MySQL索引及执行计划
索引及执行计划
什么是索引
类似书的目录

1)索引就好比一本书的目录,它能让你更快的找到自己想要的内容。
2)让获取的数据更有目的性,从而提高数据库检索数据的性能。
注意:给指定的字段,排序,添加目录功能,索引并不是越多越好,也不是每个字段都必须加索引
MySQL中索引的类型
1)BTREE:B+树索引
2)HASH:HASH索引
3)FULLTEXT:全文索引
4)RTREE:R树索引
Btree算法
-
Btree
-
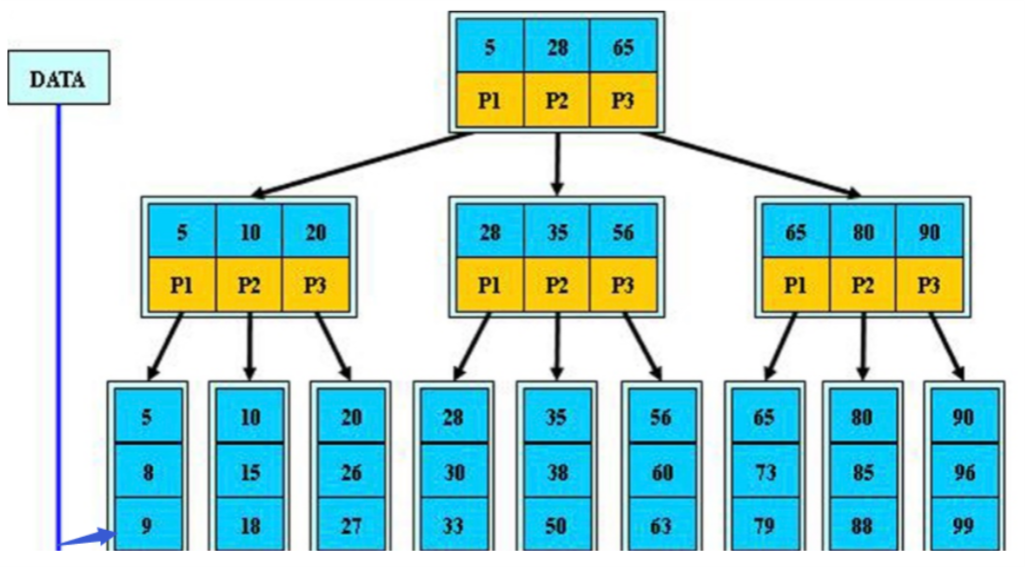
三路Btree
- 根节点
- 枝节点
- 叶子节点
select * from tb1 where id=15; 精确查询:3次IO select * from tb1 where id>10 and id<30; 范围查询:6次 -
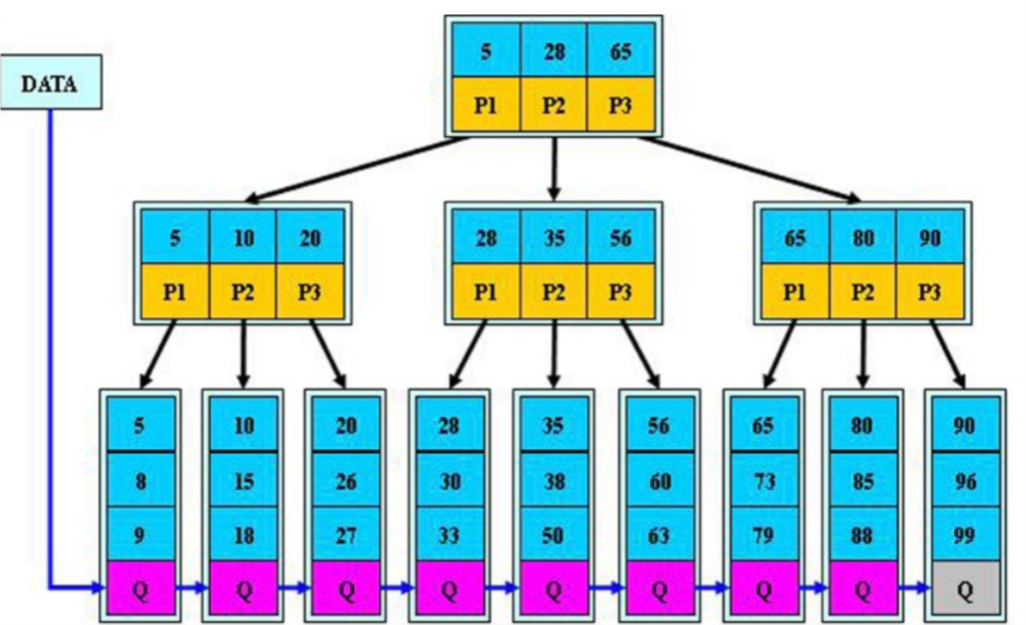
B+tree
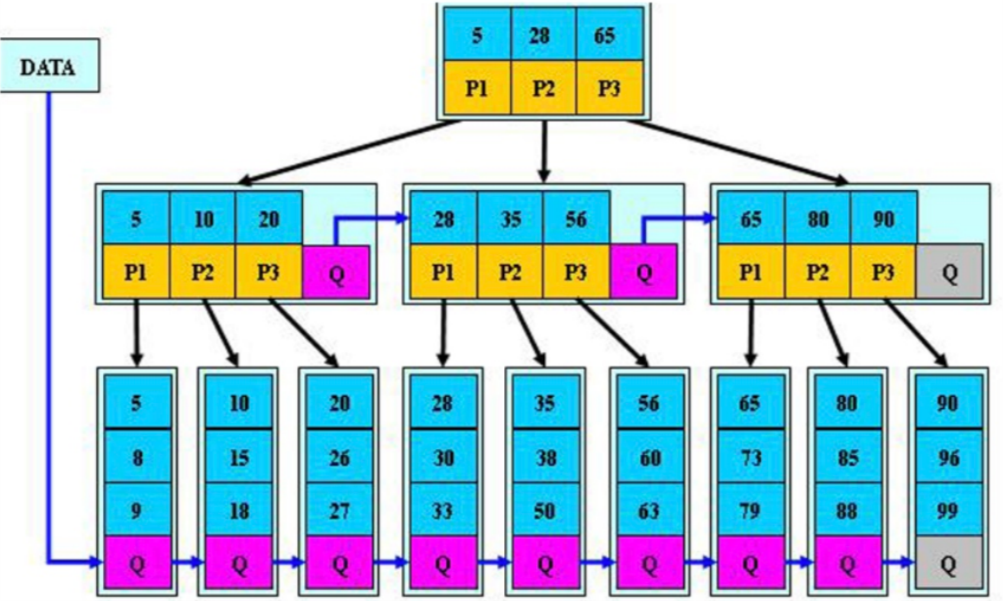
select * from tb1 where id=15; 精确查询:3次
select * from tb1 where id>10 and id<30; 范围查询:4次
# B+tree和Btree比
1.优化了范围查询
2.在叶子节点上添加了相邻的指针
- B*tree(了解即可)
索引管理
索引建立在表的列上(字段)的。 在where后面的列建立索引才会加快查询速度。
索引分类
- 主键索引
- 联合索引
- 唯一索引
- 前缀索引
- 联合索引
- 普通索引
- 前缀索引
- 联合索引
如何创建索引
# 创建普通索引
alter table stu add index 索引名(字段)
# 查看索引
show index from 表名;
desc查看索引
PRI:主键索引
UNI:唯一键索引
MUL:普通索引
# 删除索引
alter table 表名 drop index 索引;
alter table 表名 drop key 索引;
# 添加主键索引
mysql[zls]> create table test(id int,name varchar(10) not null);
mysql[zls]> desc test;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
mysql[zls]> alter table test add primary key(id);
# 删除主键索引
alter table test drop primary key;(主键)
# 添加唯一索引
alter table test add unique key uni_name(name);
mysql[zls]> alter table stu add unique key uni_name(name);
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'wc' for key 'uni_name'
添加唯一键要求:该字段的数据不能有重复的
# 判断是否可以在name字段上创建唯一键
1.先统计该字段总共有多少行
mysql[wc]> select count(字段) from 表名;
+-------------+
| count(name) |
+-------------+
| 6 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.在统计,去重后,该字段有多少行
mysql[zls]> select count(distinct(字段)) from 表名;
+-----------------------+
| count(distinct(name)) |
+-----------------------+
| 3 |
+-----------------------+
如果两个数值一样,则可以创建唯一键索引,如果两个数值不一样,则无法创建唯一键索引(有重复值)
# 删除唯一键索引
alter table test drop index 索引名;
前缀索引
给某一字段数据内容特别长的列,创建前缀索引
# 普通前缀索引的创建
mysql[world]> alter table 表名 add index 索引名(字段(4));
# 唯一索引前缀索引创建
alter table 表名 add unique key uni_name(name(3));
1.避免对大列(数据长的列)建索引
2.如果有,就使用前缀索引
联合索引
将多个字段,做成一个索引
联合索引的查询顺序要和创建时的顺序一致,才可以提高效率
使用场景:婚恋网站
gender,salary,age
# 普通联合索引创建
alter table student add index idx_all(gender,age,name);
# 主键联合索引
alter table student2 add primary key (id,name);
# 唯一主键联合
alter table student2 add unique key uni_all(id,name);
# 索引删除
普通索引
唯一索引
alter table 表名 drop index 索引名;
主键索引
alter table 表名 drop primary key;
alter table 表名 drop primary;
联合索引
idx_all(id,name,age)
alter table 表名 drop index idx_all;
索引,无法直接修改,删除索引后,重新创建。
索引效率查询
# explain(执行计划)
检测一个SQL语句的执行效率,将explain加入在要执行是的SQL语句之前即可
root@localhost:linux50>explain select * from student;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | student | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
查看SQL语句的执行效率,主要看type列
效率:
- 全表扫描
- 索引扫描
# 全表扫描
ALL:企业中绝对不会出现
1.业务确实要获取所有数据
2.不走索引导致的全表扫描
- 没索引
- 索引创建有问题
- 语句有问题
- 索引损坏
# 索引扫描
index:全索引扫描,创建索引的列,全部数据都查询出来了
root@localhost:world>explain select id from city;
range:范围查询,一般来说,一条SQL语句,只要达到range级别,就OK
root@localhost:world>explain select id from city where id>3;
ref:唯一索引的前缀扫描或者唯一索引扫描(精确查询)
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city where CountryCode='CHN';
eq_ref:连表查询,传统连接,join on
const、system:主键精确查询
mysql[world]> explain select * from city where id=10;
null:不进行表的扫描,没有这样的数据
explain select * from city where id>100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000;
# 范围查询优化
mysql[world]> explain select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA';
mysql[world]> explain select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
# 联合查询优化,or精确范围
explain select * from city where countrycode='CHN' union all select * from city wherecountrycode='USA';
索引建立的原则
索引的创建,是为了提示查询的效率,需要知道在哪些字段上创建索引
索引不是每一个字段都要创建,也不是越多越好
根据用户的喜好,被查询的越多的字段,要创建索引
1.索引首要选择,唯一键索引
判断是否可以创建唯一键索引
- select count(需要创建唯一键索引的字段) from 表;
- select count(distinct(需要创建唯一键索引的字段)) from 表;
2.其次,如果无法创建唯一索引,重复值比较多,创建联合索引
- 经常需要ORDER BY、GROUP BY、DISTINCT和UNION等操作的字段,排序操作会浪费很多时间。 如果为其建立索引,可以有效地避免排序操作。
3.为经常作为查询条件的字段,创建普通索引
- 经常查询
- 列值重复值少的
4.尽量能使用前缀索引,就用前缀索引
- 减少创建索引的排序时间
- 增加查询的效率
5.索引的数量不是越多越好
- 索引的数目不是越多越好。每个索引都需要占用磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。 修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦。越多的索引,会使更新表变得很浪费时间。
6.删除不再使用或者很少使用的索引
- 表中的数据被大量更新,或者数据的使用方式被改变后,原有的一些索引可能不再需要。数据库管理 员应当定期找出这些索引,将它们删除,从而减少索引对更新操作的影响。
不走索引的原因
数据库查询效率低,导致网站加载速度慢,如何解决?
在企业中,开启MySQL的慢日志(慢查询日志)
查看,哪一条SQL语句执行的速度慢,取出SQL语句,使用explain查看该SQL语句是否走索引
没有走索引
# 没有走索引
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city;
全表扫描,使用select * 查询没有加附加条件
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city where population>50 limit 20;
查询结果集是原表中的大部分数据,应该是25%以上
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city where population>50 limit 20;
条件本身做运算
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city where id-1=9;
不能使用字段做计算
隐式转换导致索引失效
root@localhost:world>create table test1(id int,name varchar(10),phone char(11));
root@localhost:world>alter table test1 add index idx_phone(phone);
# 走索引
explain select * from test1 where phone='133';
# 不走索引
explain select * from test1 where phone=133;
# 优化方案
1.查看字段的创建数据类型
2.告诉开发,在查询的时候,一定要按照字段的数据类型来查询
3.如果是字符串,就加引号
4.如果是整形,就不加引号
不等于 或者 not in
使用不等于或者not in 会影响到结果集
优化方案
- 使用limit优化
- 单独的>,< in 有可能走,也有可能不走,和结果集有关,尽量结合业务添加limit、or或in尽量改成union
使用like模糊查询%在前面
root@localhost:world>explain select * from city where CountryCode like '%HN';
优化方案
- 尽量不要使用%在前面的SQL语句,尽量将%放在后面
- 那就不要使用mysql,使用搜索引擎式数据库:elasticsearch
使用联合索引查数据时
不走索引,要根据联合索引创建的顺序来查询数据库
创建数据:ABC
查询顺序:ABC AB AC BC
索引损坏或失效
删了重建





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了