apache activemq 学习笔记
0、activemq的概念
activemq实现了jms(java Message server),用于接收,发送,处理消息的开源消息总线。
1、activemq和jms的区别
jms说白了就是java message service,是J2EE规范的一部分,跟jdbc差不多,sun只提供了接口,由各个厂商(provider)来进行具体的实现,然后使用者使用他们的jar包进行开发使用即可。
另外在jms的API中,jms传递消息有两种方式,一种是点对点的Queue,还有一个是发布订阅的Topic方式。区别在于: 对于Queue模式,一个发布者发布消息,下面的接收者按队列顺序接收,比如发布了10个消息,两个接收者A,B那就是A,B总共会收到10条消息,不重复。 对于Topic模式,一个发布者发布消息,有两个接收者A,B来订阅,那么发布了10条消息,A,B各收到10条消息。
关于api的简单基础可以看下:http://www.javaeye.com/topic/64707,简单的参考!
2、activemq集群
activemq使用了master-slave的方式,其中分为三种模式分别是:pure master slave 、shared file system master slave、jdbc master slave。 shared file system master slave连接了activemq的默认数据库,二jdbc可以配置自己的数据库。当一个master宕机了,就会在众多slaver中选举出来一个master,接替宕机的master继续工作,以上三种方式的集群都不支持负载均衡,但可以解决单点故障的问题,以保证消息服务的可靠性。
3、activemq在什么时候用
访问第三方组件,异步处理消息,需要花费较长的时间的。
4、有哪些实现消息的开源组件,各自的优缺点以及比较
activemq相比较其他的消息机制,好在他是使用factory来管理连接,session的
5、在linux下写activemq简单的demo
可以自己写一个demo,(安装目录/home/hongye/hongyeConfig/Server/apache-activemq-5.6.0)
(1)、解压mq的文件
(2)、在bin下启动activemq:./activemq start
(3)、在activemq的官方web平台上验证是否启动成功,注意ip是指安装mq所在服务器的ip。比如http://192.168.9.107:8161/admin/queues.jsp(端口8161是管理mq的端口,端口61616是mq通信的的端口,不要搞错了)
(4)、写生产者和消费者的例子,注意url是指安装mq所在服务器的ip。端口是mq的默认端口号61616
此外可以部署mq的集群,在linux的conf目录下配置多个activemq.xml的文件。可以调整queue的大小、改变端口号和消息存在的时间和持久化到数据库的用户名密码
生产者例子-----Producer类:

1 package com.wanghongye.activemq;
2
3 import javax.jms.Connection;
4 import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory;
5 import javax.jms.JMSException;
6 import javax.jms.MessageProducer;
7 import javax.jms.Queue;
8 import javax.jms.Session;
9 import javax.jms.TextMessage;
10
11 import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
12
13 public class Producer
14 {
15 private static String url = "failover://tcp://192.168.9.107:61616";
16 private static String queueName = "FirstQueue";
17
18 public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException
19 {
20 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
21 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url);
22 // create connection
23 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
24 connection.start();
25
26 // create session
27 Session session = connection.createSession(false,
28 Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
29 Queue queue = session.createQueue(queueName);
30
31 // createproduct
32 MessageProducer messageProducer = session.createProducer(queue);
33 TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("go into queue !!");
34 messageProducer.send(textMessage);
35
36 connection.close();
37 }
38 }
消费者例子-----Consumer类:

1 package com.wanghongye.activemq; 2 3 import javax.jms.Connection; 4 import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory; 5 import javax.jms.JMSException; 6 import javax.jms.MessageConsumer; 7 import javax.jms.Queue; 8 import javax.jms.Session; 9 10 import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory; 11 12 13 public class Consumer { 14 15 private static String url = "failover://tcp://192.168.9.107:61616"; 16 private static String queueName = "FirstQueue"; 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException{ 19 //create connection 20 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url); 21 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); 22 connection.start(); 23 24 //create session 25 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); 26 Queue destination = session.createQueue(queueName); 27 28 //create consumer 29 MessageConsumer messageConsumer = session.createConsumer(destination); 30 31 messageConsumer.receive(); 32 33 //close 34 connection.close(); 35 } 36 37 }
配置文件activemq.xml:

1 <!-- 2 Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more 3 contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with 4 this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. 5 The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 6 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with 7 the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at 8 9 http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 10 11 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 12 distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 13 WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 14 See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 15 limitations under the License. 16 --> 17 <!-- START SNIPPET: example --> 18 <beans 19 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 20 xmlns:amq="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" 21 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 22 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd 23 http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd"> 24 25 <!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file --> 26 <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> 27 <property name="locations"> 28 <value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value> 29 </property> 30 </bean> 31 32 <!-- 33 The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker. 34 --> 35 <broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="localhost" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}"> 36 37 <!-- 38 For better performances use VM cursor and small memory limit. 39 For more information, see: 40 41 http://activemq.apache.org/message-cursors.html 42 43 Also, if your producer is "hanging", it's probably due to producer flow control. 44 For more information, see: 45 http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html 46 --> 47 48 <destinationPolicy> 49 <policyMap> 50 <policyEntries> 51 <policyEntry topic=">" producerFlowControl="true" memoryLimit="1mb"> 52 <pendingSubscriberPolicy> 53 <vmCursor /> 54 </pendingSubscriberPolicy> 55 </policyEntry> 56 <policyEntry queue=">" producerFlowControl="true" memoryLimit="1mb"> 57 <!-- Use VM cursor for better latency 58 For more information, see: 59 60 http://activemq.apache.org/message-cursors.html 61 62 <pendingQueuePolicy> 63 <vmQueueCursor/> 64 </pendingQueuePolicy> 65 --> 66 </policyEntry> 67 </policyEntries> 68 </policyMap> 69 </destinationPolicy> 70 71 72 <!-- 73 The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in 74 JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by 75 the JVM. For more information, see: 76 77 http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html 78 --> 79 <managementContext> 80 <managementContext createConnector="false"/> 81 </managementContext> 82 83 <!-- 84 Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence 85 mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag). 86 For more information, see: 87 88 http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html 89 --> 90 <persistenceAdapter> 91 <kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/> 92 </persistenceAdapter> 93 94 95 <!-- 96 The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will 97 use before slowing down producers. For more information, see: 98 http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html 99 If using ActiveMQ embedded - the following limits could safely be used: 100 101 <systemUsage> 102 <systemUsage> 103 <memoryUsage> 104 <memoryUsage limit="20 mb"/> 105 </memoryUsage> 106 <storeUsage> 107 <storeUsage limit="1 gb"/> 108 </storeUsage> 109 <tempUsage> 110 <tempUsage limit="100 mb"/> 111 </tempUsage> 112 </systemUsage> 113 </systemUsage> 114 --> 115 <systemUsage> 116 <systemUsage> 117 <memoryUsage> 118 <memoryUsage limit="64 mb"/> 119 </memoryUsage> 120 <storeUsage> 121 <storeUsage limit="100 gb"/> 122 </storeUsage> 123 <tempUsage> 124 <tempUsage limit="50 gb"/> 125 </tempUsage> 126 </systemUsage> 127 </systemUsage> 128 129 <!-- 130 The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to 131 clients and other brokers. For more information, see: 132 133 http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html 134 --> 135 <transportConnectors> 136 <transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:61616"/> 137 </transportConnectors> 138 139 </broker> 140 141 <!-- 142 Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos 143 144 Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details 145 --> 146 <import resource="jetty.xml"/> 147 148 </beans> 149 <!-- END SNIPPET: example -->
其中transportConnectors节点可以更改mq的端口号。如果是集群的话,拷贝几个xml(activemq-broker01.xml)文件,更改端口号即可。
运行生产者,等待数量增加1,进队列的数量增加1
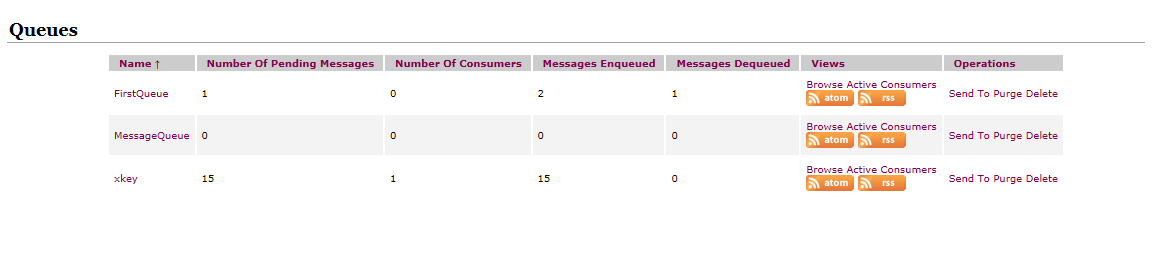
运行消费者,等待数量减1,出队列的数量增加1:
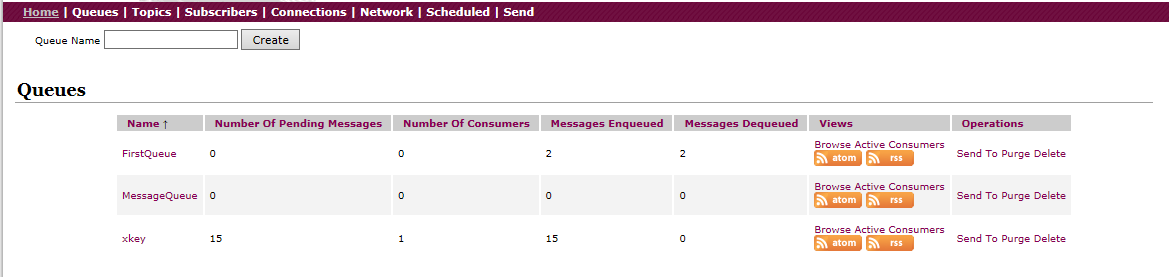
6、室内组件如何使用 activeMQ
(1)、封装了建立工厂,建立connection,建立session,关闭connection的流程,作为mqconf类
(2)、创建了生产者,初始化使用单例的模式,把消息放进queue或者topic
(3)、创建了消费者,初始化使用单例的模式,使用retrive方法消费
(4)、创建mq.xml,里面配置用户名,密码,队列名,mq服务所在的ip地址
以上的封装成为一个组件,调用即可。
7、关于 activeMQ的讨论
多翻阅官方文档。http://activemq.apache.org/clustering.html
多练习使用。
多积累常见的QA






