04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)
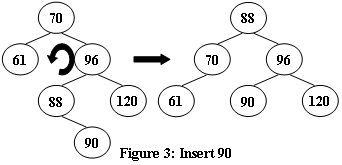
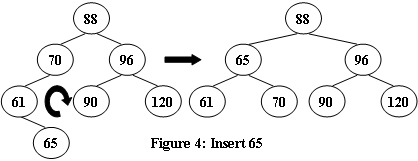
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
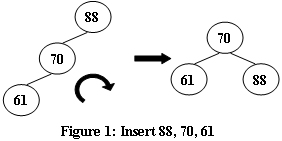
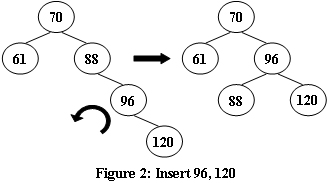
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct node{ int v,height; node* lchild,*rchild; }*root; node* newNode(int v){ node* Node = new node; Node->v = v; Node->height = 1; Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL; return Node; } int getHeight(node* root){ if(root == NULL) return 0; return root->height; } void updateHeight(node* root){ root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild)) + 1; } int getBalanceFactor(node* root){ return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild); } void R(node* &root){ node* temp = root->lchild; root->lchild = temp->rchild; temp->rchild = root; updateHeight(root); updateHeight(temp); root = temp; } void L(node* &root){ node* temp = root->rchild; root->rchild = temp->lchild; temp->lchild = root; updateHeight(root); updateHeight(temp); root = temp; } void insert(node* &root,int v){ if(root == NULL){ root = newNode(v); return; } if(root->v > v){ insert(root->lchild,v); updateHeight(root); if(getBalanceFactor(root) == 2){ if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == 1){ R(root); }else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == -1){ L(root->lchild); R(root); } } }else{ insert(root->rchild,v); updateHeight(root); if(getBalanceFactor(root) == -2){ if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild) == -1){ L(root); }else if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild) == 1){ R(root->rchild); L(root); } } } } int main(){ int n,v; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ scanf("%d",&v); insert(root,v); } printf("%d",root->v); return 0; }
分类:
2018年秋mooc课网数据结构






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)