线程《二:线程的状态---生命六周期》
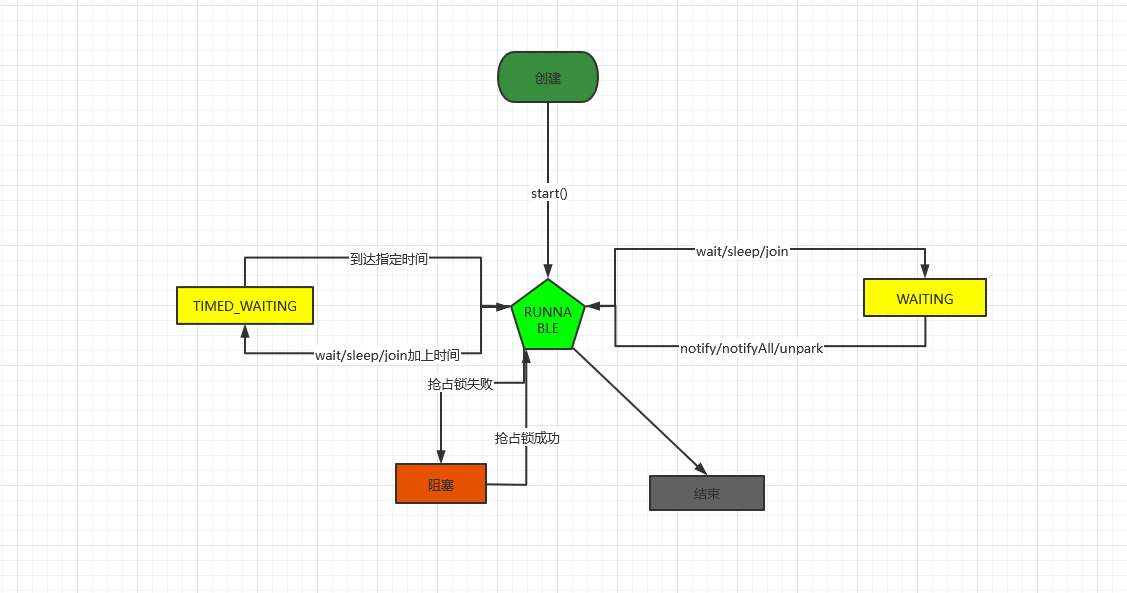
1创建,2就绪,3终止
public class ThreadState { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread myThread=new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("myThread"); }); //创建 NEW System.out.println(myThread.getState()); myThread.start(); //就绪 RUNNABLE System.out.println(myThread.getState()); Thread.sleep(1000); //终止 TERMINATED System.out.println(myThread.getState()); } }

4等待:使用jps查看当前类运行的进程,jstack根据进程查看线程的状态
public class ThreadStateWait {
public static Object obj=new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("我是one线程");
try {
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
},"one").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("我是two线程");
try {
Thread.sleep(20000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
},"two").start();
}
}
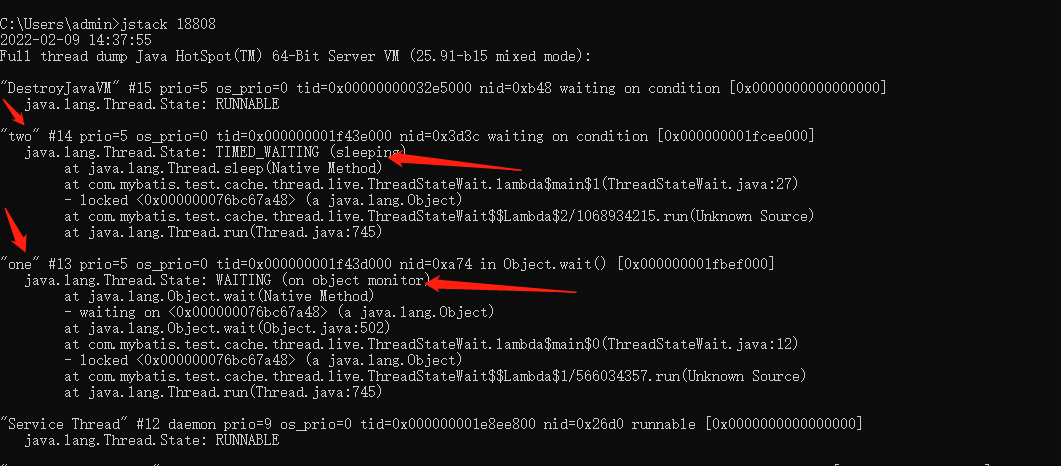
可以看到线程two是TIMED_WAITING, one是WAITING, TIMED_WAITING和WAITING状态一样,只是有一个等待时间, 一般调用如下方法时:sleep(),wait(),join(),LockSupport.parkNanos(),LockSupport.parkUntil(), 而且方法带上时间则线程会出现这个状态
5,阻塞,使用同一把锁,线程3先抢占运行,线程4阻塞
public class ThreadBlock {
static class BlockState extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (BlockState.class){
for (; ; ) {
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new BlockState(),"3").start();
new Thread(new BlockState(),"4").start();
}
}
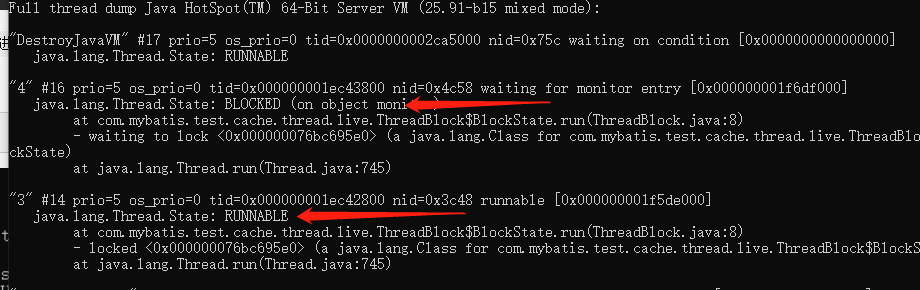
1.interrupt:给线程个中断标识, 2.isInterrupted:如果线程有interrupt时返回true表示当前线程被中断过 3.interrupted:线程如果被中断过则返回true,不过会给线程进行复位,再次调用是就返回true
//实现Runnable接口
public class MyThreadRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//非阻塞状态下中断标记
try {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();//做一个中断标记的处理
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
System.out.println("线程被中true断过:" + interrupted);
// Thread.sleep(2000);
// Thread.currentThread().wait(2000);
Thread.currentThread().join(2000);
System.out.println("线程被中断过》true复位:" + Thread.currentThread().interrupted());
System.out.println("线程是否被中断过已经false复位:" + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println("线程再次false复位:" + Thread.currentThread().interrupted());
} catch (Exception e) {
boolean isIn = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();//这里输出结果为false,这就说明当我们一个休眠/join的线程被中断后,抛出异常的同时也会对线程的中断标记进行复位,退出阻塞状态,且中断标志被清除,重新设置为false,所以此处的isIn为false
System.out.println("异常复位:"+isIn);
System.out.println("线程被中断过》false复位:" + Thread.currentThread().interrupted());
return;
}
}
}
currentThread()和this的区别指代线程

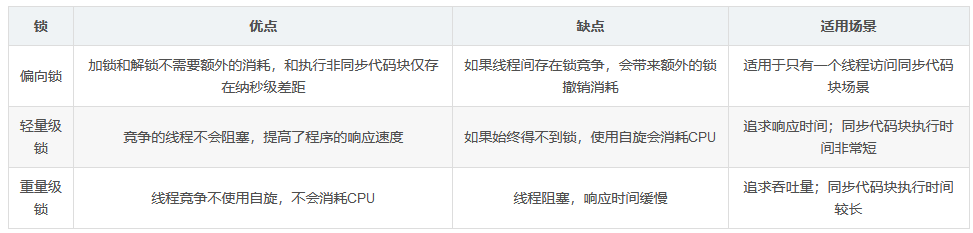
sychronized锁:偏向锁升级为轻量锁
下面BiasedLockingStartUpDelay=4000可以看出默认延迟四秒后启用偏向锁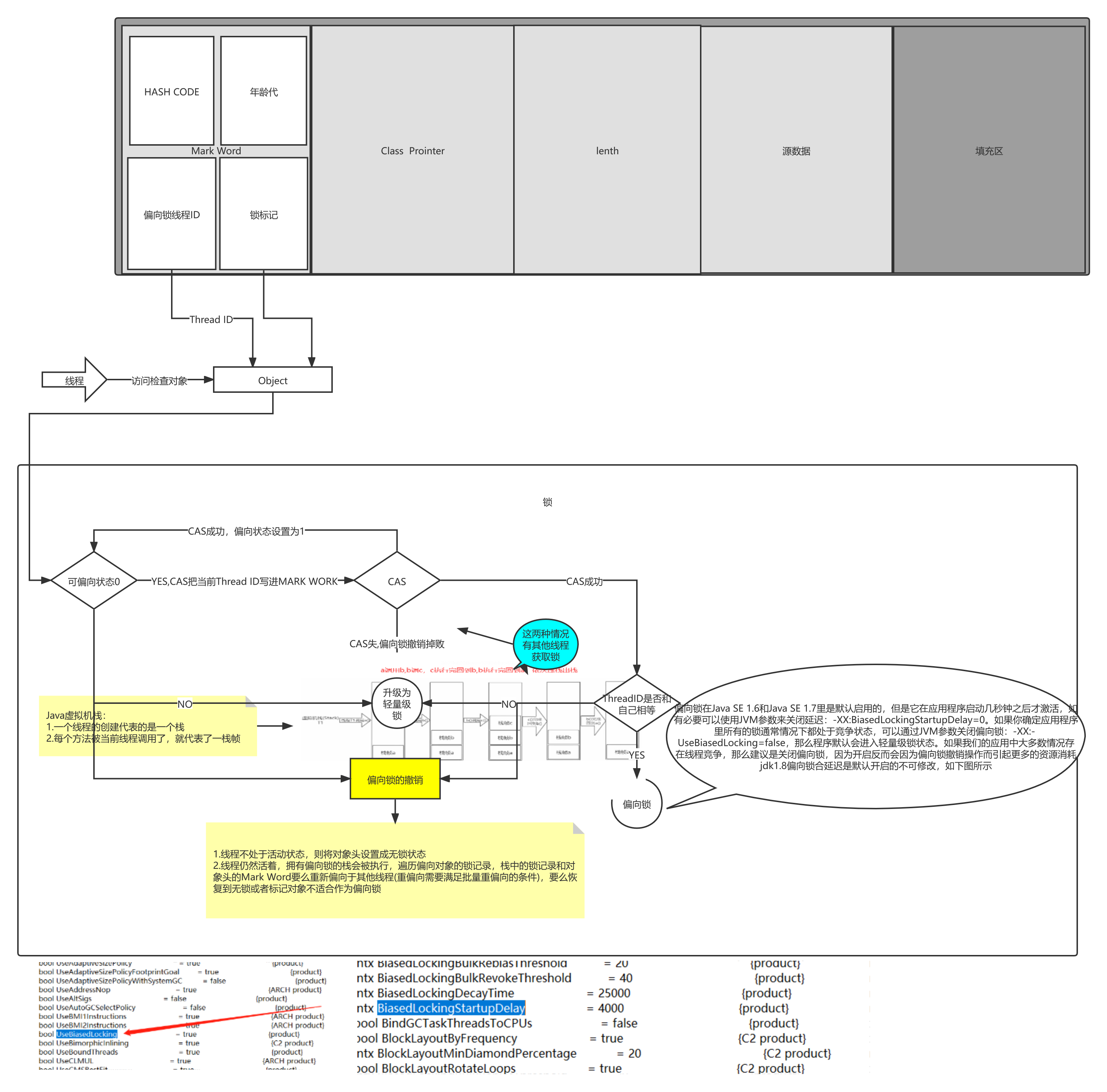
轻量锁升级重量级锁

一点点学习,一丝丝进步。不懈怠,才不会被时代淘汰



