继承
一.子类不继承父类构造函数,析构函数,默认私有继承或protected
二.using声明可在子类把父类成员改为私有
1 class B 2 { 3 public: 4 void set(){} 5 }; 6 7 class C: public B 8 { 9 private: 10 using B::set; 11 };
三.派生类成员与父类成员名字相同,会发生名字隐藏
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class B 6 { 7 public: 8 void h(float x){} 9 }; 10 11 class C: public B 12 { 13 public: 14 void h(string s){} 15 }; 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 C c; 20 c.h("abc");//ok 21 c.h(1.7);//error 22 c.B::h(1.7);//ok 23 return 0; 24 }
四.派生类可对从基类继承来的保护成员进行访问,也就是说保护成员在派生类中是可见的
派生类不能访问一个基类对象的保护乘员,因为基类对象属于基类,不属于派生类
派生类中的派生类可访问基类的保护乘员,因为派生类对象属于派生类
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class B 6 { 7 protected: 8 int get_W() const { return 0; } 9 }; 10 11 class C: public B 12 { 13 public: 14 int get_V()const { return get_W(); } 15 void base_W(const B &b) const { cout << b.get_W() << endl; }//error 16 void p(C &c)const { cout << c.get_W() << endl; } // OK 17 18 }; 19 20 int main() 21 { 22 C c; 23 c.getW(); //error, protected 24 return 0; 25 }
应避免将数据成员设置成protected,而应采用私有或者相应保护类型访问函数
五.创建派生类时,父类默构自动调用。父类若有带参构造,则必须有自定义默构,除非显示调用基类带参构造。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Base 6 { 7 public: 8 Base(int m, int n) 9 { 10 x = m; 11 y = n; 12 } 13 private: 14 int x, y; 15 }; 16 17 class Derived: public Base 18 { 19 public: 20 Derived(int m, int n, int k):Base(m, n) 21 { 22 z = k; 23 } 24 private: 25 int z; 26 }; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 Derived d(1, 2, 3); 31 return 0; 32 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Base 6 { 7 public: 8 Base(int m, int n) 9 { 10 x = m; 11 y = n; 12 } 13 private: 14 int x, y; 15 }; 16 17 class Derived: public Base 18 { 19 public: 20 Derived(int k) 21 { 22 z = k; 23 } 24 private: 25 int z; 26 }; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 Derived d(3);//error, Base没有合适的默认构造函数可用 31 return 0; 32 }
1.最先调用基类的构造函数,对基类数据成员初始化顺序取决于被继承时的说明顺序;
2.再调用数据成员是类对象的构造函数,顺序按类中定义的先后顺序;
3.最后执行派生类构造函数;
4.析构函数的调用与构造函数正好相反,由于每个类至多只有一个析构函数,调用时不会产生二义性。
六.多重继承机制下的命名冲突
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class A 6 { 7 public: 8 void f(); 9 }; 10 11 class B 12 { 13 public: 14 void f(); 15 void g(); 16 }; 17 18 class C: public A, public B 19 { 20 public: 21 void h(); 22 void g(); 23 }; 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 C c; 28 c.g();//c中g(),B中被重写 29 c.f();//error,无法确定,若B:public A则c.f()不会产生二义性 30 31 c.B::g(); 32 c.A::f(); 33 c.B::f(); 34 return 0; 35 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class B 6 { 7 public: 8 int b; 9 }; 10 11 class B1:public B 12 {}; 13 14 class B2:public B 15 {}; 16 17 class C: public B1, public B2 18 {}; 19 20 int main() 21 { 22 C c; 23 c.b;//error,b不明确 24 c.B::b;//B不明确,在VS2015中默认为B1中的B的b 25 /* 26 C->B1->B->b 27 ->B2->B->b 28 基类对象B在派生类C中存储2份 29 */ 30 return 0; 31 }
在多条继承路径上有一个公共基类,希望只存储一个公共基类时,可利用虚基类。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class B 6 { 7 public: 8 int b; 9 }; 10 11 class B1: virtual public B 12 { 13 public: 14 int b1; 15 }; 16 17 class B2: virtual public B 18 { 19 public: 20 int b2; 21 }; 22 23 class C: public B1, public B2 24 { 25 public: 26 int c; 27 }; 28 29 int main() 30 { 31 C c; 32 c.B1::b = 1; 33 c.B2::b = 2; 34 cout << c.B1::b << endl; // 2 没有同时2个virtual则为1,存储了2个B 35 cout << c.B2::b << endl; // 2 36 /* 37 B1 38 C-> ->B 39 B2 40 C中b值只存储了一份 41 */ 42 return 0; 43 }
虚基类的构造函数先于非虚基类执行
虚基类由最派生类(最后一个派生类)调用构造函数初始化
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class A 6 { 7 public: 8 A() 9 { 10 cout << "A" << endl; 11 } 12 ~A() 13 { 14 cout << "~A" << endl; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 class B: public A 19 { 20 public: 21 B() 22 { 23 cout << "B" << endl; 24 } 25 ~B() 26 { 27 cout << "~B" << endl; 28 } 29 int b; 30 }; 31 32 class B3 33 { 34 public: 35 B3() 36 { 37 cout << "B3" << endl; 38 } 39 ~B3() 40 { 41 cout << "~B3" << endl; 42 } 43 int b3; 44 }; 45 46 class B1: public B3, virtual public B 47 { 48 public: 49 B1() 50 { 51 cout << "B1" << endl; 52 } 53 ~B1() 54 { 55 cout << "~B1" << endl; 56 } 57 int b1; 58 }; 59 60 class B2: virtual public B 61 { 62 public: 63 B2() 64 { 65 cout << "B2" << endl; 66 } 67 ~B2() 68 { 69 cout << "~B2" << endl; 70 } 71 int b2; 72 }; 73 74 class D 75 { 76 public: 77 D() 78 { 79 cout << "D" << endl; 80 } 81 ~D() 82 { 83 cout << "~D" << endl; 84 } 85 int c; 86 }; 87 88 89 class E 90 { 91 public: 92 E() 93 { 94 cout << "E" << endl; 95 } 96 ~E() 97 { 98 cout << "~E" << endl; 99 } 100 int c; 101 }; 102 103 class C: public B1, public B2 104 { 105 public: 106 C() 107 { 108 cout << "C" << endl; 109 } 110 ~C() 111 { 112 cout << "~C" << endl; 113 } 114 int c; 115 D d; E e; 116 }; 117 118 int main() 119 { 120 C c; 121 return 0; 122 }
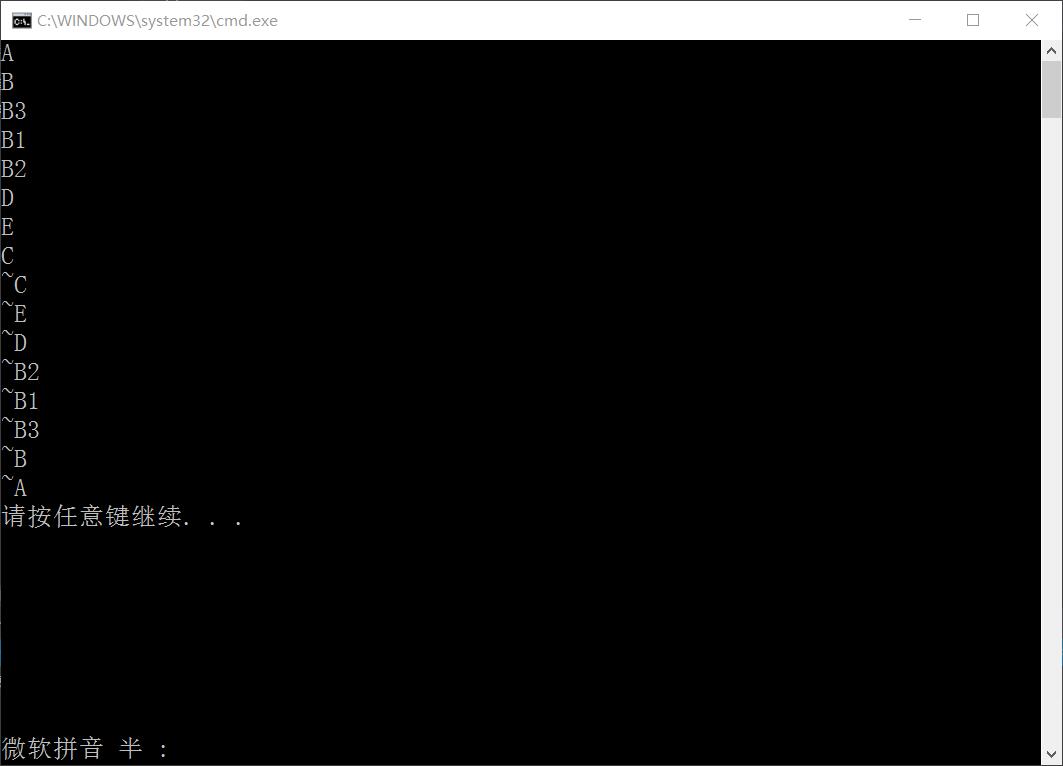
七.继承方式
1.公有继承:基类成员公有和保护在派生类中保持原有访问属性,私有成员仍为基类私有;
2.私有继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成私有成员,私有成员仍为基类私有;
3.受保护继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成保护成员,私有成员仍为基类私有。保护成员:不能被外界访问,但可被派生类成员访问
八.对基类对象操作的函数,可以对子类的对象进行操作,不可逆
1.派生类对象可以赋值给基类:Base b; Derived d; b = d;
2.Derived d; Base &b = d;初始化基类引用
3.子类地址赋值给基类指针Derived d; Base *b = &d;
必须是public继承关系,protected和private不成立


