tqdm学习-一个快速,可扩展的Python和CLI进度条
参考:https://pypi.org/project/tqdm/
1.安装:
(base) userdeMacBook-Pro:~ user$ conda activate deeplearning (deeplearning) userdeMacBook-Pro:~ user$ conda install -c conda-forge tqdm Collecting package metadata: done Solving environment: done ## Package Plan ## environment location: /anaconda3/envs/deeplearning added / updated specs: - tqdm ... Downloading and Extracting Packages python-1.6 | 3.7 MB | ##################################### | 100% tqdm-4.35.0 | 42 KB | ##################################### | 100% decorator-4.4.0 | 13 KB | ##################################### | 100% ca-certificates-2019 | 143 KB | ##################################### | 100% openssl-1.1.1c | 1.9 MB | ##################################### | 100% Preparing transaction: done Verifying transaction: done Executing transaction: done
使用这个方法安装好像将我conda的环境的python版本换成了1.6版本,不好:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:bin user$ jupyter notebook Traceback (most recent call last): File "/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/bin/jupyter", line 7, in <module> from jupyter_core.command import main ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'jupyter_core'
解决,回到原来的状态:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:bin user$ conda uninstall tqdm Collecting package metadata: done Solving environment: done ## Package Plan ## environment location: /anaconda3/envs/deeplearning removed specs: - tqdm The following packages will be REMOVED: tqdm-4.35.0-py_0 Proceed ([y]/n)? y Preparing transaction: done Verifying transaction: done Executing transaction: done (deeplearning) userdeMBP:bin user$ conda update python
The following packages will be UPDATED:
certifi pkgs/main::certifi-2019.3.9-py36_0 --> conda-forge::certifi-2019.9.11-py37_0
python 1.6-0 --> 3.7.3-h93065d6_1
readline pkgs/main::readline-7.0-h1de35cc_5 --> conda-forge::readline-8.0-hcfe32e1_0
sqlite pkgs/main::sqlite-3.27.2-ha441bb4_0 --> conda-forge::sqlite-3.29.0-hb7d70f7_1
tk pkgs/main::tk-8.6.8-ha441bb4_0 --> conda-forge::tk-8.6.9-h2573ce8_1003
wheel anaconda/pkgs/main::wheel-0.33.1-py36~ --> conda-forge::wheel-0.33.6-py37_0
在anaconda上重新安装下jupyter notebook即可
换成了下面的下载方法:
(base) userdembp:bin user$ conda activate deeplearning3.5 (deeplearning3.5) userdembp:bin user$ pip install -e git+https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm.git@master#egg=tqdm Obtaining tqdm from git+https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm.git@master#egg=tqdm Cloning https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm.git (to revision master) to ./src/tqdm Installing collected packages: tqdm Running setup.py develop for tqdm Successfully installed tqdm You are using pip version 19.0.3, however version 19.2.3 is available. You should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command.
2.使用
tqdm是通用的,能以很多种方式使用。下面给出主要的三种方式:
1)基于迭代器的方法:
即将tqdm封装在任意迭代器中
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time text = "" for char in tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"]): time.sleep(0.25) text = text + char
print(text)
运行返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py 75%|███████▌ | 3/4 [00:00<00:00, 3.97it/s]abcd 100%|██████████| 4/4 [00:01<00:00, 3.96it/s] Process finished with exit code 0
tqdm(range(i))可以使用trange(i)替换:
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time text = 0 for i in tqdm(range(10)): time.sleep(0.25) text += i print(text)
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py 100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.96it/s] 45 Process finished with exit code 0
等价于:
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import trange import time text = 0 for i in trange(10): time.sleep(0.25) text += i print(text)
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py 90%|█████████ | 9/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.96it/s]45 100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.96it/s] Process finished with exit code 0
在循环外面实例化能够实现tqdm()的手动控制:
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time pbar = tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"]) for char in pbar: time.sleep(0.25) pbar.set_description("processing %s" % char)
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py processing d: 100%|██████████| 4/4 [00:01<00:00, 3.95it/s] Process finished with exit code 0
前四步是processing a,processing b,processing c
2)手动控制
通过使用with语句来实现tqdm()的手动控制:
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time with tqdm(total=100) as pbar: for i in range(10): time.sleep(0.1) pbar.update(10)
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:01<00:00, 97.06it/s] Process finished with exit code 0
如果提供了可选变量total(或者如len()的可迭代函数),就会显示预测状态
with语句也是可选的(你也可以直接赋值tqdm()到一个变量上,重点就在于你不要忘记了在最后的时候手动del或closr()它),使用with的好处就是它会在最后自动关闭
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time pbar = tqdm(total=100) for i in range(10): time.sleep(0.1) pbar.update(10) pbar.close()
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning3.5/bin/python3.5 /Users/user/PycharmProjects/new/learning.py 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:01<00:00, 97.40it/s] Process finished with exit code 0
3)模块
可能tqdm最优美的使用就是在脚本或命令行中。简单在管道中插入tqdm(或者命令python -m tqdm),这样在打印过程到stderr时将传递所有stdin到stdout
下面的例子阐述了在当前目录中计算所有python文件中的行数的例子,并且包含这相应的记时信息:
(deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$ time find . -name '*.py' -type f -exec cat \{} \; | wc -l 8 real 0m0.015s user 0m0.004s sys 0m0.009s (deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$ time find . -name '*.py' -type f -exec cat \{} \; | tqdm | wc -l 9it [00:00, 49998.33it/s] 8 real 0m0.273s user 0m0.207s sys 0m0.053s (deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$
此时该目录下就只有一个learning.py文件,里面的代码为:
# conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time pbar = tqdm(total=100) for i in range(10): time.sleep(0.1) pbar.update(10) pbar.close()
可见除去空行的确是8行
注意tqdm通常使用的参数也能够指定:
(deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$ time find . -name '*.py' -type f -exec cat \{} \; | tqdm -unit loc --unit_scale --total 8 >> out.log 9.00loc [00:00, 33.6kloc/s] real 0m0.383s user 0m0.218s sys 0m0.076s (deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$ ls learning.py out.log (deeplearning3.5) userdembp:new user$ cat out.log # conding:utf-8 from tqdm import tqdm import time pbar = tqdm(total=100) for i in range(10): time.sleep(0.1) pbar.update(10) pbar.close()
这里即将单位换成loc,然后将得到的内容输入到out.log文件夹中
4)文档
class tqdm(): """ 装饰一个迭代器对象,返回一个表现得就像原来可迭代的迭代器;但是在每次值被请求时就打印一个动态的更新进度条 """ def __init__(self, iterable=None, desc=None, total=None, leave=True, file=None, ncols=None, mininterval=0.1, maxinterval=10.0, miniters=None, ascii=None, disable=False, unit='it', unit_scale=False, dynamic_ncols=False, smoothing=0.3, bar_format=None, initial=0, position=None, postfix=None, unit_divisor=1000):
参数:
- iterable : iterable, optional:使用一个进度条可迭代地去装饰。留下空白去手动处理更新
- desc : str, optional:进度条的前缀
- total : int, optional:期待的迭代数。如果不指定的话,就等价于len(iterable)。如果设置为float("inf")或者万不得已时,只有基本的进程统计会展示出来(无ETA,也无进度条)。如果gui=True,且该参数需要子序列去更新,指定一个初始的大的随机正整数即可,如int(9e9)
- leave : bool, optional:默认为True,即在迭代的最后保持进度条的所有踪迹,简单来说就是会把进度条的最终形态保留下来。如果为None,则仅在position=0时保留下来,即保留第一个
- file : io.TextIOWrapper or io.StringIO, optional:指定输出进程信息的地方,默认为sys.stderr。使用file.write(str)和file.flush()方法。对于encoding编码,可见write_bytes
- ncols : int, optional:整个输出信息的宽度。如果指定,将在动态地重新设置进度条的大小来将其保留在这样的边界中。如果没有指定,就会尝试去使用环境设置的宽度。回退的计量宽度为10,计数器和统计数据的大小没有限制
- mininterval : float, optional:显示更新间隔[默认值:0.1]秒的最小进度,即更新时间
- maxinterval : float, optional:显示更新间隔[默认值:10]秒的最大进度。经过长时间的显示更新滞后时会自动调整miniters参数来对应mininterval参数。只有在设置dynamic_miniters=True或显示线程开启时才工作
- miniters : int, optional:即在迭代中显示更新间隔的最小进度,即更新周期。如果设置为0或dynamic_miniters=True时就会自动调整和mininterval一样大(CPU效率更高,适合紧凑的循环)。如果设置>0,将跳过特定迭代数的显示。能够通过调整这个和mininterval参数去获得高效的循环。如果你的进度不稳定,迭代速度有快有慢(网络、跳过项目等),您应该将miniter设置为1。如果设置了该值,mininterval则会自动设为0
- ascii : bool or str, optional:如果没有指定或者设置为False,将会使用unicode编码(光滑的块)去填补计量。回退使用的是ASCII字符 ” 123456789#”
- disable : bool, optional:是否不使用整个进度条的封装,默认为False,即使用封装。如果设置为None,则在non-TTY时不使用
- unit : str, optional:用来定义每个迭代单元的字符串。默认为
"it",表示每个迭代;在下载或解压时,设为"B",代表每个“块”。
- unit_scale : bool or int or float, optional:如果设置为1或者True,迭代数量就会被自动减少或者重置,且将在国际单位制标准后面添加一个度量前缀(kilo、mega等)[默认:False],其实就是如果迭代数过大,它就会自动在后面加上M、k等字符来表示迭代进度等,比如,在下载进度条的例子中,如果为
False,数据大小是按照字节显示,设为True之后转换为Kb、Mb。
- dynamic_ncols : bool, optional:如果设置了,就会不断地更换环境的ncols参数(允许用于窗口大小重置),默认为False
- smoothing : float, optional:速度估计的指数移动平均平滑因子(在GUI模式中忽略)。范围从0(平均速度)到1(当前/瞬时速度)[默认值:0.3]。
- bar_format : str, optional:指定自定义进度栏字符串格式。可能会影响性能。(默认值: ‘{l_bar}{bar}{r_bar}’), l_bar = ’{desc}: {percentage:3.0f}%|’和r_bar = ’| {n_fmt}/{total_fmt} [{elapsed}<{remaining}, ‘ ‘{rate_fmt}{postfix}]’ 可能的var为: l_bar, bar, r_bar, n, n_fmt, total, total_fmt, percentage, rate, rate_fmt, rate_noinv, rate_noinv_fmt, rate_inv, rate_inv_fmt, elapsed, elapsed_s, remaining, remaining_s, desc, postfix, unit。注意,如果{desc}后面是空的,那么其后面的“:”将自动删除。
- initial : int, optional:初始计数器值。在重新启动进度条时有用[默认值:0]。
- position : int, optional:如果未指定,请指定要自动打印此栏的行偏移量(从0开始)。对于一次管理多个进度条是有用的(如线程)。
- postfix : dict or *, optional:指定要在进度栏末显示的其他统计信息。如果可能(dict),调用set_postfix(**postfix) 。
- unit_divisor : float, optional:默认为1000,如果unit_scale=True,则忽略它
- write_bytes : bool, optional:如果为默认值None和file未指定时,字节将会被写在python2中。如果设置为True,也是写成字节。在其他的情况下则默认写成unicode格式
- 额外的CLI可选项:
- delim : chr, optional:分隔字符[默认值:' n ']。使用“0”表示null。注意::在Windows系统中,Python将“n”转换为“rn”。
- buf_size : int, optional:指定delim时使用的以字节为单位的字符串缓冲区大小[默认值:256]。
- bytes : bool, optional:如果为真,将计数字节,忽略delim参数,并默认unit_scale为真,unit_divisor为1024,unit为' B '。
- manpath : str, optional:安装tqdm手册页的目录。
- log : str, optional:打印的日志信息类别,CRITICAL|FATAL|ERROR|WARN(ING)|[default: ‘INFO’]|DEBUG|NOTSET,默认为INFO
- 返回:
- 装饰后的迭代器
class tqdm(): def update(self, n=1): """ 手动更新进度条,对流streams有用,比如读文件 E.g.: >>> t = tqdm(total=filesize) # Initialise >>> for current_buffer in stream: ... ... ... t.update(len(current_buffer)) >>> t.close() 最后一行高度推荐使用,但是如果``t.update()`` 是在``filesize``即将完全到达和打印时调用的话可能就不需要 Parameters ---------- n : int, optional 添加到迭代内部计数器的增长数[default: 1] """ def close(self): """清除(if leave=False)和关闭进度条""" def clear(self, nomove=False): """清除当前的进度条显示.""" def refresh(self): """强迫更新该进度条的显示Force refresh the display of this bar.""" def unpause(self): """从最新运行时间重启tqdm计时器""" def reset(self, total=None): """ 为了重复使用,重设为第0次迭代。考虑和``leave=True``设置一起使用 Parameters ---------- total : int, optional. 用于新进度条的次数. """ def set_description(self, desc=None, refresh=True): """ 设置/修改进度条的描述格式 Parameters ---------- desc : str, optional refresh : bool, optional Forces refresh [default: True]. """ def set_postfix(self, ordered_dict=None, refresh=True, **kwargs): """ 设置/修改后缀(additional stats) with automatic formatting based on datatype. Parameters ---------- ordered_dict : dict or OrderedDict, optional refresh : bool, optional Forces refresh [default: True]. kwargs : dict, optional """ @classmethod def write(cls, s, file=sys.stdout, end="\n"): """通过tqdm打印信息(不覆盖进度条).""" @property def format_dict(self): """给只读权限人员访问的公用API""" def display(self, msg=None, pos=None): """ 使用``self.sp`` 去展示指定``pos``中的``msg``. 当继承使用时,要考虑重载该函数 e.g.: ``self.some_frontend(**self.format_dict)`` instead of ``self.sp``. Parameters ---------- msg : str, optional. What to display (default: ``repr(self)``). pos : int, optional. Position to ``moveto`` (default: ``abs(self.pos)``). """ def trange(*args, **kwargs): """ tqdm(xrange(*args), **kwargs)函数的缩写 Python3+版本中使用 range来替换 xrange. """ class tqdm_gui(tqdm): """Experimental GUI version""" def tgrange(*args, **kwargs): """Experimental GUI version of trange""" class tqdm_notebook(tqdm): """Experimental IPython/Jupyter Notebook widget""" def tnrange(*args, **kwargs): """Experimental IPython/Jupyter Notebook widget version of trange"""
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Benchmark for i in _range(int(1e8)): pass # Basic demo import tqdm for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8)): pass # Some decorations import tqdm for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8), miniters=int(1e6), ascii=True, desc="cool", dynamic_ncols=True): pass # Nested bars from tqdm import trange for i in trange(10): for j in trange(int(1e7), leave=False, unit_scale=True): pass # Experimental GUI demo import tqdm for i in tqdm.tgrange(int(1e8)): pass # Comparison to https://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/ try: from progressbar.progressbar import ProgressBar except ImportError: pass else: for i in ProgressBar()(_range(int(1e8))): pass # Dynamic miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=None, mininterval=0.1, smoothing=0): pass # Fixed miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=4500000, mininterval=0.1, smoothing=0): pass """ from time import sleep from timeit import timeit import re # Simple demo from tqdm import trange for i in trange(16, leave=True): sleep(0.1) # Profiling/overhead tests stmts = filter(None, re.split(r'\n\s*#.*?\n', __doc__)) for s in stmts: print(s.replace('import tqdm\n', '')) print(timeit(stmt='try:\n\t_range = xrange' '\nexcept:\n\t_range = range\n' + s, number=1), 'seconds')
一个个分析:
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Benchmark for i in _range(int(1e8)): pass """ from time import sleep from timeit import timeit import re # Simple demo from tqdm import trange for i in trange(16, leave=True): sleep(0.1) # Profiling/overhead tests stmts = filter(None, re.split(r'\n\s*#.*?\n', __doc__)) for s in stmts: print(s.replace('import tqdm\n', '')) print(timeit(stmt='try:\n\t_range = xrange' '\nexcept:\n\t_range = range\n' + s, number=1), 'seconds')
返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.59it/s] # Benchmark for i in _range(int(1e8)): pass 2.328720851000071 seconds
下面都一样,仅运行一个来分析学习
1)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Basic demo import tqdm for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8)): pass """
返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.65it/s] 0%| | 301598/100000000 [00:00<00:33, 3015975.69it/s] # Basic demo for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8)): pass 100%|██████████| 100000000/100000000 [00:18<00:00, 5407942.99it/s] 18.4932925789999 seconds
2)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Some decorations import tqdm for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8), miniters=int(1e6), ascii=True, desc="cool", dynamic_ncols=True): pass """
中间:

返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.71it/s] cool: 0%| | 0/100000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] # Some decorations for i in tqdm.trange(int(1e8), miniters=int(1e6), ascii=True, desc="cool", dynamic_ncols=True): pass cool: 100%|##########| 100000000/100000000 [00:17<00:00, 5650878.97it/s] 17.699349756000174 seconds
3)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Nested bars from tqdm import trange for i in trange(2): for j in trange(int(1e7), leave=False, unit_scale=True): pass """
返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.76it/s] 0%| | 0/2 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 0.00/10.0M [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3%|▎ | 327k/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.27Mit/s] # Nested bars from tqdm import trange for i in trange(2): for j in trange(int(1e7), leave=False, unit_scale=True): pass 7%|▋ | 667k/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.31Mit/s] 10%|█ | 1.04M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.43Mit/s] 13%|█▎ | 1.34M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.27Mit/s] 17%|█▋ | 1.70M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.38Mit/s] 21%|██ | 2.11M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.56Mit/s] 25%|██▌ | 2.55M/10.0M [00:00<00:01, 3.77Mit/s] 30%|██▉ | 2.99M/10.0M [00:00<00:01, 3.93Mit/s] 34%|███▍ | 3.44M/10.0M [00:00<00:01, 4.11Mit/s] 39%|███▉ | 3.91M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.27Mit/s] 44%|████▍ | 4.39M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.41Mit/s] 49%|████▉ | 4.88M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.54Mit/s] 54%|█████▍ | 5.38M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.67Mit/s] 59%|█████▊ | 5.87M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.74Mit/s] 64%|██████▎ | 6.35M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.77Mit/s] 68%|██████▊ | 6.83M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.76Mit/s] 73%|███████▎ | 7.31M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.64Mit/s] 78%|███████▊ | 7.77M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.48Mit/s] 82%|████████▏ | 8.22M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.44Mit/s] 87%|████████▋ | 8.71M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.55Mit/s] 92%|█████████▏| 9.20M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.67Mit/s] 97%|█████████▋| 9.68M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.69Mit/s] 50%|█████ | 1/2 [00:02<00:02, 2.30s/it] 0%| | 0.00/10.0M [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3%|▎ | 296k/10.0M [00:00<00:03, 2.96Mit/s] 6%|▌ | 586k/10.0M [00:00<00:03, 2.94Mit/s] 9%|▉ | 896k/10.0M [00:00<00:03, 2.99Mit/s] 12%|█▏ | 1.24M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.10Mit/s] 16%|█▌ | 1.59M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.21Mit/s] 19%|█▉ | 1.94M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.31Mit/s] 23%|██▎ | 2.33M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.46Mit/s] 27%|██▋ | 2.71M/10.0M [00:00<00:02, 3.57Mit/s] 31%|███ | 3.12M/10.0M [00:00<00:01, 3.69Mit/s] 35%|███▌ | 3.53M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 3.81Mit/s] 39%|███▉ | 3.93M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 3.88Mit/s] 44%|████▍ | 4.40M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.08Mit/s] 49%|████▉ | 4.88M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.27Mit/s] 54%|█████▍ | 5.38M/10.0M [00:01<00:01, 4.48Mit/s] 59%|█████▊ | 5.87M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.60Mit/s] 64%|██████▍ | 6.38M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.72Mit/s] 69%|██████▉ | 6.90M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.85Mit/s] 74%|███████▍ | 7.41M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.93Mit/s] 79%|███████▉ | 7.92M/10.0M [00:01<00:00, 4.98Mit/s] 84%|████████▍ | 8.42M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.74Mit/s] 89%|████████▉ | 8.90M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.77Mit/s] 94%|█████████▍| 9.40M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.84Mit/s] 99%|█████████▉| 9.93M/10.0M [00:02<00:00, 4.95Mit/s] 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:04<00:00, 2.32s/it] 4.642330375000256 seconds
⚠️这里返回[00:00<00:03, 2.96Mit/s]中前面的00:00表示已用时间,以秒为单位,所以在1秒前都为0,<后面的00:03表示剩余需要花的时间,2.96Mit/s表示速度
删掉参数unit_scale=True:
返回可见设置时使用M单位简化数字:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.64it/s] 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 0/10000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3%|▎ | 277015/10000000 [00:00<00:03, 2770126.22it/s] # Nested bars from tqdm import trange for i in trange(1): for j in trange(int(1e7), leave=False): pass 6%|▌ | 558583/10000000 [00:00<00:03, 2783635.65it/s] 9%|▉ | 895786/10000000 [00:00<00:03, 2937395.56it/s] 13%|█▎ | 1258399/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3114883.50it/s] 17%|█▋ | 1667463/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3354857.99it/s] 21%|██ | 2105227/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3607718.69it/s] 26%|██▌ | 2551042/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 3826706.29it/s] 30%|███ | 3028044/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 4068052.94it/s] 35%|███▌ | 3502923/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 4250850.87it/s] 40%|███▉ | 3975152/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4382092.05it/s] 44%|████▍ | 4444320/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4470580.81it/s] 49%|████▉ | 4913953/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4535991.51it/s] 54%|█████▍ | 5412819/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4662832.67it/s] 59%|█████▉ | 5903458/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4733320.55it/s] 64%|██████▍ | 6407480/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4821381.19it/s] 69%|██████▉ | 6890932/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4732373.17it/s] 74%|███████▎ | 7365457/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4589660.71it/s] 78%|███████▊ | 7828722/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4602468.26it/s] 83%|████████▎ | 8290265/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4587601.91it/s] 88%|████████▊ | 8799822/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4729019.14it/s] 93%|█████████▎| 9297792/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4801530.70it/s] 98%|█████████▊| 9806813/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4884621.49it/s] 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:02<00:00, 2.26s/it] 2.264081185000123 seconds
设置leave=True,返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.66it/s] 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 0/10000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3%|▎ | 322630/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3226280.00it/s] # Nested bars from tqdm import trange for i in trange(1): for j in trange(int(1e7), leave=True): pass 7%|▋ | 672600/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3303711.10it/s] 11%|█ | 1057128/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3449449.52it/s] 14%|█▍ | 1427037/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3520729.15it/s] 18%|█▊ | 1832741/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3666110.82it/s] 22%|██▏ | 2244986/10000000 [00:00<00:02, 3792038.55it/s] 27%|██▋ | 2691460/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 3971547.54it/s] 32%|███▏ | 3158486/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 4158176.06it/s] 36%|███▋ | 3644204/10000000 [00:00<00:01, 4345786.38it/s] 41%|████ | 4122465/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4468208.17it/s] 46%|████▌ | 4612764/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4590323.02it/s] 51%|█████ | 5111718/10000000 [00:01<00:01, 4703203.98it/s] 56%|█████▌ | 5608081/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4778414.54it/s] 61%|██████ | 6086716/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4780780.12it/s] 66%|██████▌ | 6564640/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4667924.67it/s] 70%|███████ | 7031914/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4532180.69it/s] 75%|███████▌ | 7521866/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4636454.48it/s] 80%|████████ | 8035404/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4775645.33it/s] 86%|████████▌ | 8551806/10000000 [00:01<00:00, 4885870.39it/s] 91%|█████████ | 9066446/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4961214.82it/s] 100%|██████████| 10000000/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4552905.40it/s][A 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:02<00:00, 2.20s/it] 2.2038861539999743 seconds
不同在于内部迭代保存最终的结果,即:
100%|██████████| 10000000/10000000 [00:02<00:00, 4552905.40it/s]
4)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Experimental GUI demo import tqdm for i in tqdm.tgrange(int(1e8)): pass """
返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.69it/s] # Experimental GUI demo for i in tqdm.tgrange(int(1e8)): pass
19.253753004999908 seconds
图为:
5)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Comparison to https://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/ try: from progressbar.progressbar import ProgressBar except ImportError: pass else: for i in ProgressBar()(_range(int(1e8))): pass """
返回:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.64it/s] # Comparison to https://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/ try: from progressbar.progressbar import ProgressBar except ImportError: pass else: for i in ProgressBar()(_range(int(1e8))): pass 0.0015016719999039196 seconds
6)
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Dynamic miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=None, mininterval=0.1, smoothing=0): pass """
最终:
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:01<00:00, 9.65it/s] 0%| | 313552/100000000 [00:00<00:31, 3134484.22it/s] # Dynamic miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=None, mininterval=0.1, smoothing=0): pass 100%|██████████| 100000000/100000000 [00:16<00:00, 5960460.94it/s] 16.779653078000138 seconds
即mininterval=0.1秒后更新进度栏中的进度
如果设置为miniters=2, mininterval=0:
""" # Simple tqdm examples and profiling # Dynamic miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=2, mininterval=0): pass """
返回为:
0%| | 0/100000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 2/100000000 [00:00<06:45, 246723.76it/s] 0%| | 4/100000000 [00:00<6:07:28, 4535.36it/s] 0%| | 6/100000000 [00:00<15:44:50, 1763.97it/s] 0%| | 8/100000000 [00:00<19:05:36, 1454.82it/s] ...
可见每两个迭代就更新一次
如果同时设置了这两个参数miniters=2, mininterval=1,以大的设置的时间为主。如下面的这个设置miniters仅为2,花的时间少,mininterval为1秒,所以以1秒间隔显示为主,忽略miniters设置:
0%| | 0/100000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] # Dynamic miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=2, mininterval=1): pass 3%|▎ | 3127793/100000000 [00:01<00:30, 3127793.00it/s] 6%|▌ | 5865282/100000000 [00:02<00:31, 2999494.96it/s] 9%|▉ | 9147057/100000000 [00:03<00:29, 3078945.08it/s] 12%|█▏ | 12443754/100000000 [00:04<00:27, 3141189.20it/s] ...
注意:返回[00:01<00:30, 3127793.00it/s]中的00:01表示1秒
如果设置为miniters=4500000, mininterval=0.1,4500000个间隔花的时间更长,所以以迭代数为主:
0%| | 0/100000000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] # Fixed miniters benchmark from tqdm import trange for i in trange(int(1e8), miniters=4500000, mininterval=0.1, smoothing=0): pass 4%|▍ | 4500000/100000000 [00:00<00:16, 5715229.42it/s] 9%|▉ | 9000000/100000000 [00:01<00:16, 5545180.93it/s] 14%|█▎ | 13500000/100000000 [00:02<00:15, 5635364.34it/s] 18%|█▊ | 18000000/100000000 [00:03<00:14, 5656277.70it/s] 22%|██▎ | 22500000/100000000 [00:03<00:13, 5729412.82it/s] 27%|██▋ | 27000000/100000000 [00:04<00:12, 5779243.27it/s] 32%|███▏ | 31500000/100000000 [00:05<00:11, 5820303.28it/s] 36%|███▌ | 36000000/100000000 [00:06<00:10, 5851854.45it/s] 40%|████ | 40500000/100000000 [00:06<00:10, 5873663.41it/s] 45%|████▌ | 45000000/100000000 [00:07<00:09, 5902913.08it/s]
...
Description and additional stats
定制信息可以通过设置desc和postfix参数来动态显示和更新在tqdm进度栏上:
from tqdm import trange from random import random, randint from time import sleep with trange(10) as t: for i in t: # 描述将显示在左边 t.set_description('GEN %i' % i) # 后缀将显示在右边,根据参数的数据类型自动格式化 t.set_postfix(loss=random(), gen=randint(1,999), str='h', lst=[1, 2]) sleep(0.1) with tqdm(total=10, bar_format="{postfix[0]} {postfix[1][value]:>8.2g}", postfix=["Batch", dict(value=0)]) as t: for i in range(10): sleep(0.1) t.postfix[1]["value"] = i / 2 t.update()
返回:
GEN 9: 100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:01<00:00, 9.42it/s, gen=356, loss=0.806, lst=[1, 2], str=h] Batch 4.5
记得在bar_format字符串中使用{postfix[...]}来指向:
- postfix需要在兼容格式中作为初始参数传递
- 如果postfix是类字典对象,将自动转换为一个字符串。为了防止该行为,在字典中键不是字符串的地方加入一个额外的项,即上面postfix=["Batch", dict(value=0)]中的value=0
额外的bar_format参数也能够通过复写format_dict参数来定义,进度栏本身可以用ascii码修改:
from tqdm import tqdm class TqdmExtraFormat(tqdm): """Provides a `total_time` format parameter""" @property def format_dict(self): d = super(TqdmExtraFormat, self).format_dict
#d["total"]表示总迭代数,d["n"]表示当前为第几轮迭代 print(d["elapsed"], d["total"], d["n"]) total_time = d["elapsed"] * (d["total"] or 0) / max(d["n"], 1) d.update(total_time=self.format_interval(total_time) + " in total") return d for i in TqdmExtraFormat( range(10), ascii=" .oO0", bar_format="{total_time}: {percentage:.0f}%|{bar}{r_bar}"): sleep(0.25) print(i)
返回:
00:00 in total: 0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0 10 0 00:02 in total: 10%|0 | 1/10 [00:00<00:02, 3.92it/s] 0 0.2551310062408447 10 1 00:02 in total: 20%|00 | 2/10 [00:00<00:02, 3.92it/s] 1 0.5111739635467529 10 2 00:02 in total: 30%|000 | 3/10 [00:00<00:01, 3.91it/s] 2 0.7674551010131836 10 3 00:02 in total: 40%|0000 | 4/10 [00:01<00:01, 3.92it/s] 3 1.0219080448150635 10 4 00:02 in total: 50%|00000 | 5/10 [00:01<00:01, 3.93it/s] 4 1.2738640308380127 10 5 00:02 in total: 60%|000000 | 6/10 [00:01<00:01, 3.94it/s] 5 1.525794267654419 10 6 00:02 in total: 70%|0000000 | 7/10 [00:01<00:00, 3.94it/s] 6 1.7809131145477295 10 7 00:02 in total: 80%|00000000 | 8/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.94it/s] 7 2.035114049911499 10 8 00:02 in total: 90%|000000000 | 9/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.93it/s] 8 2.2901201248168945 10 9 00:02 in total: 100%|0000000000| 10/10 [00:02<00:00, 3.93it/s] 9 2.543692111968994 10 10 2.544473886489868 10 10
参数ascii=" .oO0"指定使用0来填补进度条
参数bar_format="{total_time}: {percentage:.0f}%|{bar}{r_bar}"定义的值total_time即覆写format_dict中定义的total_time值,即输出的00:00 in total;{percentage:.0f}%即表示进度的百分比,小数位值不显示,设为0;所以l_bar = {total_time}: {percentage:.0f}%|,{bar}{r_bar}没有定义,即表示使用默认定义
注意{bar}还支持格式说明符[width][type]
- width:
- 未指定(默认值):自动填充ncols
- 设置的是整数且int >= 0: 即覆盖ncols逻辑的固定宽度
- 设置的是整数且int < 0: 则使用默认值减去该值
- type:
- a : ascii (覆写即等价于ascii=True)
- u : unicode(覆写 ascii=False)
- b : blank(覆写 ascii=" ")
这意味着可以使用以下方法创建具有右对齐文本的固定栏:bar_format="{l_bar}{bar:10}|{bar:-10b}right-justified"
Nested progress bars
tqdm支持嵌套的进度条。这里有一个例子:
from tqdm import trange from time import sleep for i in trange(4, desc='1st loop'): for j in trange(5, desc='2nd loop'): for k in trange(20, desc='3nd loop', leave=False): sleep(0.01)
返回:

1st loop: 0%| | 0/4 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 2nd loop: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.89it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.62it/s] 2nd loop: 20%|██ | 1/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.39it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 45%|████▌ | 9/20 [00:00<00:00, 86.21it/s] 3nd loop: 90%|█████████ | 18/20 [00:00<00:00, 85.41it/s] 2nd loop: 40%|████ | 2/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.29it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 95.65it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 93.32it/s] 2nd loop: 60%|██████ | 3/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.31it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.64it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.18it/s] 2nd loop: 80%|████████ | 4/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.32it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 94.50it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.41it/s] 2nd loop: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 4.27it/s] 1st loop: 25%|██▌ | 1/4 [00:01<00:03, 1.17s/it] 2nd loop: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.59it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 89.93it/s] 2nd loop: 20%|██ | 1/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.33it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.40it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.54it/s] 2nd loop: 40%|████ | 2/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.32it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 93.82it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.93it/s] 2nd loop: 60%|██████ | 3/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.34it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 96.33it/s] 3nd loop: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:00<00:00, 94.51it/s] 2nd loop: 80%|████████ | 4/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.37it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 93.01it/s] 3nd loop: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.52it/s] 2nd loop: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 4.36it/s] 1st loop: 50%|█████ | 2/4 [00:02<00:02, 1.17s/it] 2nd loop: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.09it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.62it/s] 2nd loop: 20%|██ | 1/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.33it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.28it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 89.40it/s] 2nd loop: 40%|████ | 2/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.31it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 94.83it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.97it/s] 2nd loop: 60%|██████ | 3/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.32it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.53it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 90.02it/s] 2nd loop: 80%|████████ | 4/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.33it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.51it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 89.57it/s] 2nd loop: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 4.29it/s] 1st loop: 75%|███████▌ | 3/4 [00:03<00:01, 1.17s/it] 2nd loop: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 94.66it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.52it/s] 2nd loop: 20%|██ | 1/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.41it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 45%|████▌ | 9/20 [00:00<00:00, 88.28it/s] 3nd loop: 95%|█████████▌| 19/20 [00:00<00:00, 88.91it/s] 2nd loop: 40%|████ | 2/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.36it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 45%|████▌ | 9/20 [00:00<00:00, 86.31it/s] 3nd loop: 90%|█████████ | 18/20 [00:00<00:00, 86.96it/s] 2nd loop: 60%|██████ | 3/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.31it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 45%|████▌ | 9/20 [00:00<00:00, 89.50it/s] 3nd loop: 90%|█████████ | 18/20 [00:00<00:00, 87.95it/s] 2nd loop: 80%|████████ | 4/5 [00:00<00:00, 4.27it/s] 3nd loop: 0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 3nd loop: 50%|█████ | 10/20 [00:00<00:00, 92.30it/s] 3nd loop: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:00<00:00, 91.61it/s] 2nd loop: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 4.26it/s] 1st loop: 100%|██████████| 4/4 [00:04<00:00, 1.17s/it]
参数desc='3nd loop'指定输出的l_bar的内容,即前缀
在Windows上,如果可以的话,colorama将用于保持嵌套条在各自的行上。
对于手动控制定位(例如多线程使用),可以指定位置=n,其中最外层的栏位n=0,下一栏位n=1,以此类推:
from time import sleep from tqdm import trange, tqdm from multiprocessing import Pool, freeze_support, RLock L = list(range(3)) def progresser(n): interval = 0.001 / (n + 2) total = 5000 # {:<04.2}表示左对齐,数字总共4位,其中小数两位 text = "#{}, est. {:<04.2}s".format(n, interval * total) for i in trange(total, desc=text, position=n): sleep(interval) if __name__ == '__main__': freeze_support() # for Windows support p = Pool(len(L), # 同时开启3个进程 # again, for Windows support initializer=tqdm.set_lock, initargs=(RLock(),)) p.map(progresser, L) print("\n" * (len(L) - 2)) #换行
返回:

#0, est. 2.50s: 0%| | 0/5000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 0%| | 0/5000 [00:00<?, ?it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 4%|▎ | 175/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1743.72it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 5%|▌ | 258/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2577.38it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 7%|▋ | 346/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1731.96it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 10%|█ | 500/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2525.19it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 10%|█ | 515/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1717.89it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 15%|█▍ | 729/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2447.84it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 14%|█▎ | 685/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1712.16it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 19%|█▉ | 959/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2401.48it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 17%|█▋ | 855/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1707.39it/s]] #1, est. 1.70s: 24%|██▍ | 1200/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2403.36it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 21%|██ | 1026/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1706.94it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 29%|██▊ | 1435/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2385.71it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 24%|██▍ | 1198/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1709.67it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 34%|███▎ | 1675/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2389.13it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 27%|██▋ | 1369/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1707.61it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 38%|███▊ | 1914/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2387.64it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 31%|███ | 1541/5000 [00:00<00:02, 1709.89it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 43%|████▎ | 2153/5000 [00:00<00:01, 2388.28it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 34%|███▍ | 1712/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1708.18it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 48%|████▊ | 2392/5000 [00:01<00:01, 2387.33it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 38%|███▊ | 1882/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1704.82it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 53%|█████▎ | 2632/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2388.09it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 41%|████ | 2052/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1701.67it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 57%|█████▋ | 2867/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2376.26it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 44%|████▍ | 2224/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1704.14it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 62%|██████▏ | 3106/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2379.52it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 48%|████▊ | 2395/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1702.96it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 67%|██████▋ | 3342/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2364.88it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 51%|█████▏ | 2566/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1703.43it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 72%|███████▏ | 3579/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2365.95it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 55%|█████▍ | 2736/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1702.05it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 76%|███████▋ | 3817/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2368.33it/s] #2, est. 1.20s: 100%|██████████| 5000/5000 [00:01<00:00, 3076.41it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 58%|█████▊ | 2906/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1695.95it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 62%|██████▏ | 3076/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1688.59it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 65%|██████▍ | 3245/5000 [00:01<00:01, 1687.35it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 68%|██████▊ | 3414/5000 [00:02<00:00, 1680.56it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 72%|███████▏ | 3582/5000 [00:02<00:00, 1674.84it/s] #1, est. 1.70s: 100%|██████████| 5000/5000 [00:02<00:00, 2354.49it/s] #0, est. 2.50s: 100%|██████████| 5000/5000 [00:02<00:00, 1672.28it/s]
Hooks and callbacks
tqdm可以很容易地支持回调/钩子和手动更新。下面是urllib的一个例子:
urllib.urlretrieve documentation
如果存在,钩子函数将在网络连接建立时调用一次,之后在读取每个块之后调用一次。
钩子将传递三个参数:到目前为止传输的块数、块大小(以字节为单位)和文件的总大小。
报错:
module 'urllib' has no attribute 'urlretrieve'
原因是python2 与python3的urllib不同在与python3要加上.request,更改后为:
import urllib, os from tqdm import tqdm class TqdmUpTo(tqdm): """Provides `update_to(n)` which uses `tqdm.update(delta_n)`.""" def update_to(self, b=1, bsize=1, tsize=None): """ b : int, optional Number of blocks transferred so far [default: 1]. bsize : int, optional Size of each block (in tqdm units) [default: 1]. tsize : int, optional Total size (in tqdm units). If [default: None] remains unchanged. """ if tsize is not None: self.total = tsize self.update(b * bsize - self.n) # will also set self.n = b * bsize eg_link = "https://caspersci.uk.to/matryoshka.zip" with TqdmUpTo(unit='B', unit_scale=True, miniters=1, desc=eg_link.split('/')[-1]) as t: # all optional kwargs urllib.request.urlretrieve(eg_link, filename=os.devnull, reporthook=t.update_to, data=None)
最终为:
matryoshka.zip: 262kB [00:03, 77.4kB/s]
灵感来自 twine#242。对examples/tqdm_wget.py进行函数替代。
当迭代速度存在较大差异时,建议使用miniter =1(例如,通过不完整的连接下载文件)。
Pandas Integration
受广大要求求,我们增加了对panda的支持——下面是DataFrame.progress_apply和DataFrameGroupBy.progress_apply的一个例子:
出错:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas'
解决:
(deeplearning) userdeMacBook-Pro:~ user$ conda install -n deeplearning pandas
更改后例子:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from tqdm import tqdm df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, (100000, 6))) # Register `pandas.progress_apply` and `pandas.Series.map_apply` with `tqdm` # (can use `tqdm_gui`, `tqdm_notebook`, optional kwargs, etc.) tqdm.pandas(desc="my bar!") # Now you can use `progress_apply` instead of `apply` # and `progress_map` instead of `map` df.progress_apply(lambda x: x**2) # can also groupby: # df.groupby(0).progress_apply(lambda x: x**2)
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/bin/src/tqdm/tqdm/_tqdm.py:634: FutureWarning: The Panel class is removed from pandas. Accessing it from the top-level namespace will also be removed in the next version from pandas import Panel my bar!: 100%|██████████| 6/6 [00:00<00:00, 265.34it/s]
数据大小为(100000, 6),从[0,100)中随机取值对其赋初值,然后求平方:
如果您对它的工作原理(以及如何为您自己的回调修改它)感兴趣,请参阅examples文件夹或导入模块并运行help()。
IPython/Jupyter Integration
IPython/Jupyter通过tqdm_notebook子模块支持:
出错:
IntProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets.
解决参考https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
我的操作为:
(deeplearning) userdeMacBook-Pro:~ user$ conda install -n deeplearning ipywidgets
例子:
from tqdm import tnrange, tqdm_notebook from time import sleep for i in tnrange(3, desc='1st loop'): for j in tqdm_notebook(range(100), desc='2nd loop'): sleep(0.01)
返回:
除了tqdm特性外,子模块还提供了一个本机Jupyter小部件(兼容IPython v1-v4和Jupyter),完全工作的嵌套条和颜色提示(蓝色:normal、绿色:completed、红色:error/interrupt、淡蓝色:no ETA);如下显示
from tqdm import tnrange, tqdm_notebook from time import sleep for i in tqdm_notebook(range(3), desc='1st loop'): for j in tqdm_notebook(range(100), desc='2nd loop'): sleep(0.01)
过程为:
最终为:
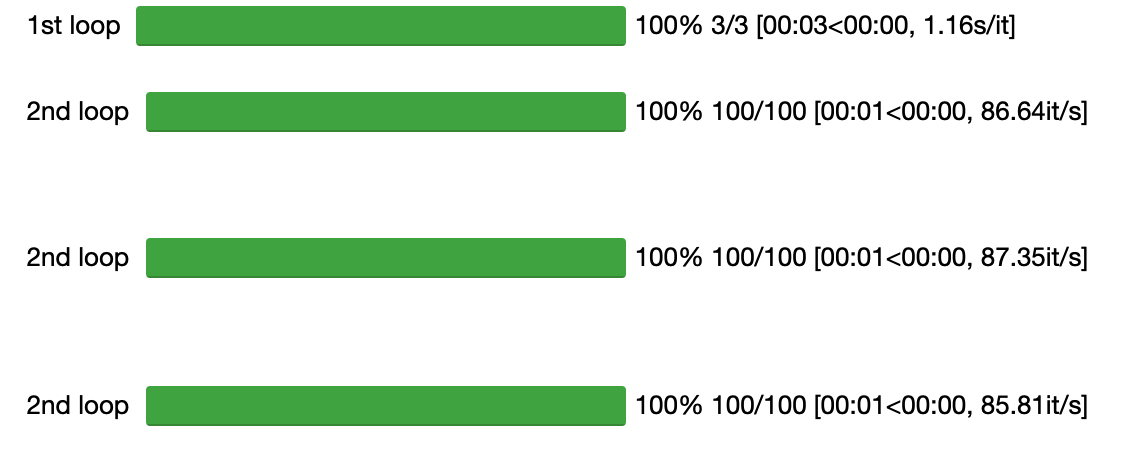
如果添加参数leave=True:
from tqdm import tnrange, tqdm_notebook from time import sleep for i in tqdm_notebook(range(3), desc='1st loop'): for j in tqdm_notebook(range(100), desc='2nd loop', leave=False): sleep(0.01)
则最后只会留下外层嵌套的结果:
![]()
如果中间点击停止按钮,则标明红色:
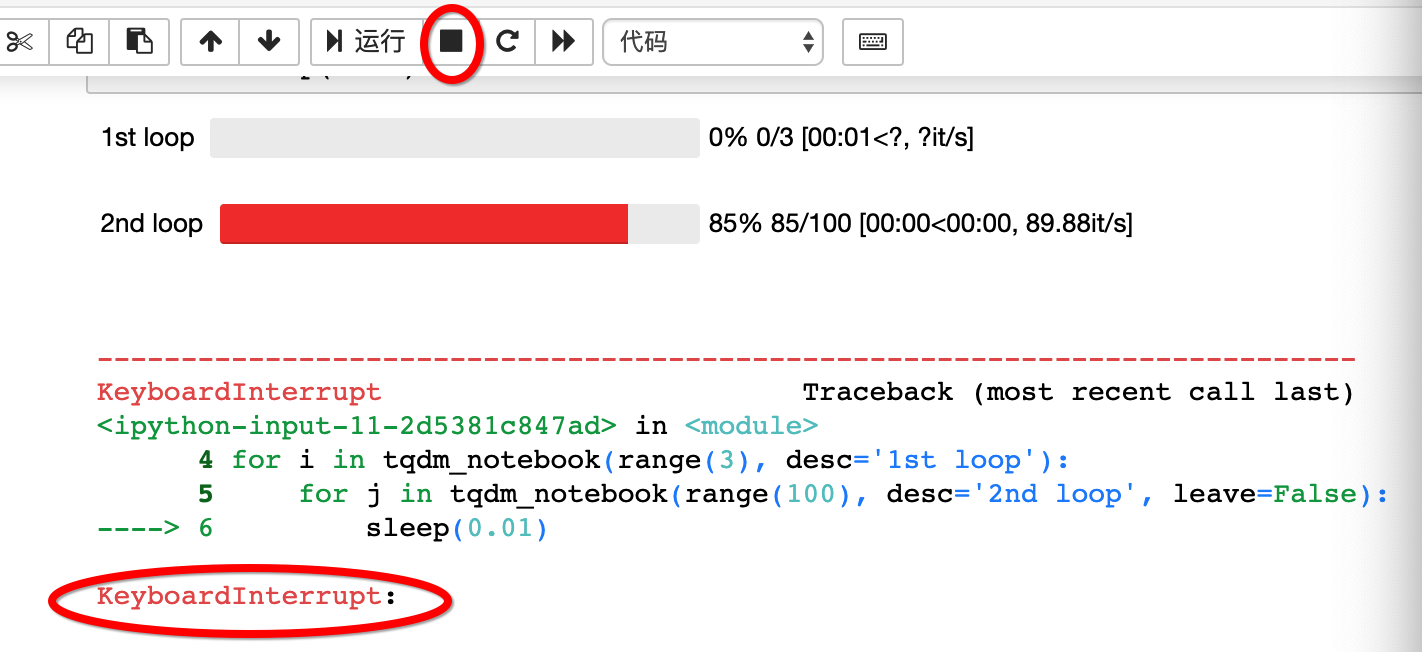
tqdm也可以通过使用autonotebook子模块自动选择控制台或笔记本版本:
from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm tqdm.pandas()
返回:
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/bin/src/tqdm/tqdm/autonotebook/__init__.py:18: TqdmExperimentalWarning: Using `tqdm.autonotebook.tqdm` in notebook mode. Use `tqdm.tqdm` instead to force console mode (e.g. in jupyter console) " (e.g. in jupyter console)", TqdmExperimentalWarning)
注意,如果运行在一个笔记本上,这将发出tqdmexperimental警告,因为其不可能区分jupyter notebook和jupyter console。使用auto而不是autonotebook来抑制这个警告。
Custom Integration
可以继承tqdm来创建自定义回调(如上面的TqdmUpTo示例)或自定义前端(例如GUIs,如笔记本或绘图包)。在后一种情况下要做的有:
- 在def __init__()中调用super().__init__(..., gui=True)来要禁用终端status_printer创建。
- 重定义close(), clear(), display()三个函数
考虑重载display()来使用self.frontend(** .format_dict)而不是self.sp(repr(self))。
Dynamic Monitor/Meter
你可以用tqdm作为一个非单调增长的meter。这可能是因为n减少(例如CPU使用监视器)或total更改。
一个例子是递归搜索文件。total是目前找到的对象数量,n是文件(而不是文件夹)的对象数量:
from tqdm import tqdm import os.path def find_files_recursively(path, show_progress=True): files = [] # total=1 assumes `path` is a file t = tqdm(total=1, unit="file", disable=not show_progress) if not os.path.exists(path): raise IOError("Cannot find:" + path) def append_found_file(f): files.append(f) t.update() def list_found_dir(path): """returns os.listdir(path) assuming os.path.isdir(path)""" listing = os.listdir(path) # subtract 1 since a "file" we found was actually this directory t.total += len(listing) - 1 # fancy way to give info without forcing a refresh t.set_postfix(dir=path[-10:], refresh=False) t.update(0) # may trigger a refresh return listing def recursively_search(path): if os.path.isdir(path): for f in list_found_dir(path): recursively_search(os.path.join(path, f)) else: append_found_file(path) recursively_search(path) t.set_postfix(dir=path) t.close() return files
使用update(0)是让tqdm决定何时触发显示刷新以避免控制台垃圾信息的一种简便方法。
Writing messages
这是一项正在进行的工作(见#737)。
由于tqdm使用简单的打印机制来显示进度条,所以在打开进度条时,不应该在终端中使用print()编写任何消息。
为了在终端中写入消息而不与tqdm bar显示发生冲突,提供了.write()方法:
from tqdm import tqdm, trange from time import sleep bar = trange(10) for i in bar: # Print using tqdm class method .write() sleep(0.1) if not (i % 3): tqdm.write("Done task %i" % i) # Can also use bar.write()
返回:
20%|██ | 2/10 [00:00<00:00, 9.48it/s] Done task 0 50%|█████ | 5/10 [00:00<00:00, 9.53it/s] Done task 3 80%|████████ | 8/10 [00:00<00:00, 9.50it/s] Done task 6 100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:01<00:00, 9.56it/s] Done task 9
默认情况下,这将打印到标准输出sys.stdout。但是您可以使用file参数指定任何类似文件的对象。例如,这可以用于将写入的消息重定向到日志文件或类。
Redirecting writing
如果使用一个可以将消息打印到控制台的库,那么用tqdm.write()替换print()来编辑库可能是不可取的。在这种情况下,重定向sys.stdout到tqdm.write()是一个选择。
重定向sys.stdout,创建一个类似于文件的类,该类将向tqdm.write()写入任何输入字符串,并提供参数file=sys.stdout, dynamic_ncols = True。
一个可重用的规范示例如下:
from time import sleep import contextlib import sys from tqdm import tqdm class DummyTqdmFile(object): """Dummy file-like that will write to tqdm""" file = None def __init__(self, file): self.file = file def write(self, x): # Avoid print() second call (useless \n) if len(x.rstrip()) > 0: tqdm.write(x, file=self.file) def flush(self): return getattr(self.file, "flush", lambda: None)() @contextlib.contextmanager def std_out_err_redirect_tqdm(): orig_out_err = sys.stdout, sys.stderr try: sys.stdout, sys.stderr = map(DummyTqdmFile, orig_out_err) yield orig_out_err[0] # Relay exceptions except Exception as exc: raise exc # Always restore sys.stdout/err if necessary finally: sys.stdout, sys.stderr = orig_out_err def some_fun(i): print("Fee, fi, fo,".split()[i]) # Redirect stdout to tqdm.write() (don't forget the `as save_stdout`) with std_out_err_redirect_tqdm() as orig_stdout: # tqdm needs the original stdout # and dynamic_ncols=True to autodetect console width for i in tqdm(range(3), file=orig_stdout, dynamic_ncols=True): sleep(.5) some_fun(i) # After the `with`, printing is restored print("Done!")
返回:
Fee, fi, fo, 100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:01<00:00, 1.97it/s] Done!
Monitoring thread, intervals and miniters
tqdm实现了一些技巧来提高效率和减少开销。
- 避免不必要的频繁刷新:mininterval定义每次刷新之间要等待多长时间。tqdm总是在后台更新,但它只显示每分钟一次。
- 减少检查系统时钟/时间的次数。
- mininterval比miniter更易于配置。一个聪明的调整系统dynamic_miniter将自动调整miniter到适合时间mininterval的迭代量。本质上,tqdm将在没有实际检查时间的情况下检查是否需要打印。这种行为仍然可以通过手动设置miniter来绕过。
然而,考虑一个结合了快速和缓慢迭代的案例。经过几次快速迭代之后,dynamic_miniter将把miniter设置为一个很大的数字。当迭代速率随后减慢时,miniter将保持较大的值,从而降低显示更新频率。为了解决这个问题:
- maxinterval定义显示刷新之间的最大时间间隔。并发监视线程检查过期的更新,并在必要时强制执行更新。
监视线程不应该有明显的开销,并且默认情况下保证至少每10秒更新一次。可以通过设置任何tqdm实例的monitor_interval(即t = tqdm.tqdm(…); t.monitor_interval = 2)直接更改此值。通过设置tqdm.tqdm.monitor_interval = 0可以在实例化任何tqdm bar之前在应用程序范围内禁用监视器线程。




