线程异步的意义和使用
public class ThreadImpl extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>123");
}
}
public class MyThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadImpl thread=new ThreadImpl();
thread.start();
System.out.println("456");
}
}
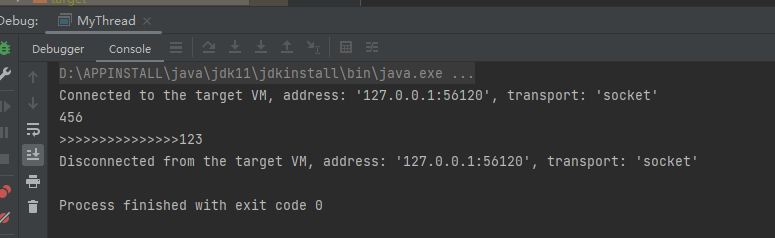
主线程:456先输出 线程ThreadImpl后输出123,可以看出ThreadImpl并没有阻塞主线程,这样就主线程可以快速执行,子线程继续执行自己的任务。
public class MyThread implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "123";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread call = new MyThread();
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(call);
Object o ;
Thread thread=new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
try {
o = futureTask.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("0000:"+o);
System.out.println("123456");
}
}
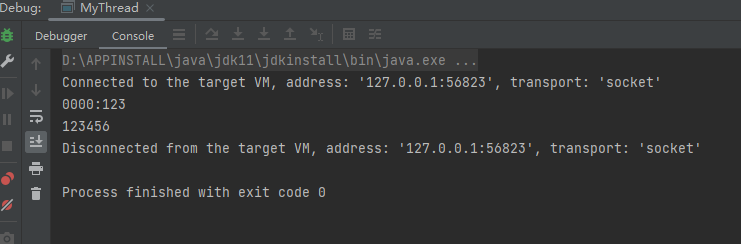
FutureTask具有阻塞作用,上面等两秒,主线程也不会先执行,必须等 futureTask.get()执行后输出123,主线程才输出12346
一点点学习,一丝丝进步。不懈怠,才不会被时代淘汰



