django2 多数据配置 sql server 2012+从已有数据库生成model.py
1.配置多数据库(sqlite + sql server 2012)
连接sql server 需要安装 django-pyodbc-azure
pip install django-pyodbc-azure
参考文章: https://blog.csdn.net/zongzhengyingzhe/article/details/80867256
新增 database_router.py
from django.conf import settings
DATABASE_MAPPING = settings.DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING
class DatabaseAppsRouter(object):
"""
A router to control all database operations on models for different
databases.
In case an app is not set in settings.DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING, the router
will fallback to the `default` database.
Settings example:
DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING = {'app1': 'db1', 'app2': 'db2'}
"""
def db_for_read(self, model, **hints):
""""Point all read operations to the specific database."""
print(DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label])
if model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING:
return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label]
return None
def db_for_write(self, model, **hints):
"""Point all write operations to the specific database."""
print(model._meta.app_label+"?")
print(DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label])
if model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING:
return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label]
return None
def allow_relation(self, obj1, obj2, **hints):
"""Allow any relation between apps that use the same database."""
db_obj1 = DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj1._meta.app_label)
db_obj2 = DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj2._meta.app_label)
if db_obj1 and db_obj2:
if db_obj1 == db_obj2:
return True
else:
return False
return None
def allow_syncdb(self, db, model):
"""Make sure that apps only appear in the related database."""
if db in DATABASE_MAPPING.values():
return DATABASE_MAPPING.get(model._meta.app_label) == db
elif model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING:
return False
return None
def allow_migrate(self, db, app_label, model=None, **hints):
"""
Make sure the auth app only appears in the 'auth_db'
database.
"""
if db in DATABASE_MAPPING.values():
return DATABASE_MAPPING.get(app_label) == db
elif app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING:
return False
return None
修改 app>model.py
# This is an auto-generated Django model module.
# You'll have to do the following manually to clean this up:
# * Rearrange models' order
# * Make sure each model has one field with primary_key=True
# * Make sure each ForeignKey has `on_delete` set to the desired behavior.
# * Remove `managed = False` lines if you wish to allow Django to create, modify, and delete the table
# Feel free to rename the models, but don't rename db_table values or field names.
from django.db import models
class AppAuthor(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
class AppBook(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
author_email = models.CharField(max_length=75)
imported = models.BooleanField()
published = models.DateField(blank=True, null=True)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, blank=True, null=True)
user_id = models.IntegerField(blank=True, null=True)
class AppBookCategories(models.Model):
book_id = models.IntegerField()
class AppCategory(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
class AppCoursemanage(models.Model):
uuid = models.CharField(primary_key=True, max_length=22)
add_time = models.DateTimeField()
modified_time = models.DateTimeField()
del_state = models.IntegerField()
remote_id = models.CharField(max_length=30)
status = models.SmallIntegerField()
class DjangoMigrations(models.Model):
app = models.CharField(max_length=255)
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
applied = models.DateTimeField()
修改配置 settings.py
# Database
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/ref/settings/#databases
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}, 'xhydb':
{
'ENGINE': 'sql_server.pyodbc',
'NAME': 'django1', # 数据库的名字
'USER': 'sa', # 登录数据库的用户名
'PASSWORD': '123456', # 登录数据库的密码
'HOST': 'localhost', # 数据库的IP地址
'PORT': '1433', # 数据库的端口
'OPTIONS':
{
'driver': 'SQL Server Native Client 11.0', # 注意,不行就试试11.0
'MARS_Connection': True,
}
}
}
DATABASE_ROUTERS = ['BatchPrinting.database_router.DatabaseAppsRouter'] # 数据库路由
DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING = {
'admin': 'default',
'auth': 'default',
'contenttypes': 'default',
'sessions': 'default',
'django': 'default',
'app': 'xhydb',
}
执行数据库迁移
python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate python manage.py migrate --database=xhydb
Sql server 运行效果
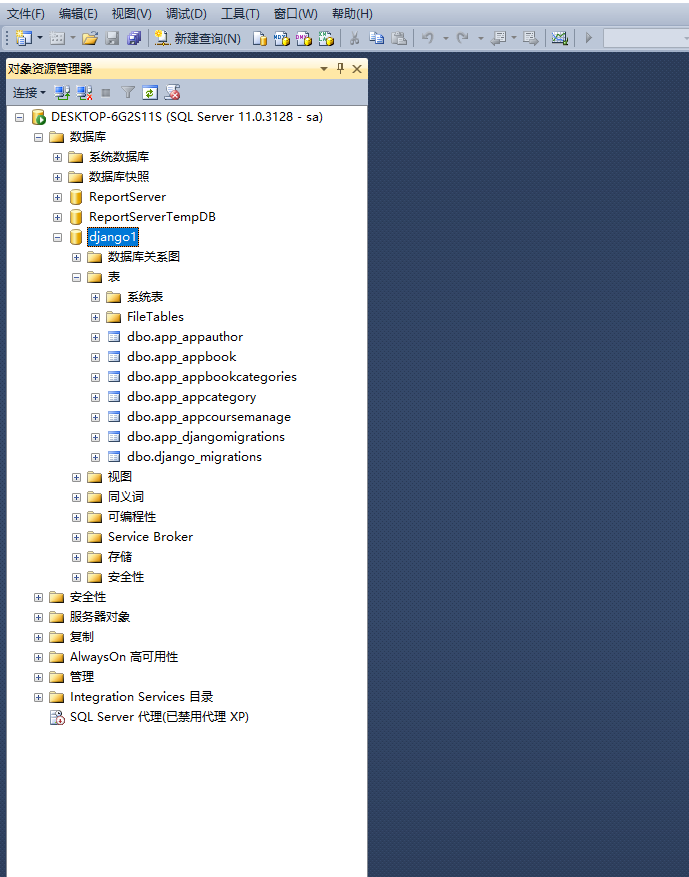
sqlite 效果

2.从现有数据库生成model.py
python manage.py inspectdb --database=xhydb > app/models.py python manage.py inspectdb 表名 > app/models.py



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号