Android11系统源码分析:屏幕旋转
Android11系统源码分析:屏幕旋转
一、概述
本文转屏流程从自动旋转这一场景出发,研究设备横屏时系统框架的动作流程。
转屏基于Sensor框架,在system_server进程的开机打开屏幕阶段借助SensorManager注册加速度传感器的监听,以66.66ms的节奏接收回调结果。当传感器加速度数据回调时,会在WindowOrientationListener#onSensorChanged方法中算法处理是否需要旋转,主要受角度和加速度的影响。如果算法确定要旋转则通知到wms,在其updateRotationUnchecked方法中发起转屏动画和通知ATMS配置变动进而回调通知Activity。
本文关注流程,下一篇文章会聚焦耗时这一指标探讨“转屏”这一模块的性能优化。
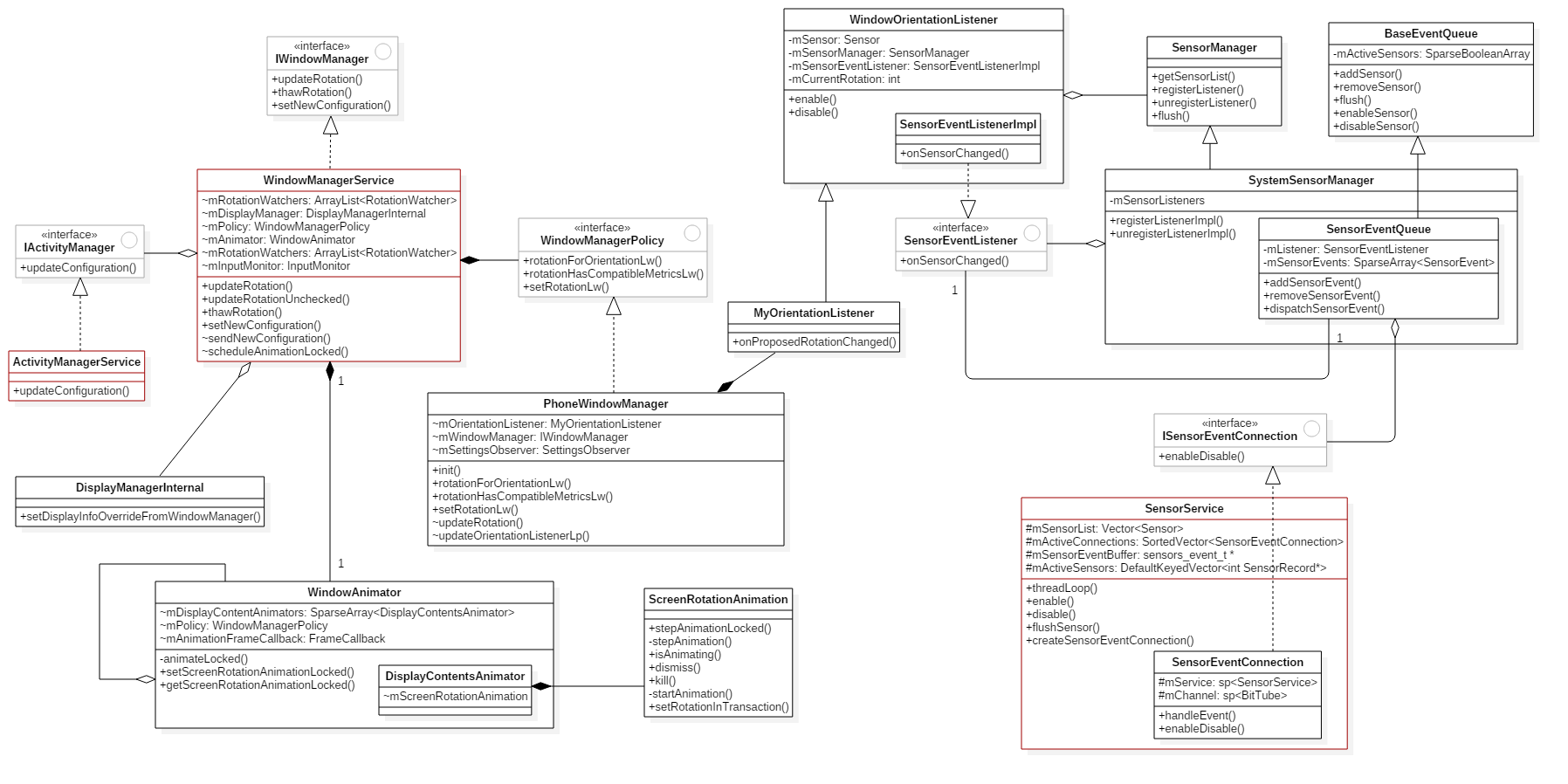
整体架构较之前版本没有变化,流程有稍许变动。类关系如下(图转自Android中的转屏流程)
图:转屏相关类关系图
二、情景分析:加速度传感器的注册监听
Android系统Sensor传感器服务框架是另外一个课题,本文的转屏基于此。推荐以下两篇文章。
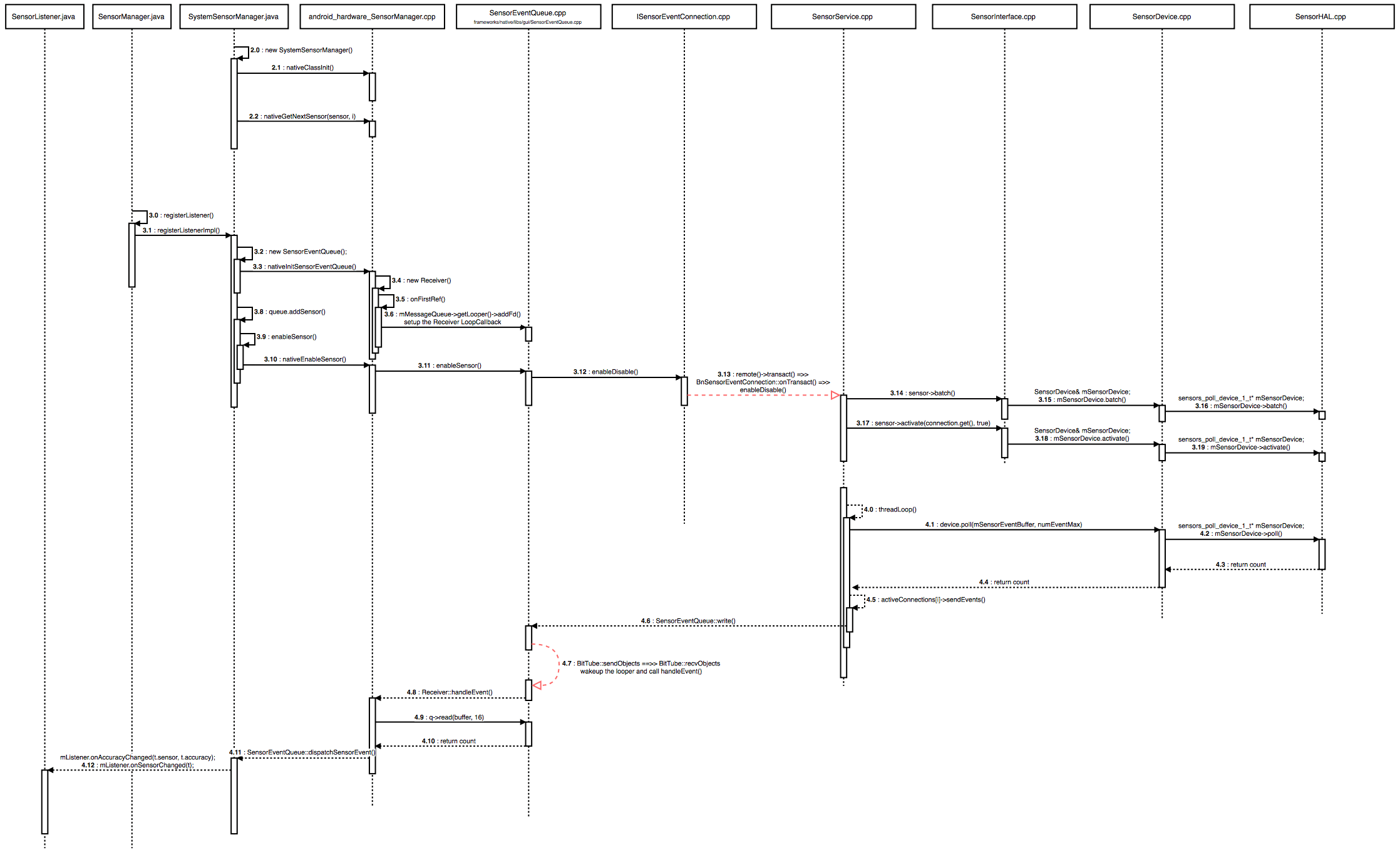
图:传感器注册及数据交互流程
上面两篇文章非常详细地剖析了sensor服务框架。
其中上图展示了上层(java)通过sdk接口:SensorManager.java#regitsterListener()监听具体传感器的调用流程。包括发起注册和注册后sensor数据传回来的流程。
转屏基于sensor框架,相对与sensor框架,转屏这个块更多可以理解为业务代码:system_server发起监听后收到sensor数据,之后才是wms中转屏的处理。所以sensor的架构流程本文不重点讨论。
下面简单过下system_server中转屏模块对加速度传感器的监听注册。
"android.ui@23798" prio=5 tid=0x14 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
blocks Binder:490_1@24058
blocks Binder:490_2@24059
blocks android.display@24062
blocks android.anim@24063
at android.hardware.SystemSensorManager.registerListenerImpl(SystemSensorManager.java:184)
- locked <0x5d11> (a java.util.HashMap)
at android.hardware.SensorManager.registerListener(SensorManager.java:854)
at com.android.server.policy.WindowOrientationListener.enable(WindowOrientationListener.java:161)
- locked <0x5e61> (a java.lang.Object)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation$OrientationListener.enable(DisplayRotation.java:1498)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation.updateOrientationListenerLw(DisplayRotation.java:971)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation.updateOrientationListener(DisplayRotation.java:897)
- locked <0x5e60> (a com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerGlobalLock)
at com.android.server.policy.PhoneWindowManager.finishScreenTurningOn(PhoneWindowManager.java:4595)
at com.android.server.policy.PhoneWindowManager.finishWindowsDrawn(PhoneWindowManager.java:4589)
at com.android.server.policy.PhoneWindowManager.access$200(PhoneWindowManager.java:235)
at com.android.server.policy.PhoneWindowManager$PolicyHandler.handleMessage(PhoneWindowManager.java:661)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:106)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:223)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:67)
at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:44)
at com.android.server.UiThread.run(UiThread.java:45)
如上是一份开机调用栈,本节的初始化流程指这个转屏传感器的监听注册。
开机流程中system_server进程默认注册传感器的监听。同样的在updateOrientationListenerLw方法的注释有详细说明,几种情况的监听动作。
需要理清的是,我们此处探讨system_server进程,而不是某个app使用了SensorManager来监听传感器。
所以当前的结论为,开机流程的开启屏幕阶段,wms会借助PhoneWindowManaegr在DisplayRotation中注册监听。如此传感器上报信息时可以回调通知(WindowOrientationListener.java$AccelSensorJudge#onSensorChanged),进而做算法处理是否转屏,做转屏动画,之后再通知atms做app的configChagne回调等。
下面就重点的代码展开分析。
DisplayRotation#updateOrientationListenerLw
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
925 /**
926 * Various use cases for invoking this function:
927 * <li>Screen turning off, should always disable listeners if already enabled.</li>
928 * <li>Screen turned on and current app has sensor based orientation, enable listeners
929 * if not already enabled.</li>
930 * <li>Screen turned on and current app does not have sensor orientation, disable listeners
931 * if already enabled.</li>
932 * <li>Screen turning on and current app has sensor based orientation, enable listeners
933 * if needed.</li>
934 * <li>screen turning on and current app has nosensor based orientation, do nothing.</li>
935 */
936 private void updateOrientationListenerLw() {
937 if (mOrientationListener == null || !mOrientationListener.canDetectOrientation()) {
938 // If sensor is turned off or nonexistent for some reason.
939 return;
940 }
941
942 final boolean screenOnEarly = mDisplayPolicy.isScreenOnEarly();
943 final boolean awake = mDisplayPolicy.isAwake();
944 final boolean keyguardDrawComplete = mDisplayPolicy.isKeyguardDrawComplete();
945 final boolean windowManagerDrawComplete = mDisplayPolicy.isWindowManagerDrawComplete();
946
947 // Could have been invoked due to screen turning on or off or
948 // change of the currently visible window's orientation.
949 ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION,
950 "screenOnEarly=%b, awake=%b, currentAppOrientation=%d, "
951 + "orientationSensorEnabled=%b, keyguardDrawComplete=%b, "
952 + "windowManagerDrawComplete=%b",
953 screenOnEarly, awake, mCurrentAppOrientation, mOrientationListener.mEnabled,
954 keyguardDrawComplete, windowManagerDrawComplete);
955
956 boolean disable = true;
957 // Note: We postpone the rotating of the screen until the keyguard as well as the
958 // window manager have reported a draw complete or the keyguard is going away in dismiss
959 // mode.
960 if (screenOnEarly && awake && ((keyguardDrawComplete && windowManagerDrawComplete))) {
961 if (needSensorRunning()) {
962 disable = false;
963 // Enable listener if not already enabled.
964 if (!mOrientationListener.mEnabled) {
965 // Don't clear the current sensor orientation if the keyguard is going away in
966 // dismiss mode. This allows window manager to use the last sensor reading to
967 // determine the orientation vs. falling back to the last known orientation if
968 // the sensor reading was cleared which can cause it to relaunch the app that
969 // will show in the wrong orientation first before correcting leading to app
970 // launch delays.
971 mOrientationListener.enable(true /* clearCurrentRotation */);
972 }
973 }
974 }
975 // Check if sensors need to be disabled.
976 if (disable && mOrientationListener.mEnabled) {
977 mOrientationListener.disable();
978 }
979 }
方法头的注释是情况说明,什么时候会注册、关闭对转屏传感器的监听。
重点关注960行的分支,在开机流程中,其值均为true。
961行,needSensorRunning方法判断是否需要传感器开启,答案为默认开启,仅在关屏和用户主动关闭情况才会关掉。
964行,开机时mEnabled为初值false
走到971行,enable方法里开始注册。需要注意的是,OrientationListener是WindowOrientationListener的子类,enable的实现在父类中,如下。
WindowOrientationListener#enable
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
private class OrientationListener extends WindowOrientationListener {
@Override
public void enable(boolean clearCurrentRotation) {
super.enable(clearCurrentRotation);
mEnabled = true;
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "Enabling listeners");
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/WindowOrientationListener.java
139 /**
140 * Enables the WindowOrientationListener so it will monitor the sensor and call
141 * {@link #onProposedRotationChanged(int)} when the device orientation changes.
142 *
143 * @param clearCurrentRotation True if the current proposed sensor rotation should be cleared as
144 * part of the reset.
145 */
146 public void enable(boolean clearCurrentRotation) {
147 synchronized (mLock) {
148 if (mSensor == null) {
149 Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot detect sensors. Not enabled");
150 return;
151 }
152 if (mEnabled) {
153 return;
154 }
155 if (LOG) {
156 Slog.d(TAG, "WindowOrientationListener enabled clearCurrentRotation="
157 + clearCurrentRotation);
158 }
159 mOrientationJudge.resetLocked(clearCurrentRotation);
160 if (mSensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER) {
161 mSensorManager.registerListener(
162 mOrientationJudge, mSensor, mRate, DEFAULT_BATCH_LATENCY, mHandler);
163 } else {
164 mSensorManager.registerListener(mOrientationJudge, mSensor, mRate, mHandler);
165 }
166 mEnabled = true;
167 }
168 }
注释说的很清楚,enable方法注册传感器监听,当传感器数据上报时回调方法#onProposedRotationChanged。
走进161行分支,看下几个关键的参数。
在WindowOrientationListener的构造函数中对mSensor和mOrientationJudge完成了初始化。
public WindowOrientationListener(Context context, Handler handler) {
this(context, handler, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
}
private WindowOrientationListener(Context context, Handler handler, int rate) {
if (mOrientationJudge == null) {
mSensor = mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(USE_GRAVITY_SENSOR
? Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY : Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
if (mSensor != null) {
// Create listener only if sensors do exist
mOrientationJudge = new AccelSensorJudge(context);
- mSensor是TYPE_ACCELEROMETER加速度传感器
模拟器上的传感器参数是这样:{Sensor name="Goldfish 3-axis Accelerometer", vendor="The Android Open Source Project", version=1, type=1, maxRange=39.300007, resolution=2.480159E-4, power=3.0, minDelay=10000}
-
mOrientationJudge是AccelSensorJudge类的实例
这个类很重要,转屏算法就在他的onSensorChanged方法中。算法内容可以参考这篇博文:Android转屏流程与优化(Google转屏算法)
-
mRate
代表延迟水平,有这几种定义。此处默认设为2,接收到的回调时间间隔66.666666ms。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SensorManager.java
317 /** get sensor data as fast as possible */ 318 public static final int SENSOR_DELAY_FASTEST = 0; 319 /** rate suitable for games */ 320 public static final int SENSOR_DELAY_GAME = 1; 321 /** rate suitable for the user interface */ 322 public static final int SENSOR_DELAY_UI = 2; 323 /** rate (default) suitable for screen orientation changes */ 324 public static final int SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL = 3; -
DEFAULT_BATCH_LATENCY
最大批量报告延迟,us微秒
-
handler
是我们的UiThread的handler,我们当前是处于system_server进程的ui线程中。堆栈信息有写。
最后阶段,看下registerListener的实现
SensorManager#registerListener
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SensorManager.java
851 public boolean registerListener(SensorEventListener listener, Sensor sensor,
852 int samplingPeriodUs, int maxReportLatencyUs, Handler handler) {
853 int delayUs = getDelay(samplingPeriodUs);
854 return registerListenerImpl(listener, sensor, delayUs, handler, maxReportLatencyUs, 0);
855 }
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
144 @Override
145 protected boolean registerListenerImpl(SensorEventListener listener, Sensor sensor,
146 int delayUs, Handler handler, int maxBatchReportLatencyUs, int reservedFlags) {
147 if (listener == null || sensor == null) {
148 Log.e(TAG, "sensor or listener is null");
149 return false;
150 }
151 // Trigger Sensors should use the requestTriggerSensor call.
152 if (sensor.getReportingMode() == Sensor.REPORTING_MODE_ONE_SHOT) {
153 Log.e(TAG, "Trigger Sensors should use the requestTriggerSensor.");
154 return false;
155 }
156 if (maxBatchReportLatencyUs < 0 || delayUs < 0) {
157 Log.e(TAG, "maxBatchReportLatencyUs and delayUs should be non-negative");
158 return false;
159 }
160 if (mSensorListeners.size() >= MAX_LISTENER_COUNT) {
161 throw new IllegalStateException("register failed, "
162 + "the sensor listeners size has exceeded the maximum limit "
163 + MAX_LISTENER_COUNT);
164 }
165
166 // Invariants to preserve:
167 // - one Looper per SensorEventListener
168 // - one Looper per SensorEventQueue
169 // We map SensorEventListener to a SensorEventQueue, which holds the looper
170 synchronized (mSensorListeners) {
171 SensorEventQueue queue = mSensorListeners.get(listener);
172 if (queue == null) {
173 Looper looper = (handler != null) ? handler.getLooper() : mMainLooper;
174 final String fullClassName =
175 listener.getClass().getEnclosingClass() != null
176 ? listener.getClass().getEnclosingClass().getName()
177 : listener.getClass().getName();
178 queue = new SensorEventQueue(listener, looper, this, fullClassName);
179 if (!queue.addSensor(sensor, delayUs, maxBatchReportLatencyUs)) {
180 queue.dispose();
181 return false;
182 }
183 mSensorListeners.put(listener, queue);
184 return true;
185 } else {
186 return queue.addSensor(sensor, delayUs, maxBatchReportLatencyUs);
187 }
188 }
189 }
两个重点,178行SensorEventQueue初始化,179行addSensor方法,都主要在native里。
queue.addSensor
上面小节,走过漫长的queue初始化,下面开始使用这个初始化后的队列,增加传感器监听。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
629 private abstract static class BaseEventQueue {
663 public boolean addSensor(
664 Sensor sensor, int delayUs, int maxBatchReportLatencyUs) {
665 // Check if already present.
666 int handle = sensor.getHandle();
667 if (mActiveSensors.get(handle)) return false;
668
669 // Get ready to receive events before calling enable.
670 mActiveSensors.put(handle, true);
671 addSensorEvent(sensor);
672 if (enableSensor(sensor, delayUs, maxBatchReportLatencyUs) != 0) {
673 // Try continuous mode if batching fails.
674 if (maxBatchReportLatencyUs == 0
675 || maxBatchReportLatencyUs > 0 && enableSensor(sensor, delayUs, 0) != 0) {
676 removeSensor(sensor, false);
677 return false;
678 }
679 }
680 return true;
681 }
670行,mActiveSensors是个缓存。
671行addSensorEvent实现在子类SensorEventQueue中。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
static final class SensorEventQueue extends BaseEventQueue {
@Override
public void addSensorEvent(Sensor sensor) {
SensorEvent t = new SensorEvent(Sensor.getMaxLengthValuesArray(sensor,
mManager.mTargetSdkLevel));
synchronized (mSensorsEvents) {
mSensorsEvents.put(sensor.getHandle(), t);
这里的mSensorsEvents也是个缓存array。
enableSensor
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
static final class SensorEventQueue extends BaseEventQueue {
private int enableSensor(
Sensor sensor, int rateUs, int maxBatchReportLatencyUs) {
if (mNativeSensorEventQueue == 0) throw new NullPointerException();
if (sensor == null) throw new NullPointerException();
return nativeEnableSensor(mNativeSensorEventQueue, sensor.getHandle(), rateUs,
maxBatchReportLatencyUs);
native的代码都略去了,详细可以阅读上面的两篇推荐文。
system_server进程中开机流程的wms屏幕开启阶段,加速度传感器的监听注册流程大致如此。
三、情景分析:点击“自动旋转”
设备中自动旋转的开关在systemui下拉菜单中,如下图
systemui进程
第一份binder trace如下
Trace: java.lang.Throwable
at android.os.BinderProxy.transact(BinderProxy.java:509)
at android.content.ContentProviderProxy.call(ContentProviderNative.java:730)
at android.provider.Settings$NameValueCache.putStringForUser(Settings.java:2667)
at android.provider.Settings$System.putStringForUser(Settings.java:3258)
at android.provider.Settings$System.putStringForUser(Settings.java:3242)
at android.provider.Settings$System.putIntForUser(Settings.java:3367)
at com.android.internal.view.RotationPolicy.setRotationLockAtAngle(RotationPolicy.java:122)
at com.android.internal.view.RotationPolicy.setRotationLock(RotationPolicy.java:114)
at com.android.systemui.statusbar.policy.RotationLockControllerImpl.setRotationLocked(RotationLockControllerImpl.java:68)
at com.android.systemui.qs.tiles.RotationLockTile.handleClick(RotationLockTile.java:62)
at com.android.systemui.qs.tileimpl.QSTileImpl$H.handleMessage(QSTileImpl.java:561)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:106)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:223)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:67)
可以看到,自动旋转暴露给app层的接口为com.android.internal.view.RotationPolicy.setRotationLock
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/view/RotationPolicy.java
109 /**
110 * Enables or disables rotation lock from the system UI toggle.
111 */
112 public static void setRotationLock(Context context, final boolean enabled) {
113 final int rotation = areAllRotationsAllowed(context) ? CURRENT_ROTATION : NATURAL_ROTATION;
114 setRotationLockAtAngle(context, enabled, rotation);
115 }
116
117 /**
118 * Enables or disables rotation lock at a specific rotation from system UI.
119 */
120 public static void setRotationLockAtAngle(Context context, final boolean enabled,
121 final int rotation) {
122 Settings.System.putIntForUser(context.getContentResolver(),
123 Settings.System.HIDE_ROTATION_LOCK_TOGGLE_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY, 0,
124 UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
125
126 setRotationLock(enabled, rotation);
127 }
跟到122行,修改的数据库字段为Settings.System.HIDE_ROTATION_LOCK_TOGGLE_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY和辅助服务有关,0代表不隐藏。此处不重点关注。
126行,在这个方法中使用AsyncTask向wms发起binder ipc
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/view/RotationPolicy.java
146 private static void setRotationLock(final boolean enabled, final int rotation) {
147 AsyncTask.execute(new Runnable() {
148 @Override
149 public void run() {
150 try {
151 IWindowManager wm = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowManagerService();
152 if (enabled) {
153 wm.freezeRotation(rotation);
154 } else {
155 wm.thawRotation();
156 }
157 } catch (RemoteException exc) {
158 Log.w(TAG, "Unable to save auto-rotate setting");
159 }
160 }
161 });
162 }
同样的在trace中体现如下
Trace: java.lang.Throwable
at android.os.BinderProxy.transact(BinderProxy.java:509)
at android.view.IWindowManager$Stub$Proxy.thawRotation(IWindowManager.java:3902)
at com.android.internal.view.RotationPolicy$1.run(RotationPolicy.java:155)
at android.os.AsyncTask$SerialExecutor$1.run(AsyncTask.java:305)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1167)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:641)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:923)
接下来进入system_server进程,看下wms的处理
system_server进程
binder trace如下
Trace: java.lang.Throwable
at android.os.BinderProxy.transact(BinderProxy.java:509)
at com.android.internal.statusbar.IStatusBar$Stub$Proxy.setTopAppHidesStatusBar(IStatusBar.java:1652)
at com.android.server.statusbar.StatusBarManagerService$1.setTopAppHidesStatusBar(StatusBarManagerService.java:423)
at com.android.server.wm.StatusBarController.setTopAppHidesStatusBar(StatusBarController.java:102)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayPolicy.finishPostLayoutPolicyLw(DisplayPolicy.java:2748)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayContent.applySurfaceChangesTransaction(DisplayContent.java:3940)
at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.applySurfaceChangesTransaction(RootWindowContainer.java:1068)
at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.performSurfacePlacementNoTrace(RootWindowContainer.java:845)
at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.performSurfacePlacement(RootWindowContainer.java:802)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowSurfacePlacer.performSurfacePlacementLoop(WindowSurfacePlacer.java:178)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowSurfacePlacer.performSurfacePlacement(WindowSurfacePlacer.java:127)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowSurfacePlacer.performSurfacePlacement(WindowSurfacePlacer.java:116)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.updateRotationUnchecked(WindowManagerService.java:3844)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.thawDisplayRotation(WindowManagerService.java:3776)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.thawRotation(WindowManagerService.java:3746)
at android.view.IWindowManager$Stub.onTransact(IWindowManager.java:1948)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.onTransact(WindowManagerService.java:1350)
at android.os.Binder.execTransactInternal(Binder.java:1154)
at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:1123)
binder trace、有时候并不能如你的意,因为只有ipc才会被收集调用栈,oneway的情况就只可以看到发起进程的栈了。另外,服务端进程的栈有些进程内部的动作,也无法体现在trace上。例如上面这份trace,显示wms里bidner ipc沟通statusbar,这个动作不是我们主要关注的内容,wms内部的处理流程才是。
所以binder trace不一定完全切合我们需求,具体情景具体分析。下面我们跟踪这份trace看wms内部的处理。
WindowManagerService.thawRotation
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
3754 @Override
3755 public void thawRotation() {
3756 thawDisplayRotation(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
3757 }
3763 @Override
3764 public void thawDisplayRotation(int displayId) {
3765 if (!checkCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.SET_ORIENTATION,
3766 "thawRotation()")) {
3767 throw new SecurityException("Requires SET_ORIENTATION permission");
3768 }
3769
3770 ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "thawRotation: mRotation=%d", getDefaultDisplayRotation());
3771
3772 long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
3773 try {
3774 synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
3775 final DisplayContent display = mRoot.getDisplayContent(displayId);
3776 if (display == null) {
3777 Slog.w(TAG, "Trying to thaw rotation for a missing display.");
3778 return;
3779 }
3780 display.getDisplayRotation().thawRotation();
3781 }
3782 } finally {
3783 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
3784 }
3785
3786 updateRotationUnchecked(false, false);
3787 }
3765行鉴权,这是系统api。
3780行,在DisplayRotation中设置settings lib 数据库。
3786行,updateRotationUnchecked方法是重点。
DisplayRotation.thawRotation
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
826 void thawRotation() {
827 setUserRotation(WindowManagerPolicy.USER_ROTATION_FREE, mUserRotation);
828 }
790 @VisibleForTesting
791 void setUserRotation(int userRotationMode, int userRotation) {
792 if (isDefaultDisplay) {
793 // We'll be notified via settings listener, so we don't need to update internal values.
794 final ContentResolver res = mContext.getContentResolver();
795 final int accelerometerRotation =
796 userRotationMode == WindowManagerPolicy.USER_ROTATION_LOCKED ? 0 : 1;
797 Settings.System.putIntForUser(res, Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION,
798 accelerometerRotation, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
799 Settings.System.putIntForUser(res, Settings.System.USER_ROTATION, userRotation,
800 UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
801 return;
802 }
803
804 boolean changed = false;
805 if (mUserRotationMode != userRotationMode) {
806 mUserRotationMode = userRotationMode;
807 changed = true;
808 }
809 if (mUserRotation != userRotation) {
810 mUserRotation = userRotation;
811 changed = true;
812 }
813 mDisplayWindowSettings.setUserRotation(mDisplayContent, userRotationMode,
814 userRotation);
815 if (changed) {
816 mService.updateRotation(true /* alwaysSendConfiguration */,
817 false /* forceRelayout */);
818 }
819 }
797、799行更新两个重要的数据库值
Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION
Settings.System.USER_ROTATION
设置之后监听这些值的地方会触发ContentResolver回调,例如进程外的systemui、launcher和进程内DisplayRotation。
我们关注系统进程的数据库监听。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
1511 private class SettingsObserver extends ContentObserver {
1512 SettingsObserver(Handler handler) {
1513 super(handler);
1514 }
1515
1516 void observe() {
1517 final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
1518 resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
1519 Settings.Secure.SHOW_ROTATION_SUGGESTIONS), false, this,
1520 UserHandle.USER_ALL);
1521 resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
1522 Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION), false, this,
1523 UserHandle.USER_ALL);
1524 resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
1525 Settings.System.USER_ROTATION), false, this,
1526 UserHandle.USER_ALL);
1527 updateSettings();
1528 }
1529
1530 @Override
1531 public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
1532 if (updateSettings()) {
1533 mService.updateRotation(true /* alwaysSendConfiguration */,
1534 false /* forceRelayout */);
1535 }
1536 }
1537 }
1531行的回调得到触发。1532行默认为true,代表需要wms做进一步处理。
走到1533行,wms的updateRotation方法。参数1代表要更新配置,参数2为不强制更新布局。
WindowManagerService.updateRotation
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
3806 /**
3807 * Recalculate the current rotation.
3808 *
3809 * Called by the window manager policy whenever the state of the system changes
3810 * such that the current rotation might need to be updated, such as when the
3811 * device is docked or rotated into a new posture.
3812 */
3813 @Override
3814 public void updateRotation(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
3815 updateRotationUnchecked(alwaysSendConfiguration, forceRelayout);
3816 }
3818 private void updateRotationUnchecked(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
3819 ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "updateRotationUnchecked:"
3820 + " alwaysSendConfiguration=%b forceRelayout=%b",
3821 alwaysSendConfiguration, forceRelayout);
3822
3823 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "updateRotation");
3824
3825 long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
3826
3827 try {
3828 synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
3829 boolean layoutNeeded = false;
3830 final int displayCount = mRoot.mChildren.size();
3831 for (int i = 0; i < displayCount; ++i) {
3832 final DisplayContent displayContent = mRoot.mChildren.get(i);
3833 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "updateRotation: display");
3834 final boolean rotationChanged = displayContent.updateRotationUnchecked();
3835 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3836
3837 if (rotationChanged) {
3838 mAtmService.getTaskChangeNotificationController()
3839 .notifyOnActivityRotation(displayContent.mDisplayId);
3840 }
3841
3842 if (!rotationChanged || forceRelayout) {
3843 displayContent.setLayoutNeeded();
3844 layoutNeeded = true;
3845 }
3846 if (rotationChanged || alwaysSendConfiguration) {
3847 displayContent.sendNewConfiguration();
3848 }
3849 }
3850
3851 if (layoutNeeded) {
3852 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER,
3853 "updateRotation: performSurfacePlacement");
3854 mWindowPlacerLocked.performSurfacePlacement();
3855 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3856 }
3857 }
3858 } finally {
3859 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
3860 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3861 }
3862 }
3834行displayContent.updateRotationUnchecked()计算是否需要旋转。由于这次我们的点击操作是在屏幕竖起时,所以计算不做旋转,如下图。那另一种情况,横屏时点击的话,自然就触发旋转了。这也符合我们的认知。
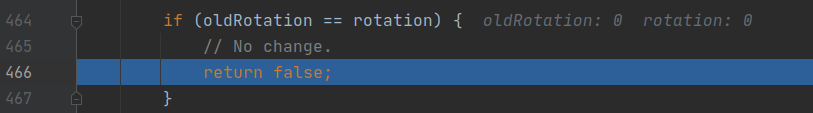
图:displayContent.updateRotationUnchecked检查不做旋转
3837行,rotationChanged为false,所以不需要更新配置。
3842、3846、3851行本次流程没什么需要关注的。
总结一下
- 点击自动旋转涉及两个进程三个角色。
两个进程:systemui、system_server
三个角色:systemui界面按钮、settingslib数据库、DisplayRotation
- 动作流程
人点击systemui的自动旋转按钮,binder沟通wm.thawRotation
wms写settingslib:Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION、Settings.System.USER_ROTATION
DisplayRotation监听这俩数据库值,触发转屏检查mService.updateRotation
四、情景分析:转屏流程
转屏从人的操作体验上来说,可以这样描述:把屏幕横过来,经过短暂的等待看到屏幕上图像开始旋转,然后是图像旋转结束。
从代码流程上看,可以分为三部分
一是硬件、驱动检测到加速度变化然后传给监听者(WindowOrientationListener)
二是WindowOrientationListener的转屏算法,确定是否要转
三是wms里做转屏动画
3.1硬件、驱动参数上报
本文不讨论这块
3.2转屏算法确认是否转屏
见性能优化篇。
3.3 转屏动画
"android.ui@23942" prio=5 tid=0x14 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation$OrientationListener.onProposedRotationChanged(DisplayRotation.java:1487)
at com.android.server.policy.WindowOrientationListener$AccelSensorJudge.onSensorChanged(WindowOrientationListener.java:818)
at android.hardware.SystemSensorManager$SensorEventQueue.dispatchSensorEvent(SystemSensorManager.java:837)
at android.os.MessageQueue.nativePollOnce(MessageQueue.java:-1)
at android.os.MessageQueue.next(MessageQueue.java:335)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:183)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:67)
at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:44)
at com.android.server.UiThread.run(UiThread.java:45)
这是一份堆栈信息,展示了转屏流程的第一阶段,是在system_server进程android.ui线程。
回调是looper的epoll对fd的监听,详细可以看第一节的两篇文章和学习下looper的监听机制。
转屏算法处理在WindowOrientationListener$AccelSensorJudge.onSensorChanged回调方法中,本文不展开。
走出了onSensorChanged方法即代表算法认可当前需要旋转,所以下一步是wms做处理动作,我们继续往下看。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
@Override
public void onProposedRotationChanged(int rotation) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "onProposedRotationChanged, rotation=%d", rotation);
Runnable r = mRunnableCache.get(rotation, null);
if (r == null) {
r = new UpdateRunnable(rotation);
mRunnableCache.put(rotation, r);
}
getHandler().post(r);
}
执行runnable
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayRotation.java
private class UpdateRunnable implements Runnable {
final int mRotation;
UpdateRunnable(int rotation) {
mRotation = rotation;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Send interaction hint to improve redraw performance.
mService.mPowerManagerInternal.powerHint(PowerHint.INTERACTION, 0);
if (isRotationChoicePossible(mCurrentAppOrientation)) {
final boolean isValid = isValidRotationChoice(mRotation);
sendProposedRotationChangeToStatusBarInternal(mRotation, isValid);
} else {
mService.updateRotation(false /* alwaysSendConfiguration */,
false /* forceRelayout */);
if判断为false,走到mService.updateRotation。这个是wms暴露的转屏接口,上一节的自动转屏也是走到这个API。
先放一下调用栈
"android.ui@23972" prio=5 tid=0x14 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
blocks android.fg@24280
blocks android.display@24282
blocks android.anim@24283
blocks ActivityManager@24287
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation.setRotationTransform(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:270)
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation.setRotation(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:332)
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation.<init>(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:254)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.startFreezingDisplay(WindowManagerService.java:5610)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.startFreezingDisplay(WindowManagerService.java:5562)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation.prepareNormalRotationAnimation(DisplayRotation.java:549)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation.updateRotationUnchecked(DisplayRotation.java:491)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayContent.updateRotationUnchecked(DisplayContent.java:1700)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.updateRotationUnchecked(WindowManagerService.java:3834)
- locked <0x5f48> (a com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerGlobalLock)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.updateRotation(WindowManagerService.java:3815)
at com.android.server.wm.DisplayRotation$OrientationListener$UpdateRunnable.run(DisplayRotation.java:1479)
at android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:938)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:99)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:223)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:67)
at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:44)
at com.android.server.UiThread.run(UiThread.java:45)
这是冻结屏幕准备参数的的调用栈
"android.display@23994" prio=5 tid=0x16 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
blocks android.anim@23993
blocks Binder:486_D@24124
blocks Binder:486_E@23997
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation$SurfaceRotationAnimationController.startScreenRotationAnimation(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:576)
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation.startAnimation(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:427)
at com.android.server.wm.ScreenRotationAnimation.dismiss(ScreenRotationAnimation.java:445)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.stopFreezingDisplayLocked(WindowManagerService.java:5682)
at com.android.server.wm.ActivityRecord.stopFreezingScreen(ActivityRecord.java:5311)
at com.android.server.wm.ActivityRecord.onAppFreezeTimeout(ActivityRecord.java:5272)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService$H.handleMessage(WindowManagerService.java:4932)
- locked <0x5e42> (a com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerGlobalLock)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:106)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:223)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:67)
at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:44)
这是过渡动画启动的调用栈
动画的启动流程此处不展开,细节可参考:Android 11--横竖屏旋转时背景色异常?
需要关注的主要有两处,一是动画,二是通知ATMS做config的变动进而通知activity响应转屏,都在wms的updateRotationUnchecked方法里
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
3818 private void updateRotationUnchecked(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
3819 ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "updateRotationUnchecked:"
3820 + " alwaysSendConfiguration=%b forceRelayout=%b",
3821 alwaysSendConfiguration, forceRelayout);
3822
3823 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "updateRotation");
3824
3825 long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
3826
3827 try {
3828 synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
3829 boolean layoutNeeded = false;
3830 final int displayCount = mRoot.mChildren.size();
3831 for (int i = 0; i < displayCount; ++i) {
3832 final DisplayContent displayContent = mRoot.mChildren.get(i);
3833 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "updateRotation: display");
3834 final boolean rotationChanged = displayContent.updateRotationUnchecked();
3835 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3836
3837 if (rotationChanged) {
3838 mAtmService.getTaskChangeNotificationController()
3839 .notifyOnActivityRotation(displayContent.mDisplayId);
3840 }
3841
3842 if (!rotationChanged || forceRelayout) {
3843 displayContent.setLayoutNeeded();
3844 layoutNeeded = true;
3845 }
3846 if (rotationChanged || alwaysSendConfiguration) {
3847 displayContent.sendNewConfiguration();
3848 }
3849 }
3850
3851 if (layoutNeeded) {
3852 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER,
3853 "updateRotation: performSurfacePlacement");
3854 mWindowPlacerLocked.performSurfacePlacement();
3855 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3856 }
3857 }
3858 } finally {
3859 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
3860 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
3861 }
3862 }
重点1:3834行处理转屏动画
重点2:3838,3847行通知ATMS处理旋转和配置变动
五、参考
本文来自博客园,作者:秋城,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghongzhu/p/14907681.html