C#委托和事件
委托
委托与事件,经常拿来就用,往往忘记其实现原理,对其使用方式也越来越局限。周家安老师在《C# 6.0 学习笔记》中对委托和事件的讲解,深入浅出,清晰明了,故特意摘抄一篇随笔,勤看勤思。
首先,委托是一种形式上与方法签名相似的类型。
定义一个委托:
public delegate void DoSome(string msg);
使用关键字 delegate, 类型名称为 DoSome(string msg).
创建一个DoSome(string msg)委托类型对象,并实例化。
1 static void TestDo(string str) 2 { 3 // ToDo 4 } 5 6 7 DoSome d1 = new DoSome(TestDo); 8 9 10 // 或者 11 12 DoSome d2; 13 14 d2 = TestDo;
委托列表
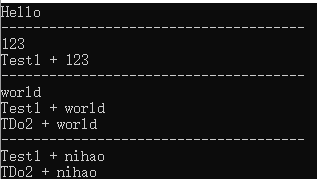
1 public delegate void DoSome(string msg); 2 static void Main(string[] args) 3 { 4 DoSome d = new DoSome(TestDo); 5 d("Hello"); 6 Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------"); 7 d += new DoSome(Test1); 8 d("123"); 9 Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------"); 10 d += TDo2; 11 d("world"); 12 Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------"); 13 d -= TestDo; 14 d("nihao"); 15 } 16 17 static void TestDo(string str) 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine(str); 20 } 21 22 static void Test1(string str) 23 { 24 Console.WriteLine("Test1 + " + str); 25 } 26 static void TDo2(string str) 27 { 28 Console.WriteLine("TDo2 + " + str); 29 }
输出:
事件
事件自身就是委托类型。
1 class MyApp 2 { 3 public delegate void SpaceKeyPressedEventHandler(); 4 5 // 声明事件 6 public event SpaceKeyPressedEventHandler SpaceKeyPressed; 7 8 // 通过该方法引发事件 9 protected virtual void OnSpaceKeyPressed() 10 { 11 12 if (this.SpaceKeyPressed != null) 13 { 14 // 将事件分发 15 SpaceKeyPressed(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 // 启动事件监听的接口 20 public void StartRun() 21 { 22 // 监听事件 23 while (true) 24 { 25 ConsoleKeyInfo keyinfo = Console.ReadKey(); 26 if (keyinfo.Key == ConsoleKey.Spacebar) 27 { 28 // 引发事件 29 OnSpaceKeyPressed(); 30 } 31 32 if (keyinfo.Key == ConsoleKey.Escape) 33 { 34 // 跳出循环 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 class Program 42 { 43 44 static void Main(string[] args) 45 { 46 MyApp app = new MyApp(); 47 // 订阅事件,指定处理事件的方法 48 app.SpaceKeyPressed += app_SpaceKeyPressed; 49 app.SpaceKeyPressed += app_SecondEventHandler; 50 51 // 启动事件监听 52 app.StartRun(); 53 54 } 55 56 // 事件处理1 57 private static void app_SpaceKeyPressed() 58 { 59 Console.WriteLine("{0} 按下空格键。", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString()); 60 } 61 // 事件处理2 62 private static void app_SecondEventHandler() 63 { 64 Console.WriteLine("事件的第二个处理方法。"); 65 } 66 67 }
通常,作为事件委托,有两个参数,一个是Object类型,表示引发事件的对象,即是谁引发了事件的,多数情况下在调用事件时是把类的当前实例引用(this)传递过去。另一个参数是从System.EventArgs派省的类的实例。这是一个标准的事件处理程序的签名,为了规范事件的处理,.NET类库已经定义好一个System.EventHandler委托,用于声明事件。它的原型如下:
1 public delegate void EventHandler(object sender, EventArgs e);
引发事件的对象实例将传递给sender参数,而与事件相关的数据则传递给e参数。如果不需要传递过多的数据,可以通过System.EventArgs.Empty静态成员返回一个空的EventArgs对象类传递。
但是,由于不同的事件要传递的参数不同,更多时候是从EventArgs类派生的子类的实例,显然一个EventHandler委托是不能满足各种情况的。如果针对不同的事件也顶一个一个对应的委托,水量一旦多起来,既混乱,也不好管理。为了解决这个问题,.NET类库又提供了一个带有泛型参数的事件处理委托。原型如下:
1 public delegate void EventHandler<TEventArgs>(object sender, TEventArgs e);
TEventArgs 是一个泛型参数,应该是System.EventArgs类或者System.EventArgs类的派生类型。
泛型参数的事件,实例:
1 // EventArgs 派生类 2 // 创建泛型参数 KeyPressedEventArgs 类 3 public class KeyPressedEventArgs : EventArgs 4 { 5 public ConsoleKey pressedKey { get; private set; } 6 public KeyPressedEventArgs(ConsoleKey key) 7 { 8 pressedKey = key; 9 } 10 } 11 12 public class MyApp 13 { 14 // 捕捉按键的事件 声明一个泛型参数KeyPressedEventArgs类型的 15 public event EventHandler<KeyPressedEventArgs> KeyPressed; 16 17 // 通过该方法引发事件 18 protected virtual void OnKeyPressed(KeyPressedEventArgs e) 19 { 20 if (this.KeyPressed != null ) 21 { 22 this.KeyPressed(this, e); 23 } 24 } 25 26 // 事件监听端口启动 27 public void Start() 28 { 29 while (true) 30 { 31 ConsoleKeyInfo keyInfo = Console.ReadKey(); 32 // 如果按下了ESC键,则退出循环 33 if (keyInfo.Key == ConsoleKey.Escape) 34 { 35 break; 36 } 37 // 引发事件 38 OnKeyPressed(new KeyPressedEventArgs(keyInfo.Key)); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 44 class Program 45 { 46 47 static void Main(string[] args) 48 { 49 50 MyApp app = new MyApp(); 51 // 订阅事件,指定处理事件的方法 52 app.KeyPressed += app_KeyPressed; 53 // 启动事件监听 54 app.Start(); 55 } 56 57 // 事件处理 58 private static void app_KeyPressed(Object sender, KeyPressedEventArgs e) 59 { 60 Console.WriteLine("已按下 {0} 键", e.pressedKey.ToString()); 61 } 62 63 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号