04 drf 认证,权限
1 drf认证功能介绍
- 认证,频率,权限
- 用户是否登录到系统中
- 后期基本上会用JWT的认证
- 自定制的认证
2 认证功能源码分析
2.1:drf 认证流程
1 APIView--->dispatch--->self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)-->self.perform_authentication(request)--->Request.user--->self._authenticate(self):Request类的方法--->self.authenticators:Request类的属性--->在Request对象实例化的时候传入的---->Request在什么时候实例化的?dispatch的时候--->APIView:self.get_authenticators()-->return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]---->如果在自己定义的视图类中写了authentication_classes=[类1,类2]---->Request的self.authenticators就变成了我们配置的一个个类的对象
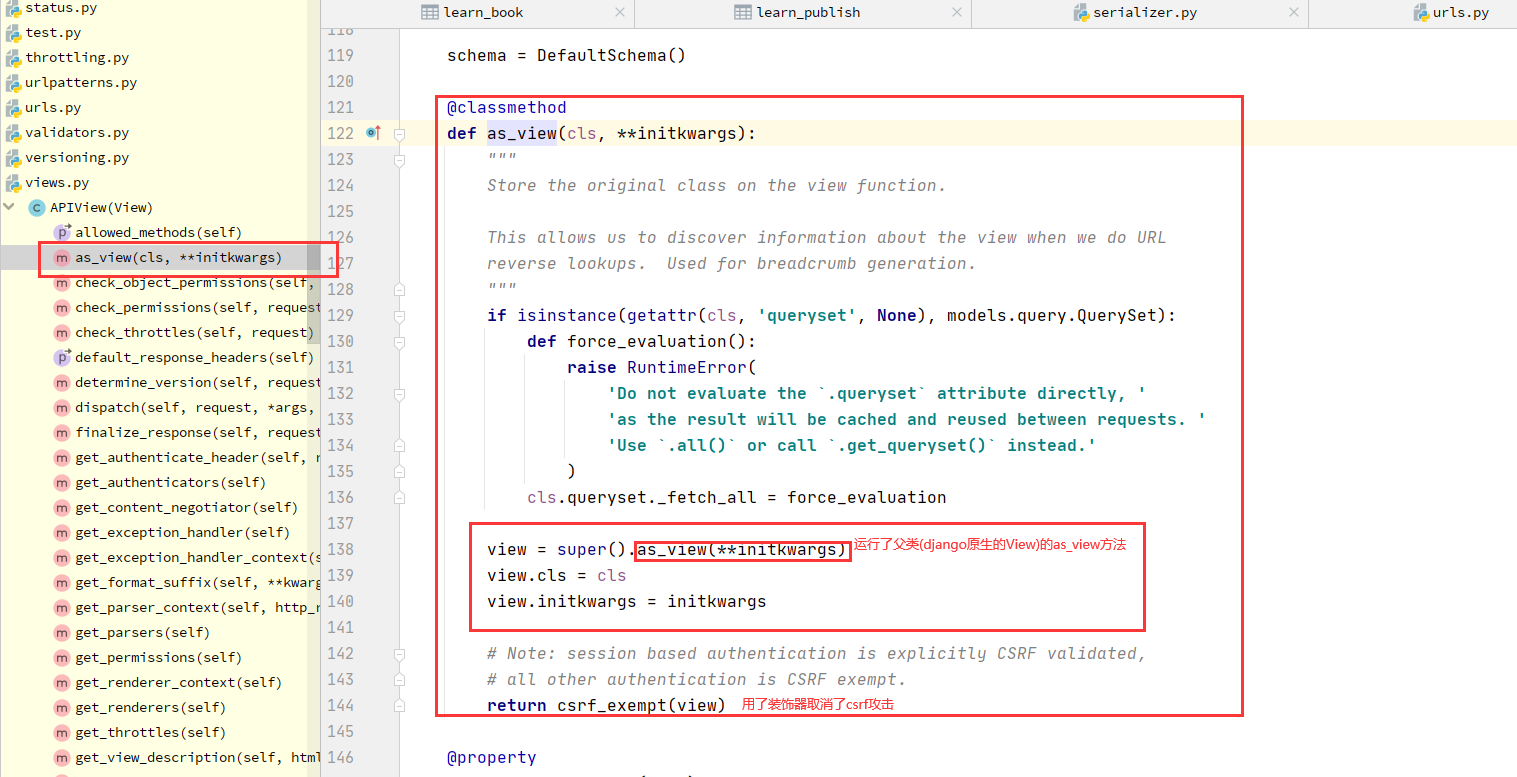
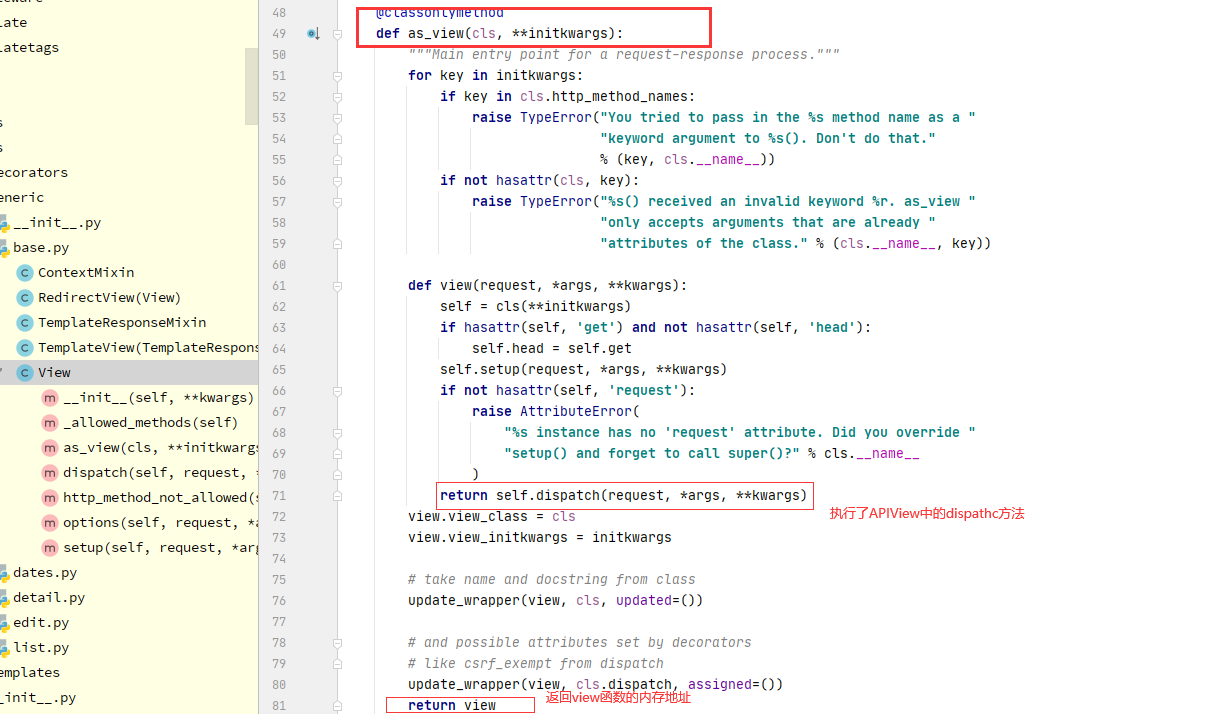
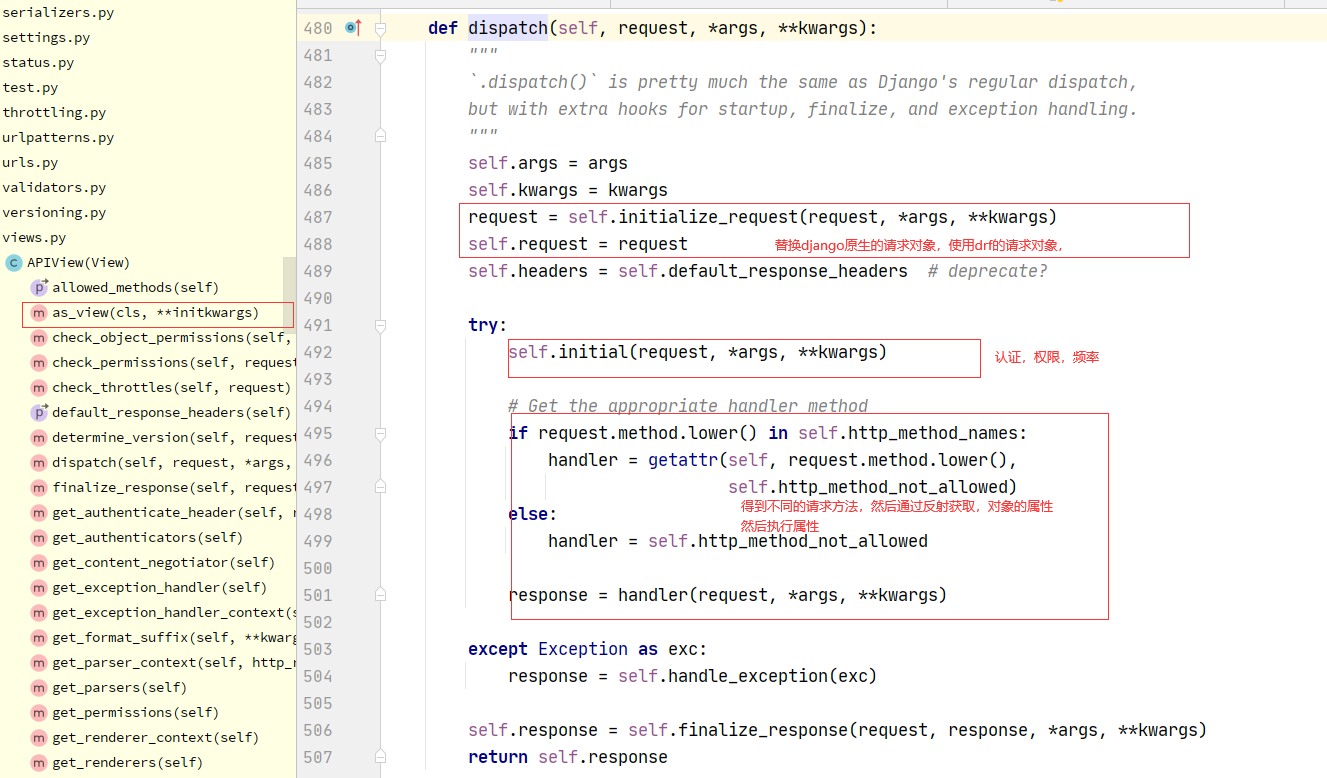
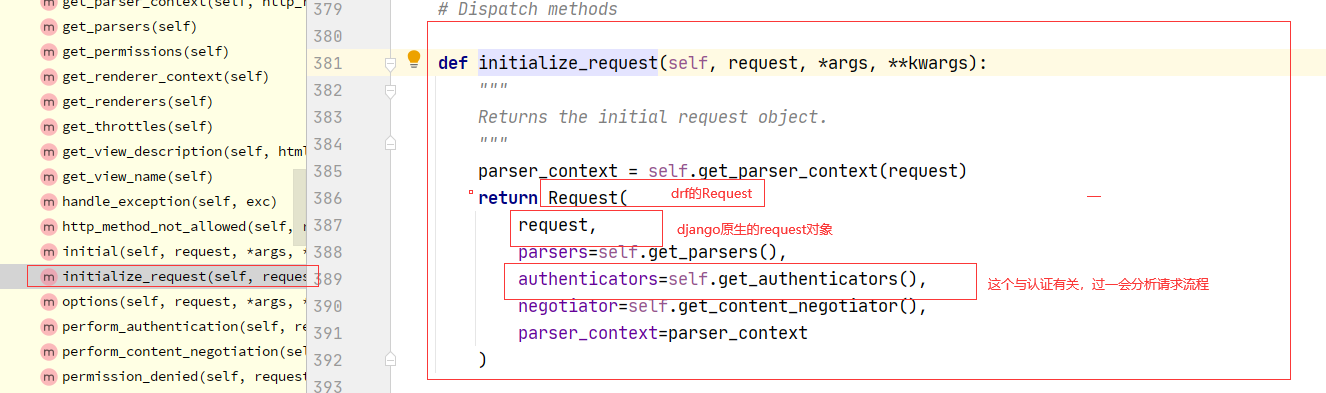
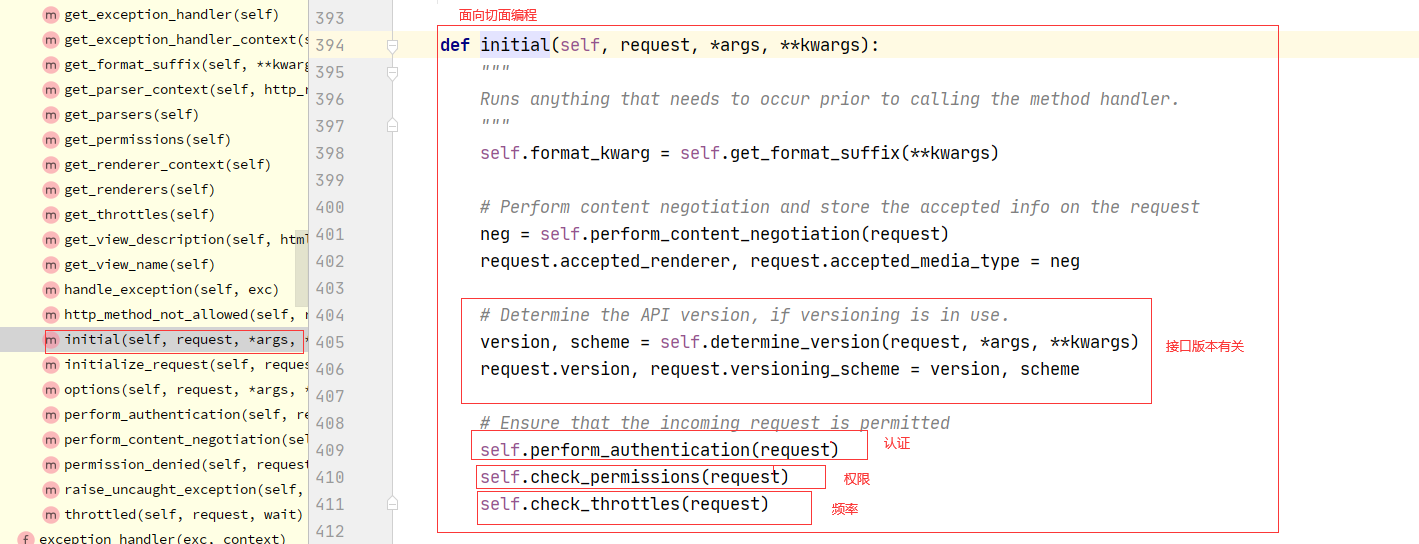
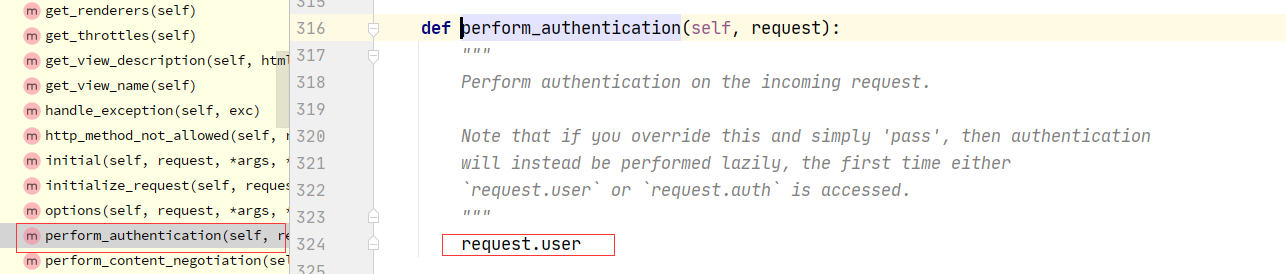
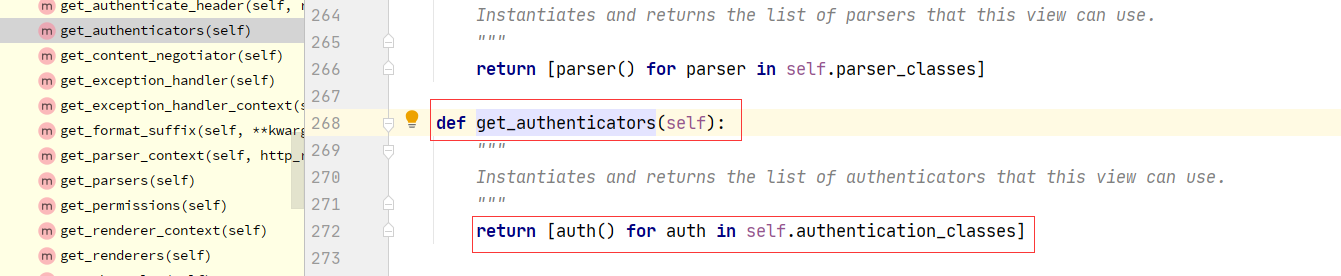
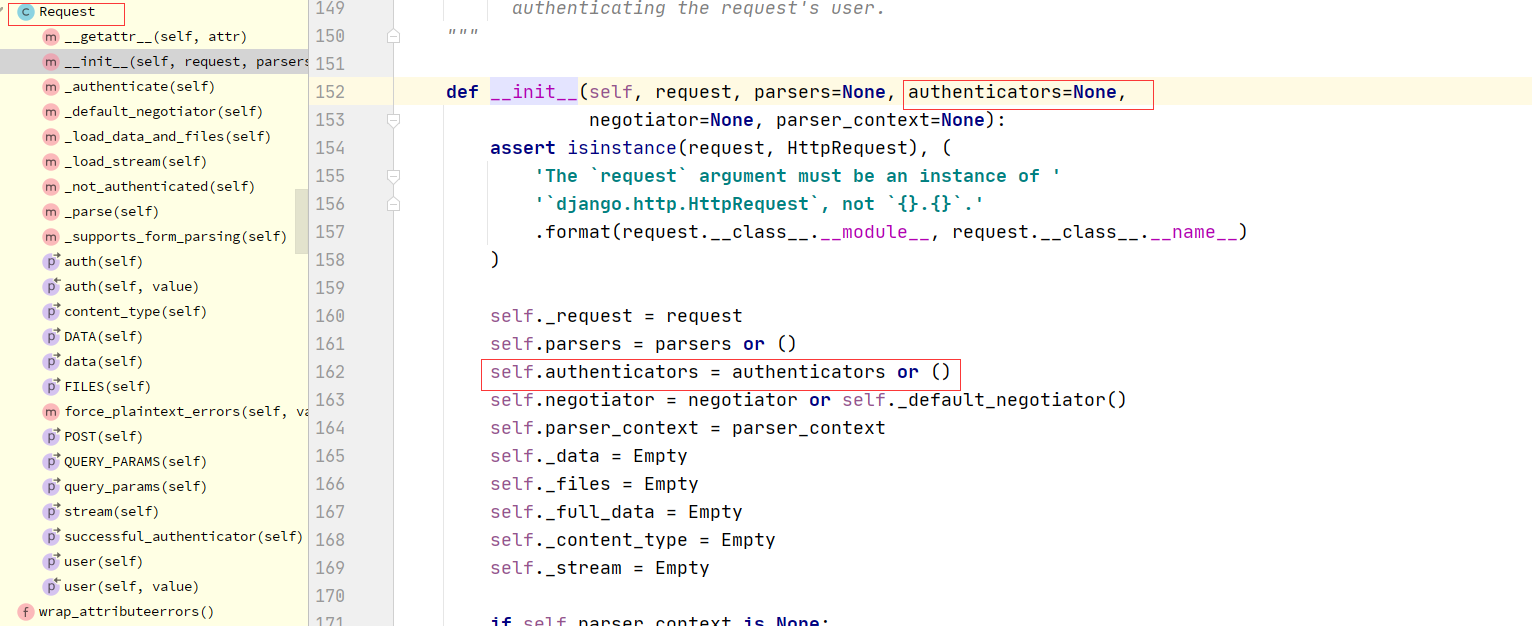
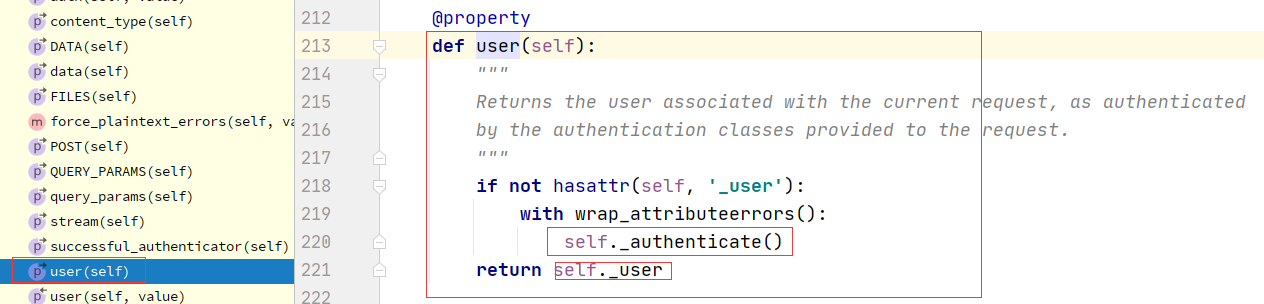
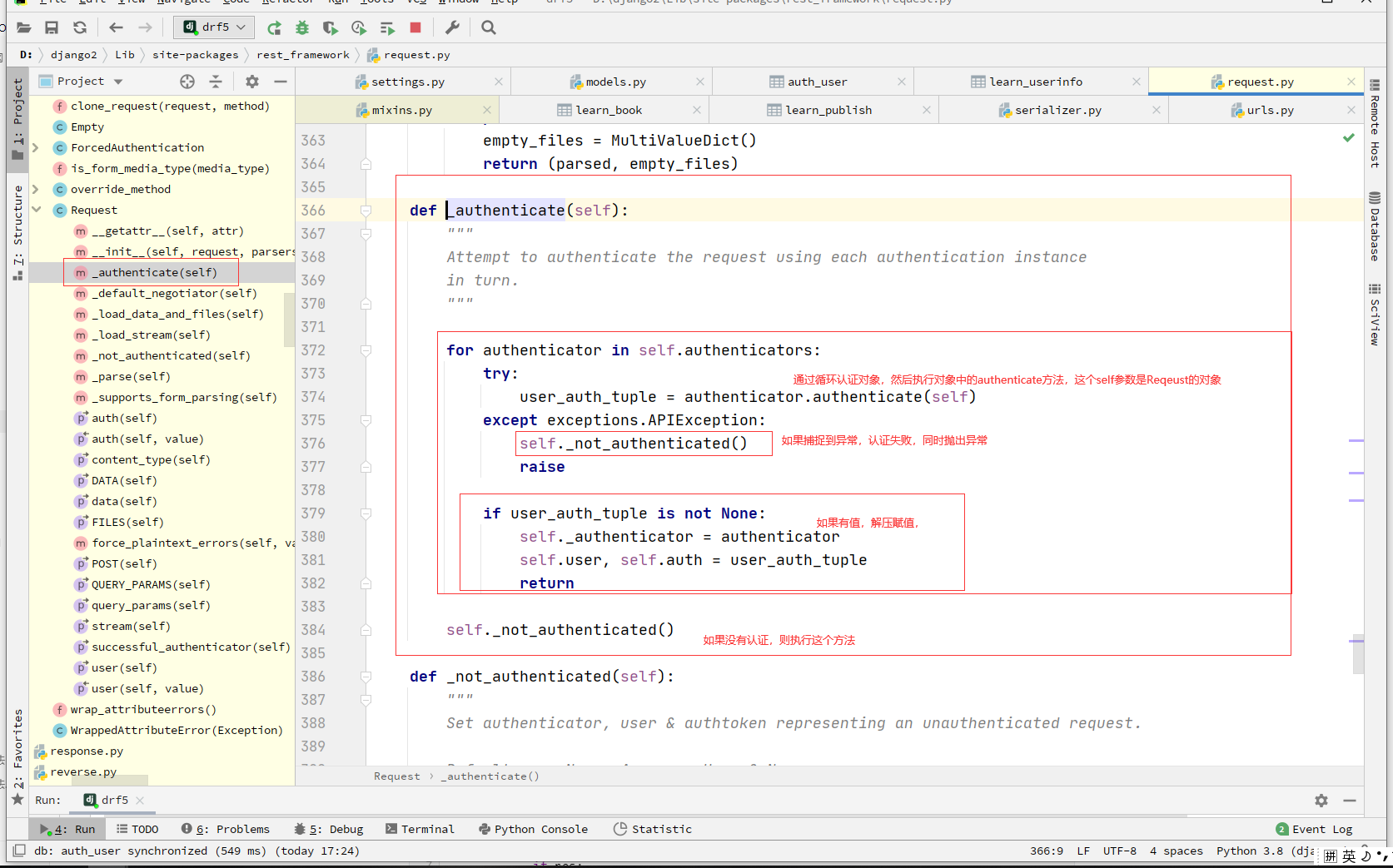
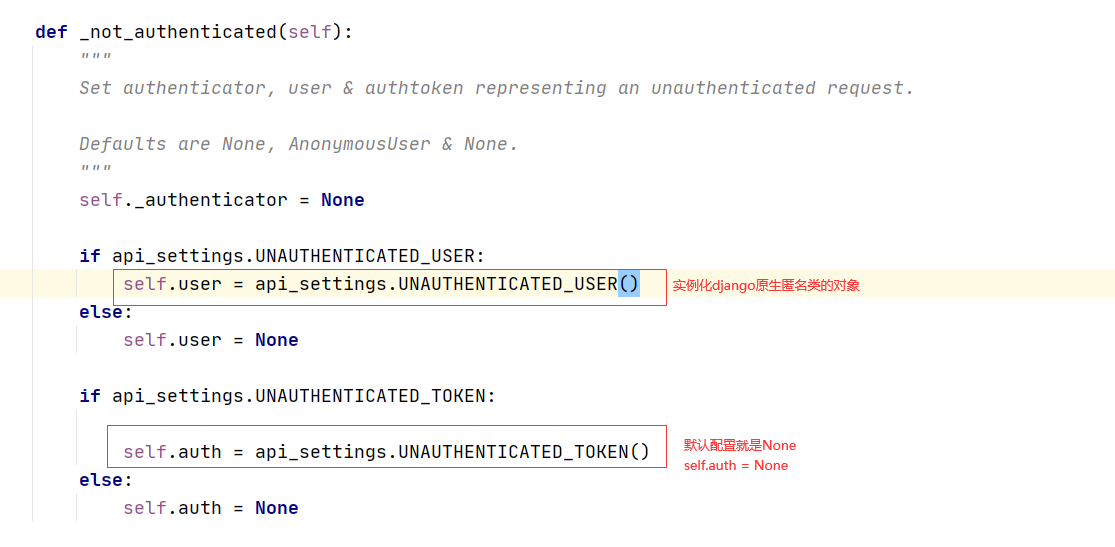
2.2:drf认证核心代码
#self._authenticate(self):Request类的方法
def _authenticate(self):
for authenticator in self.authenticators: # BookView中配置的一个个类的对象
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
2.3:局部配置认证类
只要在视图类中配置authentication_classes = [MyAuthen.LoginAuth, ],就会执行上面的方法,执行认证
3 自定义认证类(重点)
3.1:如何自定义认证类
-定义一个类,继承BaseAuthentication
class LoginAuth(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.GET.get('token')
res = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if res:
return 元组
else:
raise AuthenticationFailed('您没有登录')
3.2:全局,局部使用认证,局部禁用
3.2.1局部使用
在视图类中配置(只要配置了,就是登录以后才能访问,没配置,不用登录就能访问)
class Test(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthen.LoginAuth, ]
pass
3.2.2:全局使用
全局使用(所有接口,都需要登录才能访问)
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ["app01.MyAuthen.LoginAuth", ]
}
3.2.3:局部禁用
在想禁用的视图类上,如下操作
class Test(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
pass
3.3:注意
- 认证类,认证通过可以返回一个元组,有两个值,第一个值会给,request.user,第二个值会个request.auth
- 认证类可以配置多个,按照从前向后的顺序执行,如果前面有返回值,认证就不再继续往下走了
4:示例
models.py
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class UserInfo(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='用户名')
password = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='密码')
mobile = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='手机')
email = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='邮箱')
token = models.CharField(max_length=255,null=True)
user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=((1,'vip'),(3,'generic')),default=1)
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='书名')
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2,help_text='价格')
publish = models.ForeignKey(to="Publish", on_delete=models.SET_NULL, null=True, db_constraint=False,help_text='出版社')
@property
def publish_name(self):
return {'id':self.publish_id,'name':self.publish.name,'addr':self.publish.addr}
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='出版社名称')
addr = models.CharField(max_length=255,help_text='出版社地址')
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.mixins import CreateModelMixin,\
ListModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin,DestroyModelMixin,RetrieveModelMixin
from . import models
from . import serializer
from .util import LearnBaseAuthentication
from .util import LearnBasePermission
from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet
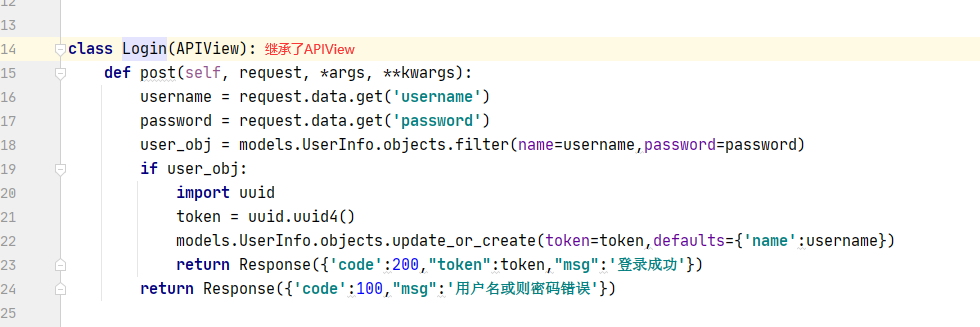
class Login(APIView):
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
username = request.data.get('username')
password = request.data.get('password')
user_obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(name=username, password=password)
if user_obj:
import uuid
token = uuid.uuid4()
models.UserInfo.objects.update_or_create(name=username, defaults={'token': token})
return Response({'code': 200, "token": token, "msg": '登录成功'})
return Response({'code': 100, "msg": '用户名或则密码错误'})
class Book(GenericViewSet, ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin,DestroyModelMixin,RetrieveModelMixin):
authentication_classes = [LearnBaseAuthentication, ]
permission_classes = [LearnBasePermission, ]
queryset = models.Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = serializer.BookModelSerializer
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get_one(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return self.retrieve(request,*args,**kwargs)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs)
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.destroy(request, *args, **kwargs)
util.py
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from . import models
class LearnBaseAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.data.get('token')
print(token, 11)
user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(token=token)
if user:
return user.last().name, token
else:
raise AuthenticationFailed('用户名或者密码错误')
# class LearnBaseAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
# def authenticate(self, request):
# token = request.data.get('token')
# try:
# user = models.UserInfo.objects.get(token=token)
# if user:
# return user.username, token
# except Exception:
# raise AuthenticationFailed('用户名或者密码错误!')
class LearnBasePermission(BasePermission):
message = '您没有权限'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
user_type = models.UserInfo.objects.get(name=request.user).user_type
if user_type == 1:
return True
else:
return False
serializer
from rest_framework import serializers
from . import models
class BookModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = ['id', 'title', 'price', 'publish_name', 'publish']
extra_kwargs = {
'id': {'required': False},
'publish_name': {'read_only': True},
'publish': {'write_only': True},
}
class PublishModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Publish
fields = '__all__'
extra_kwargs = {
'id': {'required': False}
}
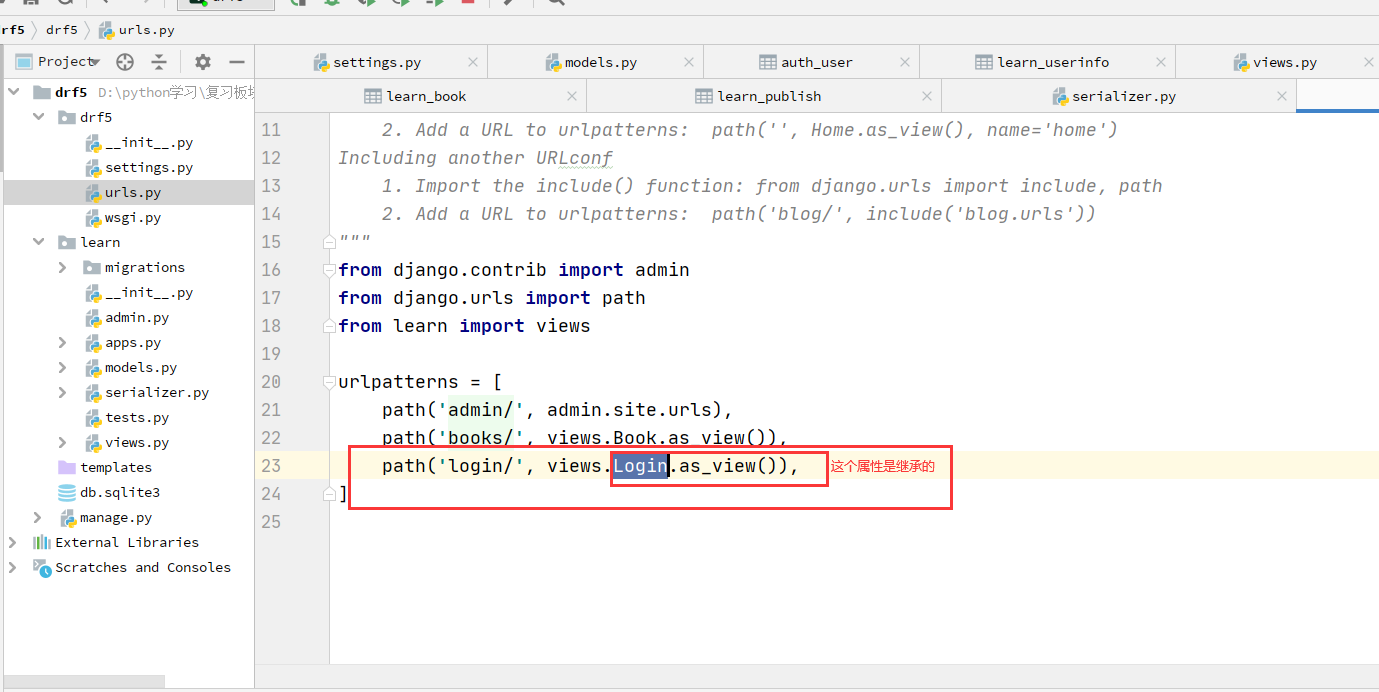
urls.py
from django.urls import path
from learn import views
urlpatterns = [
path('books/', views.Book.as_view()),
path('login/', views.Login.as_view()),
]
5 自定义权限功能(重点)
5.1:为什么要有权限限制
登录成功以后,超级用户可以干某些事,普通用户不能干---》超级用户可以查看某些接口,普通用户不能查看
5.2:自定义权限
使用写一个类继承BasePermission,重写has_permission
class SuperPermission(BasePermission):
message='权限不够'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
# Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
# 超级用户可以访问,除了超级用户以外,都不能访问
if request.user.user_type == '1':
return True
else:
return False
5.3:权限(局部使用,局部禁用,全局使用)
5.3.1:局部使用
class Test():
permission_classes = [MyAuthen.SuperPermission]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
pass
5.3.2:局部禁用
class Test():
permission_classes = []
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
pass
5.3.3:全局使用
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES": ["....SuperPermission", ]
}
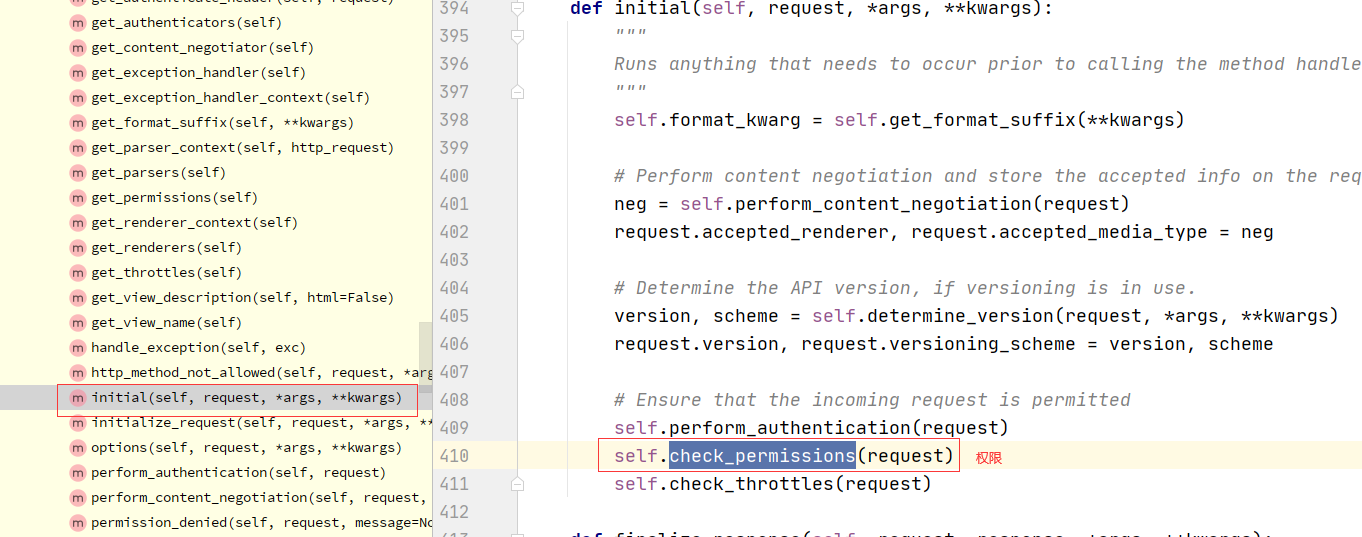
6 权限源码分析
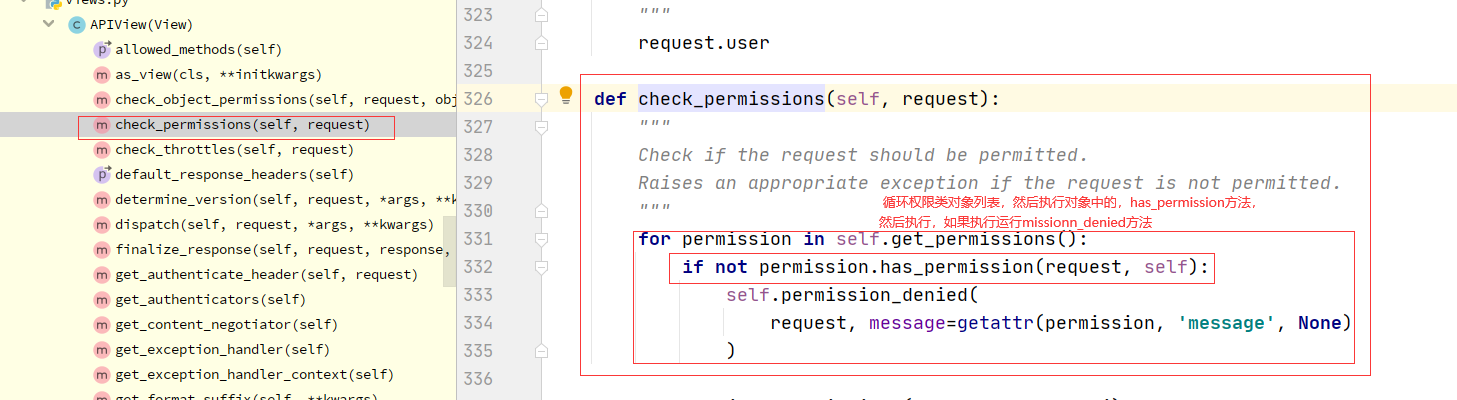
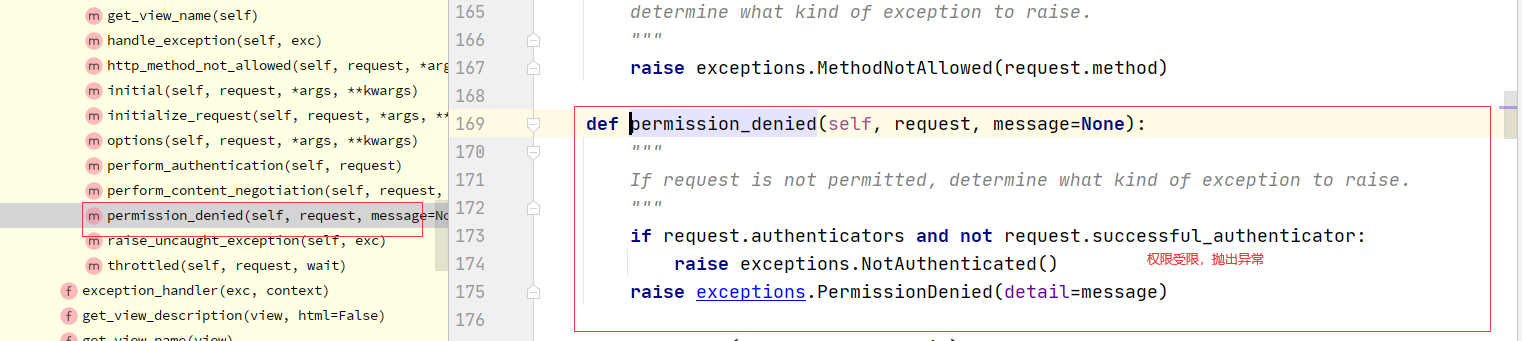
核心代码
def check_permissions(self, request):
"""
Check if the request should be permitted.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is not permitted.
"""
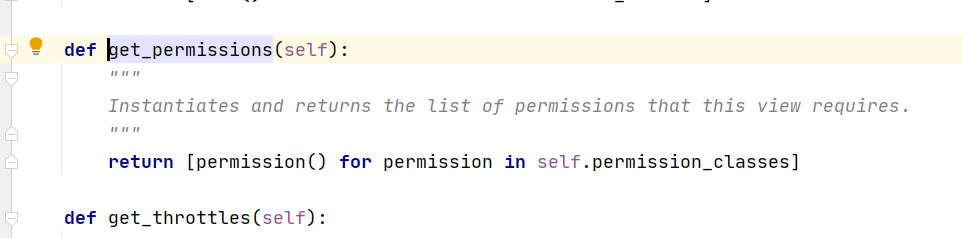
for permission in self.get_permissions():
if not permission.has_permission(request, self):
self.permission_denied(
request, message=getattr(permission, 'message', None)
)
默认配置文件
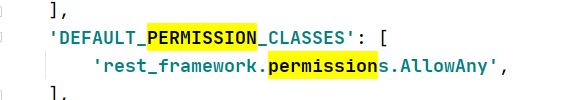
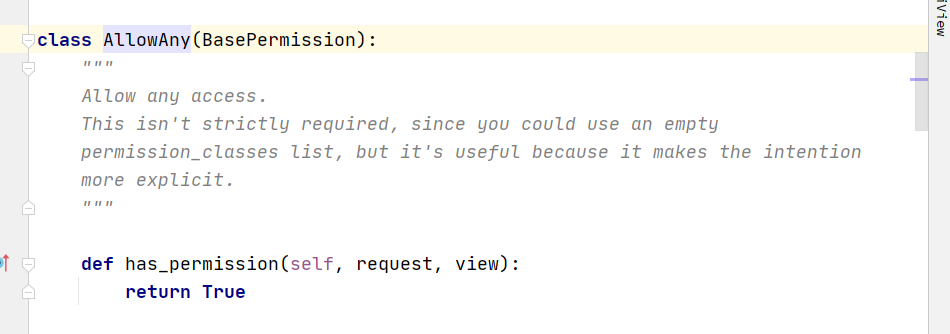
7:内置的权限和认证类
# 内置认证类
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
# 内置权限类
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
8:示例2
需求
写一个图书的5个接口出版社的5个接口和登录接口
1:用户必须登录才能访问图书的5个接口
2:必须超级用户登录后才能访问出版社5个接口
models.py
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)
publish = models.ForeignKey(to='Publish', on_delete=models.SET_NULL, null=True, db_constraint=False)
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
addr = models.CharField(max_length=255)
class UserInfo(models.Model):
username = models.CharField(max_length=255)
password = models.CharField(max_length=255)
mobile = models.CharField(max_length=25)
email = models.EmailField()
token = models.CharField(max_length=255,null=True)
user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=((1, 'vip'), (2, 'svip'), (3, 'generic')))
urls.py
from django.urls import path
from work import views
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', views.Login.as_view()),
path('books/', views.Book.as_view({'get': "list", 'post': 'create'})),
path('book/<int:pk>/', views.Book.as_view({'get': "retrieve", 'delete': 'destroy', 'put': 'update'})),
path('publishes/', views.Publish.as_view({'get': "list", 'post': 'create'})),
path('publish/<int:pk>/', views.Publish.as_view({'get': "retrieve", 'delete': 'destroy', 'put': 'update'}))
]
serializer.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from . import models
class BookModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = ['id', 'title', 'price', 'publish']
class PublishModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Publish
fields = ['id', 'name', 'addr']
util.py
from . import models
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
# token认证
class TokenBaseAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
visit_path = request.get_full_path()
token = request.data.get('token')
if not token:
raise AuthenticationFailed('先登录后访问')
print(token)
try:
user_obj = models.UserInfo.objects.get(token=token)
return user_obj, token
except Exception:
raise AuthenticationFailed('用户名或者者密码错误')
# 权限管理
class TokenBasePermission(BasePermission):
message = '权限不够'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
user_obj = request.user
visit = view.__class__.__name__.lower()
print(visit)
if user_obj.user_type == 1 and visit == 'book':
return True
elif user_obj.user_type == 2 and visit == 'publish':
return True
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
import uuid
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from . import serializer
from . import models
from . import util
class Login(APIView):
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
msg = {'code': 200, 'msg': None}
username = request.data.get('username')
password = request.data.get('password')
user_obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username, password=password)
if not user_obj:
msg['code'] = 100
msg['msg'] = '用户名或者密码错误!'
return Response(msg)
token = uuid.uuid4()
models.UserInfo.objects.update_or_create(defaults={'token': token}, username=username)
msg['msg'] = '登录成功'
msg['token'] = token
msg['username'] = username
return Response(msg)
class Book(ModelViewSet):
authentication_classes = [util.TokenBaseAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [util.TokenBasePermission,]
queryset = models.Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = serializer.BookModelSerializer
class Publish(ModelViewSet):
authentication_classes = [util.TokenBaseAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [util.BasePermission,]
queryset = models.Publish.objects.all()
serializer_class = serializer.PublishModelSerializer


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号