
except (LookupError, ValueError):
fd = None
srv = make_server(
hostname,
port,
application,
threaded,
processes,
request_handler,
passthrough_errors,
ssl_context,
fd=fd,
)
if fd is None:
log_startup(srv.socket)
srv.serve_forever()
if use_reloader:
'''省略部分代码'''
else:
inner()
从上面的代码中,可以看到 Flask 框架是通过调用 Werkzeug 这个第三方库来创建 web 服务,监听用户的请求的。
make_server() 函数在 werkzeug/serving.py 中,核心代码如下:
def make_server(
host=None,
port=None,
app=None,
threaded=False,
processes=1,
request_handler=None,
passthrough_errors=False,
ssl_context=None,
fd=None,
):
"""Create a new server instance that is either threaded, or forks
or just processes one request after another.
"""
if threaded and processes > 1:
raise ValueError("cannot have a multithreaded and multi process server.")
elif threaded:
return ThreadedWSGIServer(
host, port, app, request_handler, passthrough_errors, ssl_context, fd=fd
)
elif processes > 1:
return ForkingWSGIServer(
host,
port,
app,
processes,
request_handler,
passthrough_errors,
ssl_context,
fd=fd,
)
else:
return BaseWSGIServer(
host, port, app, request_handler, passthrough_errors, ssl_context, fd=fd
)
从上面的代码,可以看出,通过传入的 threaded 和 processes 两个值,来确定是使用 单进程单线程?单进程多线程?多进程?的方式运行 server 的。
因为 Flask 中设置了 threaded=True,那么这时我们将进入到 ThreadedWSGIServer 类中。
ThreadedWSGIServer 类在 werkzeug/serving.py 中,核心代码如下:
class ThreadedWSGIServer(ThreadingMixIn, BaseWSGIServer):
"""A WSGI server that does threading."""
multithread = True
daemon_threads = True
这个类的实现很简单,通过继承 ThreadingMixIn 和 BaseWSGIServer 两个类实现多线程的 socket,通过分析,我们可以发现,这两个类最终对应的源头是 Python 基本库中的 socketserver 库的 ThreadingMixIn 和 TCPServer 两个类。
- 这两个类最终对应的源头是 Python 基本库中的 socketserver.py 模块中的 ThreadingMixIn 和 TCPServer 这两个类
ThreadedWSGIServer --继承--> ThreadingMixIn, BaseWSGIServer
BaseWSGIServer --继承--> HTTPServer --继承--> socketserver.TCPServer --继承--> BaseServer
ThreadingMixIn 类的实现
socketserver.py --> ThreadingMixIn
class ThreadingMixIn:
"""Mix-in class to handle each request in a new thread."""
# Decides how threads will act upon termination of the
# main process
daemon_threads = False
# If true, server_close() waits until all non-daemonic threads terminate.
block_on_close = True
# For non-daemonic threads, list of threading.Threading objects
# used by server_close() to wait for all threads completion.
_threads = None
def process_request_thread(self, request, client_address):
"""Same as in BaseServer but as a thread.
In addition, exception handling is done here.
"""
try:
self.finish_request(request, client_address)
except Exception:
self.handle_error(request, client_address)
finally:
self.shutdown_request(request)
def process_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Start a new thread to process the request."""
t = threading.Thread(target = self.process_request_thread,
args = (request, client_address))
t.daemon = self.daemon_threads
if not t.daemon and self.block_on_close:
if self._threads is None:
self._threads = []
self._threads.append(t)
t.start()
def server_close(self):
super().server_close()
if self.block_on_close:
threads = self._threads
self._threads = None
if threads:
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
这个类重写了类 BaseServer 中的 process_request() 方法,而 BaseServer 是类 TCPServer 的父类,这个重写也就相当于是重写了 TCPServer 中的该方法,当 server 接受到请求,如果 threaded 被设为 True,则会执行 ThreadingMixIn 中的 process_request(),该方法内创建了一个新的线程来处理请求。
socketserver.py --> BaseServer
class BaseServer:
"""省略部分代码"""
def serve_forever(self, poll_interval=0.5):
"""Handle one request at a time until shutdown.
Polls for shutdown every poll_interval seconds. Ignores
self.timeout. If you need to do periodic tasks, do them in
another thread.
"""
self.__is_shut_down.clear()
try:
# XXX: Consider using another file descriptor or connecting to the
# socket to wake this up instead of polling. Polling reduces our
# responsiveness to a shutdown request and wastes cpu at all other
# times.
with _ServerSelector() as selector:
selector.register(self, selectors.EVENT_READ)
while not self.__shutdown_request:
ready = selector.select(poll_interval)
# bpo-35017: shutdown() called during select(), exit immediately.
if self.__shutdown_request:
break
if ready:
self._handle_request_noblock()
self.service_actions()
finally:
self.__shutdown_request = False
self.__is_shut_down.set()
"""省略部分代码"""
def _handle_request_noblock(self):
"""Handle one request, without blocking.
I assume that selector.select() has returned that the socket is
readable before this function was called, so there should be no risk of
blocking in get_request().
"""
try:
request, client_address = self.get_request()
except OSError:
return
if self.verify_request(request, client_address):
try:
self.process_request(request, client_address)
except Exception:
self.handle_error(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
except:
self.shutdown_request(request)
raise
else:
self.shutdown_request(request)
"""省略部分代码"""
def process_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Call finish_request.
Overridden by ForkingMixIn and ThreadingMixIn.
"""
self.finish_request(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
"""省略部分代码"""
5. 总结
Flask 框架是通过 多线程/多进程 + 阻塞的 socket 实现非阻塞,其本质上是基于 Python 的源库 socketserver 实现的。
Flask 默认是基于多线程来处理请求的,即来一个请求,创建一个新线程处理,处理结束后,再销毁线程。
(三) 编写代码测试
app.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, jsonify
import time
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello world'
@app.route('/test')
def test():
return render_template('test.html')
@app.route('/getsleep')
def getsleep():
time.sleep(20)
return jsonify({"getsleep": '延迟'})
@app.route('/getapi')
def getapi():
return jsonify({"getapi": '不延迟'})
if __name__ == '__main__':
# app.run(threaded=False)
app.run()
test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
hello world
<button id="id-getsleep">点击 卡顿</button>
<button id="id-getapi">点击获取 api</button>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$('#id-getsleep').bind('click', function() {
console.log("id-getsleep");
$.ajax({
url: '/getsleep',
type: 'get',
success: function(data, textStatus, jqxhr) {
console.log("id-getsleep success data = ", data);
},
error: function(jqxhr, textStatus, error) {
console.log("id-getsleep error = ", error);
}
})
})
$('#id-getapi').bind('click', function() {
console.log("id-getapi");
$.ajax({
url: '/getapi',
type: 'get',
success: function(data, textStatus, jqxhr) {
console.log("id-getapi success data = ", data);
},
error: function(jqxhr, textStatus, error) {
console.log("id-getapi error = ", error);
}
})
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
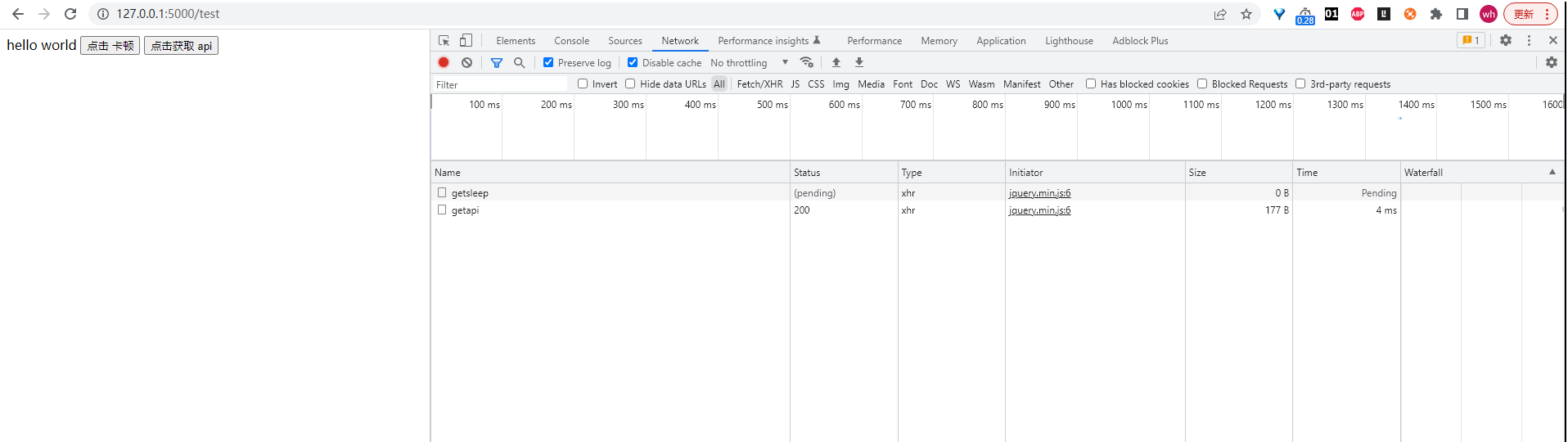
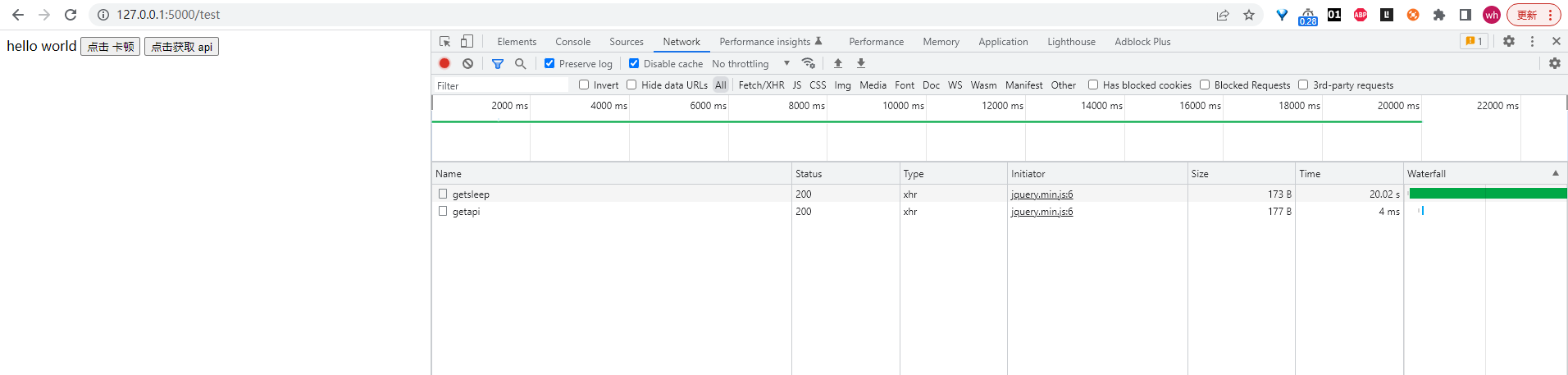
通过上面的代码结合浏览器,可以看到,/getsleep 路由执行的时候,后台会睡眠 20 秒,因此浏览器发送这个请求之后,这个请求的状态将会处于等待的状态(ajax 是异步的,所以即使等待也不会影响画面的操作),这时候点击网页其他操作,发送其它请求到后台,也可以很快就得到反馈,因此某一个请求的阻塞并不影响其他请求的操作。/getsleep 路由则是睡眠 20 秒之后,再给浏览器返回响应。