【大数据】复合数据类型,英文词频统计
1.列表,元组,字典,集合分别如何增删改查及遍历。
(1)列表
print("增") # append:末尾添加 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.append('fellow') print(s) # insert:指定位置添加 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.insert(2, 'fellow') print(s) # extend:分解在末尾添加 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.extend('fellow') print(s) print("删") # pop:指定位置删除 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.pop(1) print(s) # remove:删除指定元素 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.remove('there') print(s) # clear:清空列表元素 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s.clear() print(s) # del:删除列表 或切片删除 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] del s[0:2] print(s) print("改") # 元素赋值 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s[2] = 'fellow' print(s) # 分片赋值 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] s[0:2] = 'fellow' print(s) print("查") # 下标取值 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] print(s[1]) print("遍历") # 使用for循环 s = ['there', 'you', 'are'] num = 1 for i in s: print("列表的第%d的值:"%(num),i) num += 1
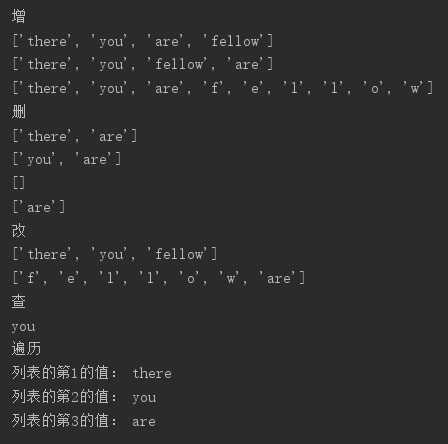
(2)元组
tr=['30','50'] tr2=['20','30']
del tr #删除整个元组
tr3=tr+tr2 #把两个元组组合在一起,结果为tr3=['30','50','20','30']
printf(tr[0]) #查找元组中的第一个元素
for i in range(len(tr)): printf(tr[i]) #遍历
(3)字典
d={'a':10,'b':20,'c':30}
d['a']=11 #修改键a 的值
del d['a'] #删除键a
a=d['a'] #查看键a的值
d.clear() #删除字典中的所有条目
str(d) #输出字典
for key in d:printf(d[key]) #遍历
(4)集合
a=set('a')
a.add('b') #增加元素
a.remove('b') 或者 a.discard('b') #删除元素
a.pop() #随机删除元素
2.总结列表,元组,字典,集合的联系与区别。参考以下几个方面:
- 括号
- 有序无序
- 可变不可变
- 重复不可重复
- 存储与查找方式
(1)列表是最常用的Python数据类型,它可以作为一个方括号[]内的逗号分隔值出现。列表的数据项不需要具有相同的类型。列表是有序、可重复的,可以任意修改。
(2)元组也是存一组数据,只是一旦创建,便不能修改,所以又叫只读列表。元组创建很简单,只需要在括号()中添加元素,并使用逗号隔开即可。只包含一个元素时,需要在元素后面加个逗号。元组也是有序、可重复的。
(3)字典是另一种可变容器模型,且可存储任意类型对象。字典的每个键值对()用冒号(:)分割,每个对之间用逗号(,)分割,整个字典包括在花括号{}中。键必须是唯一的,但值则不必。值可以取任何数据类型,但键必须是不可变的,如字符串,数字或元组。字典是无序、不可重复的,通过关键字索引。
(4)集合是一个无序的,不重复的数据组合。集合可以使用花括号 { } 或者 set() 函数创建集合,注意:创建一个空集合必须用 set() 而不是 { },因为 { } 是用来创建一个空字典。集合可以改变。不能通过索引进行访问。
3.词频统计
-
1.下载一长篇小说,存成utf-8编码的文本文件 file
2.通过文件读取字符串 str
3.对文本进行预处理
4.分解提取单词 list
5.单词计数字典 set , dict
6.按词频排序 list.sort(key=lambda),turple
7.排除语法型词汇,代词、冠词、连词等无语义词
- 自定义停用词表
- 或用stops.txt
8.输出TOP(20)
- 9.可视化:词云
排序好的单词列表word保存成csv文件
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data=word).to_csv('big.csv',encoding='utf-8')
线上工具生成词云:
https://wordart.com/create
#打开文件 f = open(r'Crimes and Punishments.txt', encoding='utf8') #读取内容 text = f.read() f.close() #文本预处理 text = text.lower() print(text) sep = "~`*()!<>?,./;'\:[]{}-=_+" for s in sep: text = text.replace(s, ' ') #分解提取单词 textList = text.split() #排除常用词 stop = {'a','the','and','i','you','in','but','not','with','by','its','for','of','an','to','my','myself','we','our','ours','ourelves','about','no','nor'} textSet = set(textList) stop = set(stop) textSet = textSet - stop print(textSet) #单词计数 counts = {} print(len(textList)) for i in textSet: counts[i] = textList.count(i) print(counts) print(counts.items()) i = list(counts.items()) #词频排序 i.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True) print(i) #前20 for q in range(20): print(i[q]) #保存为csv import pandas as pd pd.DataFrame(data=i).to_csv("text.csv", encoding='utf-8')
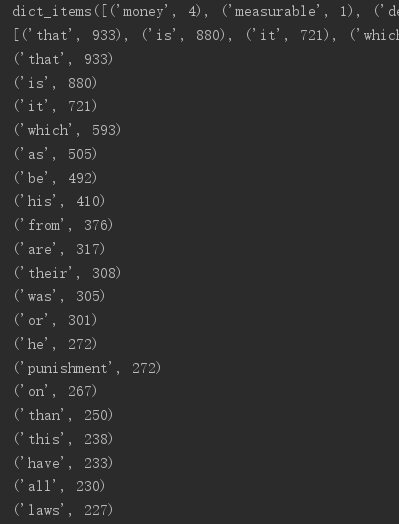
pandas包一直导入不成功,弄了真的很久






