labelme的安装及生成json后批处理
一、 labelme的安装
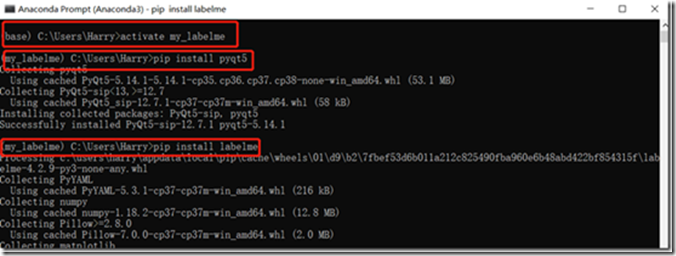
1、 打开anaconda prompt,先在Anaconda中新建了一个虚拟环境,作为我的一个标注环境。
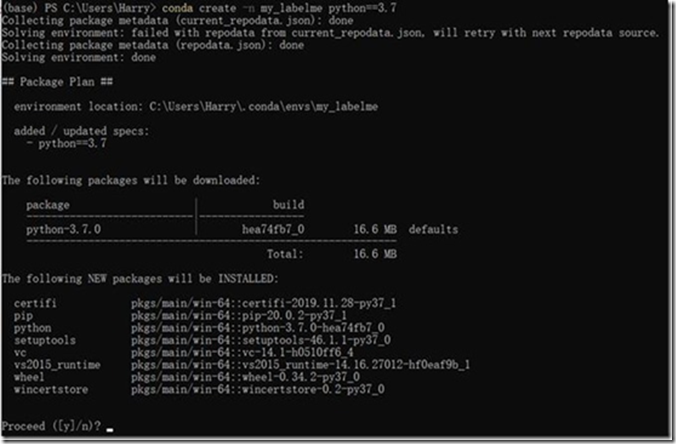
conda create -n my_labelme python==3.72、 安装labelme
首先激活环境
activate my-labelme
然后先安装pyqt5
pip install pyqt5
安装好后安装labelme
pip install labelme
二、使用labelme
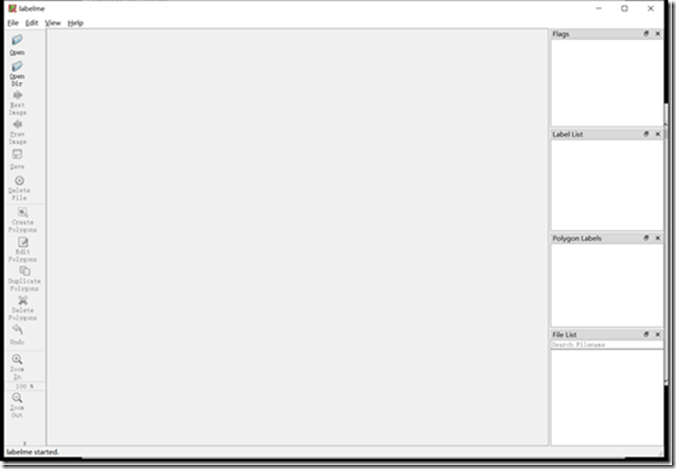
直接在激活后的环境内输入labelme可以弹出窗口进行操作,具体的使用教程有很多不错的资料,不画蛇添足了。
三、label生成的json文件转png
我们标注完成后会生成相应的json文件,文件里有label的详细信息。生成的json文件并不能直接用,我们需要对他进行处理才能变为需要形式。
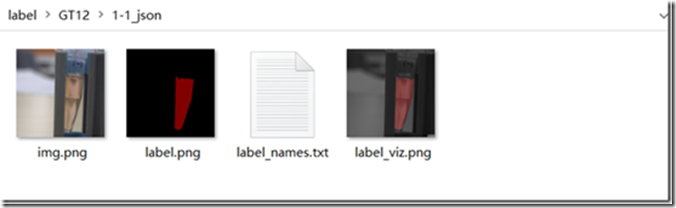
1、单个json文件的转换,这里我生成的json文件名为1-1.json,位于C:\Users\Harry\Desktop\label\GT12目录下,在激活my_labelme环境的anaconda prompt中,直接输入
labelme_json_to_dataset C:\Users\Harry\Desktop\label\GT12\1-1.json
运行后可以在json文件所在文件夹下,生成一个文件夹,文件夹中有对应的4个生成文件。
2、labelme标注工具再转化.json文件有一个缺陷,一次只能转换一个.json文件,我们通常需要大量的数据,可以对labelme做出了改进,可以实现批量转换.json文件。
①找到虚拟环境的安装位置,具体的位置和系统有一些关系,以我电脑为例,一般在C:\Users\Harry\.conda\envs\****或者 C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\envs\**** 中。
②按照自己路径进入cli文件夹,我的是 C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\envs\labelme\Lib\site-packages\labelme\cli
③共有四个.py 文件,我们备份一下,然后更改json_to_dataset.py中的文件,文件中内容如下:
import argparse import json import os import os.path as osp import warnings import numpy as np import PIL.Image import yaml from labelme import utils def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('json_file') parser.add_argument('-o', '--out', default=None) args = parser.parse_args() json_file = args.json_file list = os.listdir(json_file) for i in range(0, len(list)): path = os.path.join(json_file, list[i]) if os.path.isfile(path): data = json.load(open(path)) img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data['imageData']) lbl, lbl_names = utils.labelme_shapes_to_label(img.shape, data['shapes']) captions = ['%d: %s' % (l, name) for l, name in enumerate(lbl_names)] lbl_viz = utils.draw_label(lbl, img, captions) out_dir = osp.basename(list[i]).replace('.', '_') out_dir = osp.join(osp.dirname(list[i]), out_dir) if not osp.exists(out_dir): os.mkdir(out_dir) PIL.Image.fromarray(img).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'img.png')) PIL.Image.fromarray(lbl).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'label.png')) PIL.Image.fromarray(lbl_viz).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_viz.png')) with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_names.txt'), 'w') as f: for lbl_name in lbl_names: f.write(lbl_name + '\n') warnings.warn('info.yaml is being replaced by label_names.txt') info = dict(label_names=lbl_names) with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'info.yaml'), 'w') as f: yaml.safe_dump(info, f, default_flow_style=False) print('Saved to: %s' % out_dir) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
④假设我的json文件放在d:\my_jsondata中,生成的文件我想放到d:\my_data中
这个时候就可以使用,就可以看到生成的文件里
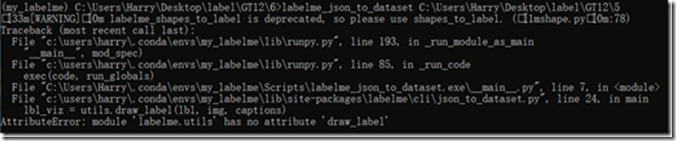
#先进入存储生成文件的文件夹 cd D:\my_jsondata #运行 labelme_json_to_dataset d:\my_data
但是这个时候运行,一般会出现这个错误,显示缺少draw_label,这个应该是版本的原因,最新版本缺少了这个文件。
这个坑我填了好久…
⑤在envs\my_labelme\Lib\site-packages\labelme\utils中添加draw.py,内容如下:
import io import os.path as osp import numpy as np import PIL.Image import PIL.ImageDraw import PIL.ImageFont def label_colormap(N=256): def bitget(byteval, idx): return ((byteval & (1 << idx)) != 0) cmap = np.zeros((N, 3)) for i in range(0, N): id = i r, g, b = 0, 0, 0 for j in range(0, 8): r = np.bitwise_or(r, (bitget(id, 0) << 7 - j)) g = np.bitwise_or(g, (bitget(id, 1) << 7 - j)) b = np.bitwise_or(b, (bitget(id, 2) << 7 - j)) id = (id >> 3) cmap[i, 0] = r cmap[i, 1] = g cmap[i, 2] = b cmap = cmap.astype(np.float32) / 255 return cmap def _validate_colormap(colormap, n_labels): if colormap is None: colormap = label_colormap(n_labels) else: assert colormap.shape == (colormap.shape[0], 3), \ 'colormap must be sequence of RGB values' assert 0 <= colormap.min() and colormap.max() <= 1, \ 'colormap must ranges 0 to 1' return colormap # similar function as skimage.color.label2rgb def label2rgb( lbl, img=None, n_labels=None, alpha=0.5, thresh_suppress=0, colormap=None, ): if n_labels is None: n_labels = len(np.unique(lbl)) colormap = _validate_colormap(colormap, n_labels) colormap = (colormap * 255).astype(np.uint8) lbl_viz = colormap[lbl] lbl_viz[lbl == -1] = (0, 0, 0) # unlabeled if img is not None: img_gray = PIL.Image.fromarray(img).convert('LA') img_gray = np.asarray(img_gray.convert('RGB')) # img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_gray, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB) lbl_viz = alpha * lbl_viz + (1 - alpha) * img_gray lbl_viz = lbl_viz.astype(np.uint8) return lbl_viz def draw_label(label, img=None, label_names=None, colormap=None, **kwargs): """Draw pixel-wise label with colorization and label names. label: ndarray, (H, W) Pixel-wise labels to colorize. img: ndarray, (H, W, 3), optional Image on which the colorized label will be drawn. label_names: iterable List of label names. """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt backend_org = plt.rcParams['backend'] plt.switch_backend('agg') plt.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1, top=1, bottom=0, wspace=0, hspace=0) plt.margins(0, 0) plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) if label_names is None: label_names = [str(l) for l in range(label.max() + 1)] colormap = _validate_colormap(colormap, len(label_names)) label_viz = label2rgb( label, img, n_labels=len(label_names), colormap=colormap, **kwargs ) plt.imshow(label_viz) plt.axis('off') plt_handlers = [] plt_titles = [] for label_value, label_name in enumerate(label_names): if label_value not in label: continue fc = colormap[label_value] p = plt.Rectangle((0, 0), 1, 1, fc=fc) plt_handlers.append(p) plt_titles.append('{value}: {name}' .format(value=label_value, name=label_name)) plt.legend(plt_handlers, plt_titles, loc='lower right', framealpha=.5) f = io.BytesIO() plt.savefig(f, bbox_inches='tight', pad_inches=0) plt.cla() plt.close() plt.switch_backend(backend_org) out_size = (label_viz.shape[1], label_viz.shape[0]) out = PIL.Image.open(f).resize(out_size, PIL.Image.BILINEAR).convert('RGB') out = np.asarray(out) return out def draw_instances( image=None, bboxes=None, labels=None, masks=None, captions=None, ): import matplotlib # TODO(wkentaro) assert image is not None assert bboxes is not None assert labels is not None assert masks is None assert captions is not None viz = PIL.Image.fromarray(image) draw = PIL.ImageDraw.ImageDraw(viz) font_path = osp.join( osp.dirname(matplotlib.__file__), 'mpl-data/fonts/ttf/DejaVuSans.ttf' ) font = PIL.ImageFont.truetype(font_path) colormap = label_colormap(255) for bbox, label, caption in zip(bboxes, labels, captions): color = colormap[label] color = tuple((color * 255).astype(np.uint8).tolist()) xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = bbox draw.rectangle((xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax), outline=color) draw.text((xmin, ymin), caption, font=font) return np.asarray(viz)
⑥修改__init__.py中的内容
添加几行
from .draw import label_colormap
from .draw import _validate_colormap
from .draw import label2rgb
from .draw import draw_label
from .draw import draw_instances





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步