python内置模块
1、系统的内置模块
sys
hashlib
hmac
base64
time
datetime
sys
hashlib
hmac
base64
time
datetime
sys模块:
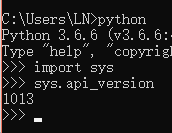
|-- sys.argv() # 在Python脚本传参使用(很重要)
argv代表多个参数
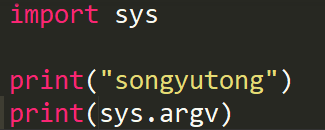
输出名字,格式为列表,也会把传的数据封装给它。可以完善脚本
|-- sys.exit() # 系统退出 系统立马终结,相当于右上点×关掉系统
|-- sys.getdefaultencoding() # 获取系统默认编码
|-- getfilesystemencoding() # 获取文件编码
两者编码最好保存一致,小心乱码
|-- getrecursionlimit() # 获取系统默认递归的最大层数
可以改(但不建议)
|-- setrecursionlimit(num) # 设置递归的最大层数
|-- getrefcount() # 获取对象的引用计数的数量
与垃圾回收机制有关,堆中的内存在有数据指向他得时候,指向就成为引用计数。
hashlib:内置模块之一,主要用于加密,用算法将特定算法混淆
加密,散列加密(hash加密):银行密码
加密是否可逆:
|-- 可逆加密
根据加密和解密的秘钥是否是同一个,比如压缩包。能还原回去
|-- 对称加密
DES
|-- 非对称加密
RSA
|-- 不可逆加密:值唯一
hash是典型的不可逆加密
MD5、shal256
加密,散列加密(hash加密):银行密码
加密是否可逆:
|-- 可逆加密
根据加密和解密的秘钥是否是同一个,比如压缩包。能还原回去
|-- 对称加密
DES
|-- 非对称加密
RSA
|-- 不可逆加密:值唯一
hash是典型的不可逆加密
MD5、shal256
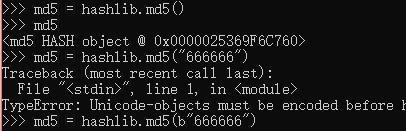
encode(utf-8)把字符串转换为字节
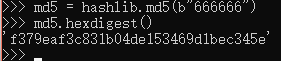
但是其实并不安全。
import hashlib
md5 = hashlib.md5("需要加密的数据".encode("utf-8"))
base64模块
|-- b64encode() 编码 Python encode() 方法以 encoding 指定的编码格式编码字符串。errors参数可以指定不同的错误处理方案。
str = "this is string example....wow!!!";
print "Encoded String: " + str.encode('base64','strict')
print "Encoded String: " + str.encode('base64','strict')
|-- b64decode() 解码 Python decode() 方法以 encoding 指定的编码格式解码字符串。默认编码为字符串编码。
str = "this is string example....wow!!!";
str = str.encode('base64','strict');
print "Encoded String: " + str;
print "Decoded String: " + str.decode('base64','strict')
str = str.encode('base64','strict');
print "Encoded String: " + str;
print "Decoded String: " + str.decode('base64','strict')
主要做编码转换,把图片转换成base64
time模块:
|-- asctime() # 获取系统当前时间
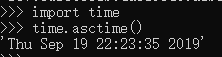
美国格式,我们在生活中用的不多
|-- ctime() # 获取系统当前时间

会得到一个时间戳
|-- time() # 获取当前的时间戳
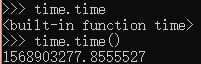
|-- localtime() # 返回当前时间,以类似于元组的对象
t = time.localtime()
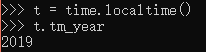
print("当前时间是%s-%s-%s %s:%s:%s" %(t.tm_year, t.tm_mon, t.tm_mday, t.tm_hour, t.tm_min, t.tm_sec))
|-- time.strftime() # 将时间对象格式化成字符串
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
|-- time.strptime() # 时间字符串转换为时间对象
time.strptime('2019/09/18 21:02:44', "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
|-- time.strptime() # 时间字符串转换为时间对象
time.strptime('2019/09/18 21:02:44', "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")





