pydensecrf的inference.py代码的学习
https://github.com/lucasb-eyer/pydensecrf/blob/master/examples/inference.py
1.运行
先运行看看实现的结果:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:examples user$ python inference.py im1.png anno1.png out1.png Found a full-black pixel in annotation image, assuming it means 'unknown' label, and will thus not be present in the output! If 0 is an actual label for you, consider writing your own code, or simply giving your labels only non-zero values. 2 labels plus "unknown" 0: {0, 1, 2} Using generic 2D functions KL-divergence at 0: -543957.3854815669 KL-divergence at 1: -890605.7866870646 KL-divergence at 2: -919933.3682610085 KL-divergence at 3: -921683.1852052805 KL-divergence at 4: -922674.4361045817
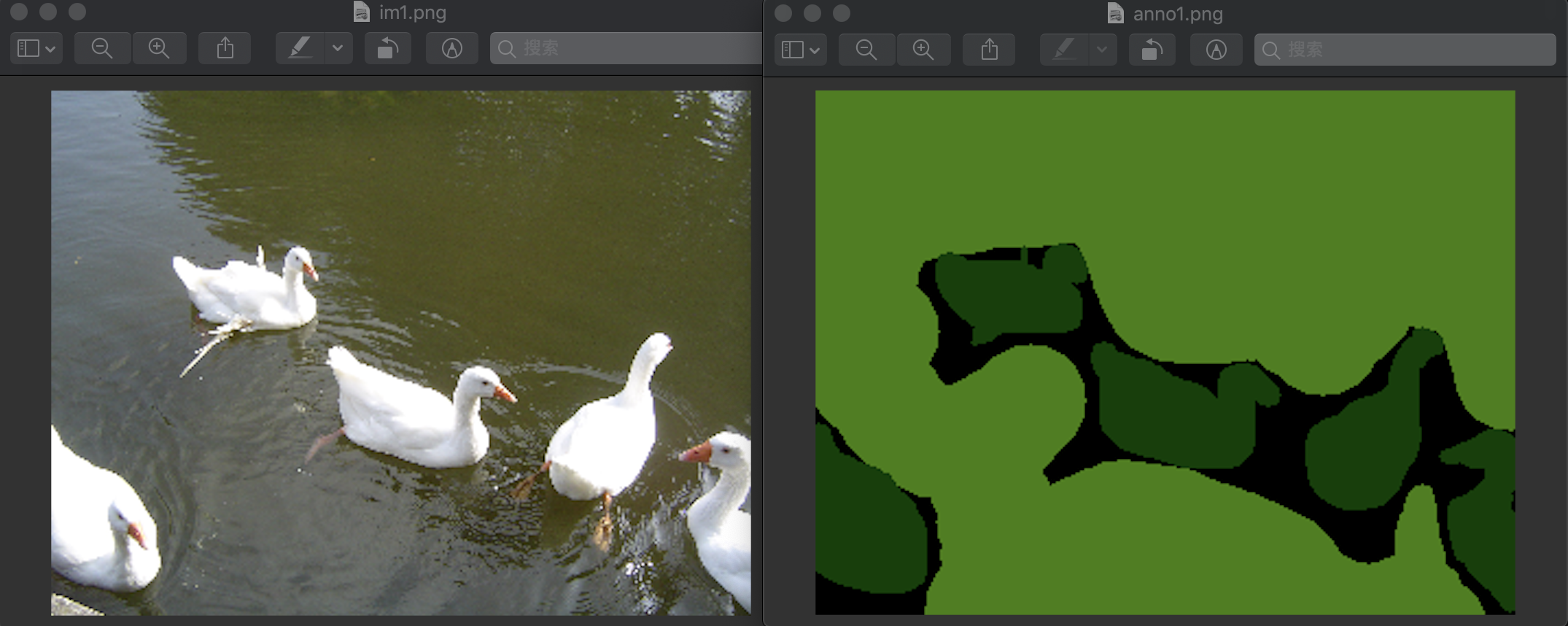
im1.png和anno1.png是输入图片,out1.png为进行crf处理后的输出图片
im1.png和anno1.png为:
得到的输出结果是:

可见效果变得很好
2.代码分析
""" Adapted from the inference.py to demonstate the usage of the util functions. """ import sys import numpy as np import pydensecrf.densecrf as dcrf # Get im{read,write} from somewhere. try: from cv2 import imread, imwrite except ImportError: # Note that, sadly, skimage unconditionally import scipy and matplotlib, # so you'll need them if you don't have OpenCV. But you probably have them. from skimage.io import imread, imsave imwrite = imsave # TODO: Use scipy instead. from pydensecrf.utils import unary_from_labels, create_pairwise_bilateral, create_pairwise_gaussian if len(sys.argv) != 4: print("Usage: python {} IMAGE ANNO OUTPUT".format(sys.argv[0])) print("") print("IMAGE and ANNO are inputs and OUTPUT is where the result should be written.") print("If there's at least one single full-black pixel in ANNO, black is assumed to mean unknown.") sys.exit(1) fn_im = sys.argv[1]#输入的图片 print(fn_im) fn_anno = sys.argv[2]#输入的图片fn_im经过训练后的网络进行预测得到的结果 print(fn_anno) fn_output = sys.argv[3]#指定进行crf处理后的结果输出 print(fn_output) ############################################################## ### Read images and annotation读取输入的两个图片fn_im和fn_anno### ############################################################## img = imread(fn_im) # Convert the annotation's RGB color to a single 32-bit integer color 0xBBGGRR #将fn_anno的三个uint8表示的RGB像素值放到一个uint32像素值中表示 #[0,7]位为R层的值,[8,15]为G层的值,[16,23]为B层的值 anno_rgb = imread(fn_anno).astype(np.uint32)#shape为(240, 320, 3) anno_lbl = anno_rgb[:,:,0] + (anno_rgb[:,:,1] << 8) + (anno_rgb[:,:,2] << 16)#shape变为了(240, 320) # Convert the 32bit integer color to 1, 2, ... labels. # Note that all-black, i.e. the value 0 for background will stay 0. # np.unique该函数是去除数组中的重复数字,并进行排序之后输出 # 这就得到了整张图中有的像素值序列 # #colors返回为[0,16384,4227072],说明图片fn_anno只有这三种像素值 # labels的shape为(76800,),其为anno_lbl中所有的像素值标上了对应的label # 在这里color=0时,对应的label为0;color=16384时,对应的label为1;color=4227072时,对应的label为2 # 黑色的像素值为0 colors, labels = np.unique(anno_lbl, return_inverse=True) # But remove the all-0 black, that won't exist in the MAP! # 移除像素值为0,即黑色的值 HAS_UNK = 0 in colors#若0存在于colors中,则HAS_UNK为True #在annotation图像中的黑色像素,即color=0的像素,被假设为label='unknown',不会在output中输出 #如果0是一个对你来说有意义的label,那么更改你的代码,或者尽量让你的label为非0的数值 if HAS_UNK: print("Found a full-black pixel in annotation image, assuming it means 'unknown' label, and will thus not be present in the output!") print("If 0 is an actual label for you, consider writing your own code, or simply giving your labels only non-zero values.") colors = colors[1:]#然后将color=0从数组中移除 #else: # print("No single full-black pixel found in annotation image. Assuming there's no 'unknown' label!") # And create a mapping back from the labels to 32bit integer colors. # np.empty()返回一个随机元素的矩阵,值类型为uint8,大小按照参数定义,这里 colorize = np.empty((len(colors), 3), np.uint8)#colorize.shape为(2,3) #下面将之前合并成0xBBGGRR格式的像素值又分成三层,得到各层像素值的值 colorize[:,0] = (colors & 0x0000FF)#得到R层的值,为[0,0], dtype=uint8 colorize[:,1] = (colors & 0x00FF00) >> 8#得到G层的值,为[ 64, 128], dtype=uint8 colorize[:,2] = (colors & 0xFF0000) >> 16#得到B层的值,[ 0, 64] # Compute the number of classes in the label image. # We subtract one because the number shouldn't include the value 0 which stands # for "unknown" or "unsure". # set(labels.flat)返回{0, 1, 2} # flat将数组变为一个迭代器,可以用for访问数组每一个元素,可以使用索引labels.flat[0]来访问第一个元素 # set(迭代对象) 函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据 n_labels = len(set(labels.flat)) - int(HAS_UNK) #返回2,得到除去了label=0后还有两个label print(n_labels, " labels", (" plus \"unknown\" 0: " if HAS_UNK else ""), set(labels.flat)) ########################### ### Setup the CRF model ### ########################### #上面处理完图片fn_anno,得到labels和colors #接下来就是设置CRF模型了 use_2d = False #是否使用二维指定函数DenseCRF2D,这里设置为False,则说明使用的是一般函数DenseCRF # use_2d = True if use_2d: print("Using 2D specialized functions") # Example using the DenseCRF2D code d = dcrf.DenseCRF2D(img.shape[1], img.shape[0], n_labels) # get unary potentials (neg log probability) U = unary_from_labels(labels, n_labels, gt_prob=0.7, zero_unsure=HAS_UNK) d.setUnaryEnergy(U) # This adds the color-independent term, features are the locations only. # 创建颜色无关特征,这里只有位置特征,并添加到CRF中 d.addPairwiseGaussian(sxy=(3, 3), compat=3, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) # This adds the color-dependent term, i.e. features are (x,y,r,g,b). # 根据原始图像img创建颜色相关特征和位置相关并添加到CRF中,特征为(x,y,r,g,b) d.addPairwiseBilateral(sxy=(80, 80), srgb=(13, 13, 13), rgbim=img, compat=10, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) else: print("Using generic 2D functions") # Example using the DenseCRF class and the util functions # 使用DenseCRF类和util函数 # n_labels为2,从上面对fn_anno的分析可知有两个label d = dcrf.DenseCRF(img.shape[1] * img.shape[0], n_labels) # get unary potentials (neg log probability) # 得到一元势(即去负对数),labels为对所有像素值标注label后的数组,label类型n_labels=2, U = unary_from_labels(labels, n_labels, gt_prob=0.7, zero_unsure=HAS_UNK) #U.shape为(2, 76800),即(n_labels,len(labels)) d.setUnaryEnergy(U) #将一元势添加到CRF中 # This creates the color-independent features and then add them to the CRF # 创建颜色无关特征,这里只有位置特征,并添加到CRF中 feats = create_pairwise_gaussian(sdims=(3, 3), shape=img.shape[:2]) #shape为(240, 320) d.addPairwiseEnergy(feats, compat=3, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) # This creates the color-dependent features and then add them to the CRF # 根据原始图像img创建颜色相关和位置相关特征并添加到CRF中,特征为(x,y,r,g,b) feats = create_pairwise_bilateral(sdims=(80, 80), schan=(13, 13, 13), img=img, chdim=2) d.addPairwiseEnergy(feats, compat=10, kernel=dcrf.DIAG_KERNEL, normalization=dcrf.NORMALIZE_SYMMETRIC) #################################### ### Do inference and compute MAP ### #################################### #上面就将相应的CRF构建好了 #然后要做的就是对img根据fn_anno得到的label和colors结果进行CRF推理 #然后得到输出值fn_output了 # Run five inference steps.迭代5次 Q = d.inference(5) # Find out the most probable class for each pixel. # 找出每个像素最可能的类 # np.argmax取出Q元素中最大的值对应的索引,axis=0按列查找 MAP = np.argmax(Q, axis=0) # MAP,MAP.shape返回 # (array([1, 1, 1, ..., 1, 1, 1]), (76800,)) # 将MAP(标签)转换回相应的颜色并保存图像。 #注意,这里不再有“unknown”标签,不管我们一开始拥有什么。 #colorize返回两个label的color[16384,4227072]对应的RGB的值 #16384对应[ 0, 64, 0],4227072对应[ 0, 128, 64] #array([[ 0, 64, 0], # [ 0, 128, 64]], dtype=uint8) #MAP中1值对应的是4227072即[ 0, 128, 64] MAP = colorize[MAP,:] #MAP.shape为(76800, 3),这就是最后的结果 #将MAP转成img相同的大小,就能够得到最后的结果了 imwrite(fn_output, MAP.reshape(img.shape)) # Just randomly manually run inference iterations # 这里是手动实现迭代推理 Q, tmp1, tmp2 = d.startInference() for i in range(5): print("KL-divergence at {}: {}".format(i, d.klDivergence(Q))) d.stepInference(Q, tmp1, tmp2)





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端