设计模式五: 原型模式(Prototype)
简介
原型模式是属于创建型模式的一种,是通过拷贝原型对象来创建新的对象.
万能的Java超类Object提供了clone()方法来实现对象的拷贝.
可以在以下场景中使用原型模式:
- 构造函数创建对象成本太大(性能或安全成本)
- 要保存对象的状态, 且状态变化较小, 不会过多占用内存时(状态变化较大的使用状态模式会更合适)
意图
使用原型实例指定要创建的对象类型,并通过拷贝这个原型来创建新对象。
类图
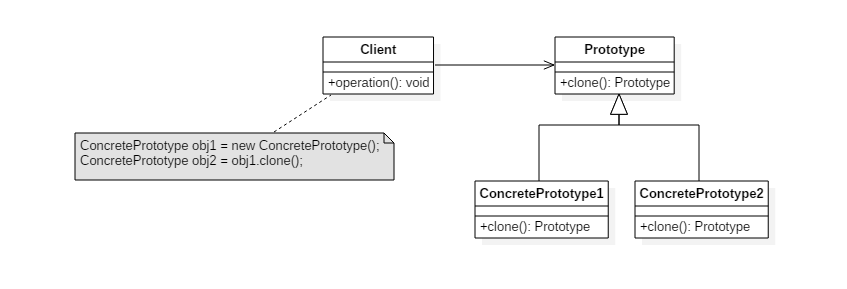
实现
一. 浅拷贝和深拷贝的概念
Object.clone()方法实现的是对象的浅拷贝, 所谓浅拷贝就是当对象中有复杂引用类型的域变量时, 只拷贝该域变量的引用而不是内容, 当有任一方法修改域变量的状态时会同时影响原型对象及拷贝对象, 实际上他们共用了同一个堆内存. 深拷贝创建的对象即是对原对象的完全拷贝,对任一对象的操作不会影响其他对象的状态.
java中提供了Cloneable接口, 约定实现接口Cloneable且重写Object.clone()方法的类可以用来拷贝自身. Cloneable是一个标记接口, 其中没有定义任何方法.
二. 下面的代码演示了使用clone()方法实现的深拷贝,这种方式更适合用于比较简单的对象,否则clone()方法的实现可能会变得异常复杂.
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CarProperty implements Cloneable {
private String power;
private double maxSpeed;
private double oilPerKm;
public Object clone(){
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Car implements Cloneable {
private String brand;
private double price;
private CarProperty carProperty;
/**
* 深拷贝在此实现,对于复杂的应用类型, 这里的代码可能会相当复杂,如果类有修改(新增成员变量等),这里也需要相应修改
* @return
*/
public Object clone(){
Object car = null;
try {
car = super.clone();
CarProperty carPropertyClone = (CarProperty)this.getCarProperty().clone();
((Car)car).setCarProperty(carPropertyClone);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return car;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CarProperty carProperty = new CarProperty("8匹",250,30);
Car car= new Car("BMW",200,carProperty);
Car copy = (Car) car.clone();
System.out.println("copy最大速度为: "+copy.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
System.out.println("原型最大速度为: "+car.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
car.getCarProperty().setMaxSpeed(360);
System.out.println("copy最大速度为: "+copy.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
System.out.println("原型最大速度为: "+car.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
}
}
三. 深拷贝的其他实现方式: 除了上面的方法,还可以使用反射机制创建对象的深拷贝, 另外一种更简单的方式是使用序列化;
下面的代码使用序列化方式实现对象的深拷贝,需实现Serializable接口.
import java.io.*;
public class DeepCloneBase implements Serializable {
public Object deepClone() {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = null;
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
try {
byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(this);
byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
return objectInputStream.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
objectOutputStream.close();
byteArrayInputStream.close();
objectInputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MyCar extends DeepCloneBase {
private String brand;
private double price;
private CarProperty carProperty;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 注意CarProperty也需要实现Serializable接口,代码不再单独列出
CarProperty carProperty = new CarProperty("8匹",250,30);
MyCar car= new MyCar("BMW",200,carProperty);
MyCar copy = (MyCar)car.deepClone();
if (copy!=null){
System.out.println("copy最大速度为: "+copy.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
System.out.println("原型最大速度为: "+car.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
car.getCarProperty().setMaxSpeed(360);
System.out.println("copy最大速度为: "+copy.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
System.out.println("原型最大速度为: "+car.getCarProperty().getMaxSpeed());
}else{
System.out.println("对象没拷贝成功....");
}
}
}
总结
优点: 1. 如果对象创建比较复杂, 可以简化创建过程, 提高效率;2. 可以保留对象状态;
缺点: 对于clone()方式,如果类有修改则需要修改clone()的实现,不符合开闭原则; 复杂对象的clone逻辑可能较复杂;

