Spring 对事务的整理
事务回顾
什么是事务:
- 事务(TRANSACTION) 是作为单个逻辑工作单元执行的一系列操作。
- 多个操作作为一个整体向系统提交,要么都执行,要么都不执行。
- 事务是一个不可分割的逻辑单元。
事务的特性:
事务具备以下四个特性,简称ACID属性。
原子性(Atomicity):
事务是一个完整的操作,事务的各步操作都是不可再分的,要么都执行, 要么都不执行。
一致性(Consistency):
当事务完成时,数据必须处于一致的状态。
隔离性(Isolation):
并发事务之间相互独立、隔离,它不应以任何方式依赖于或影响其他事 务。
持久性(Durability):
事务完成后,它对数据库的修改被永久保持。
Spring中对事务的整合
在Spring中,所有操作事务的类都继承自 PlatformTransactionManager
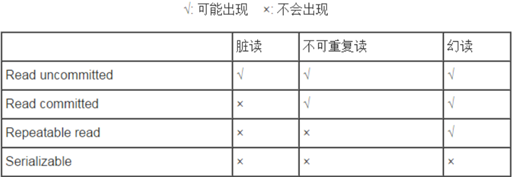
(Orcale 和 SQLSever)默认:读已提交
MySql默认 可重复读
- ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:读未提交
- ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:读已提交
- ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:可重复读
- ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:串行化
脏读:
A事务读取B事务尚未提交的更改数据,并在这个数据的基础上进行操作,这时候如果事务B回滚,那么A事务读到的数据是不被承认的。
例如常见的取款事务和转账事务
不可重复读:
不可重复读是指A事务读取了B事务已经提交的更改数据。假如A在取款事务的过程中,B往该账户转账100,A两次读取的余额发生不一致。
幻读:
A事务读取B事务提交的新增数据,会引发幻读问题。幻读一般发生在计算统计数据的事务中,例如银行系统在同一个事务中两次统计存款账户的总金额,
在两次统计中,刚好新增了一个存款账户,存入了100,这时候两次统计的总金额不一致
事务的七种传播行为:
什么是事务的传播行为:事务传播行为用来描述由某一个事务传播行为修饰的方法被嵌套进另一个方法的时事务如何传播。

下边以银行转账为例:
(Spring的事务有三种实现方式:事务代理工厂bean ,AOP事务 和 注解方式)
事务代理工厂方式:
首先搭建dao层:(两个方法一个转出一个转入)
package cn.affair.dao; public interface IBankDao { public int rollOutMoney(String card,Double oumoney); public int rollInMoney(String card,Double oumoney); }
package cn.affair.dao.impl; import cn.affair.dao.IBankDao; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import javax.annotation.Resource; @Repository("iBankDao") public class IBankDaoImpl implements IBankDao { @Resource private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public int rollOutMoney(String card, Double oumoney) { String sql="update bankcard set bmoney=bmoney-? where bcard=?"; int wout = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, card, oumoney); return wout; } public int rollInMoney(String card, Double oumoney) { String sql="update bankcard set bmoney=bmoney+? where bcard=?"; int win = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, card, oumoney); return win; } }
Service层:(定义为一个方法)
package cn.affair.service; public interface IBankService { public int transfer(String outCard,String inCard,Double money); }
import cn.affair.service.IBankService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import javax.annotation.Resource; @Service("iBankService") public class IBankServiceImpl implements IBankService { @Resource(name = "iBankDao") private IBankDao iBankDao; //@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ ,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public int transfer(String outCard, String inCard, Double money) { int out = iBankDao.rollOutMoney(outCard, money); if(true){ throw new RuntimeException(); } int ins = iBankDao.rollInMoney(inCard, money); return out+ins; } }
然后是application.xml配置文件
<!--扫描注解--> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.affair"/> <!--识别到配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> <tx:annotation-driven/> <!--配置数据源--> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> </bean> <!--配置数据源--> <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--事务管理--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--事务代理工厂bean--> <bean id="transactionProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property> <property name="target" ref="iBankService"></property> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="transfer">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试:
import cn.affair.service.IBankService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BankAffairTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext apct=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); IBankService service = (IBankService) apct.getBean("transactionProxy"); try { service.transfer("411255655897","411255987455", (double) 100); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("11111!"); } }
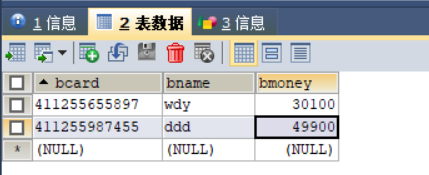
执行后会发现数据库数据已经改变
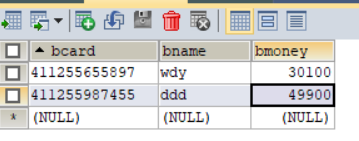
如果出现异常则事务回滚,数据库数据不会被修改:
注:Spring事务不会对所有异常都进行回滚,只会对运行时异常进行回滚!
AOP事务:
<!--AOP事务--> <tx:advice id="transactionAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="trans*" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" propagation="NESTED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="pointuct" expression="execution(* *..service.impl.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="transactionAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointuct"></aop:advisor> </aop:config>
测试:
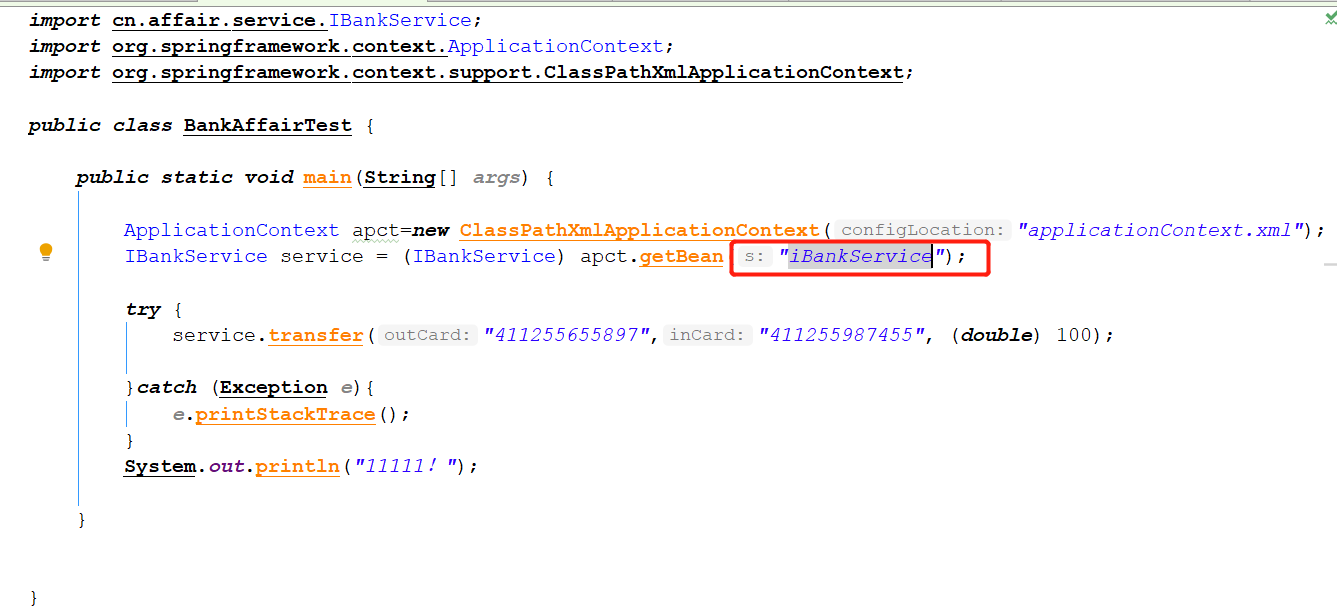
执行结果(自定义了一个异常:程序运行时出现异常,事务回滚,不会修改数据库数据)
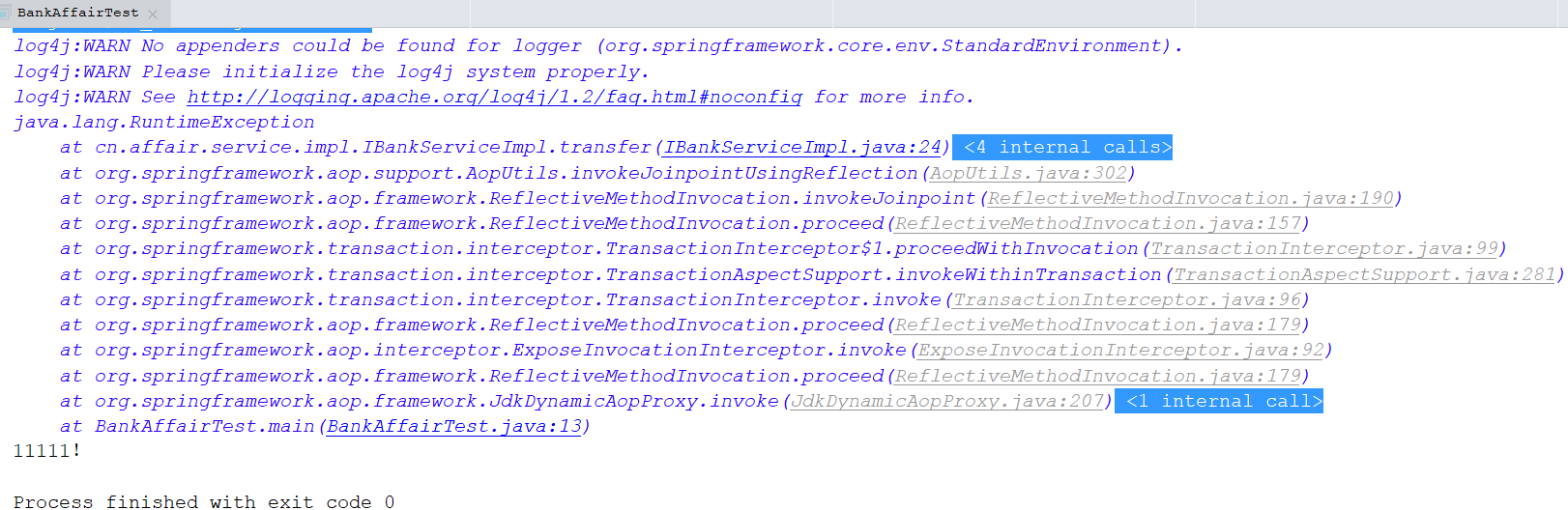
数据库:

、 注解方式就更简单了:

在大配置文件添加如下代码:
<!--支持注解--> <tx:annotation-driven/>
然后进行测试就🆗了!
<测试结果和上次一样,就不写出来了!>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号