就是这么简单!使用Rest-assured 测试Restful Web Services
使用 Rest-assured 测试 Restful Web Services
转载注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wade-xu/p/4298819.html
这里向大家介绍一个测试Restful web service 的框架,叫Rest-assured.
他提供了一系列好的功能,像DSL式的语法, XPath-Validate, 文件上传,Specification重用, 使用代理, Spring MVC mock module测试Controllers等等,让你在Java里面测试Rest service 和那些动态语言Ruby, Groovy一样灵活。
目录
1. 前提
2. 配置
3. Example详解
4. Troubleshooting
5. 参考来源
前提条件
- JDK >= 1.6
- Maven 3
配置Maven工程pom文件如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.restassured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Example
a) 测试一个GET 请求方法,
请求URL : http://10.46.28.193:8080/service/v1/user/login
返回JSON内容如下
{
"userInfo": {
"password": null,
"userId": "wadexu",
"accessSecurityCodes": "10000000000000000000",
"firstName": "Wade",
"lastName": "Xu",
"status": 8,
"officePhone": "58730",
"email": "wadexu@test.com",
"homePhone": "123"
},
"success": true,
"error": null
}
测试代码如下:
@Before
public void setUp() {
RestAssured.baseURI= "http://10.46.28.193";
RestAssured.port = 8080;
RestAssured.basePath = "/service/v1";
}
@Test
public void testUserLogin() {
expect().
statusCode(200).
body(
"success", equalTo(true),
"userInfo.userId", equalTo("wadexu"),
"userInfo.firstName", equalTo("Wade"),
"userInfo.lastName", equalTo("Xu"),
"error", equalTo(null)).
when().
get("/user/login?userName=wadexu&password=NzrmRcIfIW4=");
}
注意我这里请求时的参数直接塞进了URL里, 稍后会讲到如何指明参数。
b) 如何使用JSON path
还是同上面的例子, 测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testUserLogin_JsonPath() {
Response response = get("/user/login?userName=wadexu&password=NzrmRcIfIW4=");
assertEquals(200, response.getStatusCode());
String json = response.asString();
JsonPath jp = new JsonPath(json);
assertEquals("wadexu", jp.get("userInfo.userId"));
assertEquals("Wade", jp.get("userInfo.firstName"));
assertEquals("Xu", jp.get("userInfo.lastName"));
assertEquals("123", jp.get("userInfo.homePhone"));
}
c) 如何使用参数
Get请求是用queryParam, 如果你直接写param,在这个case里也可以,Rest Assured 会自动判断参数类型(query or form parameter), 在有些case里, Put 或 Post 你得指明参数类型
@Test public void testUserLogin_Parameter() { final String userName = "wadexu"; final String password = "NzrmRcIfIW4="; given(). queryParam("userName", userName).queryParam("password", password). expect(). statusCode(200). body("success", equalTo(true), "userInfo.userId", equalTo("wadexu"), "userInfo.firstName", equalTo("Wade"), "userInfo.lastName", equalTo("Xu"), "error", equalTo(null)).when() .get("/user/login"); }
另外,有些Post 请求URL后面是有参数的, 这时候 你可以这样写
post("/reserve/{hotelId}/{roomNumber}", "My Hotel", 23);
或者
given(). pathParam("hotelId", "My Hotel"). pathParam("roomNumber", 23). when(). post("/reserve/{hotelId}/{roomNumber}"). then(). ..
d) 再来看一个POST 请求, 这时候需要请求消息体body了,request body是JSON体如下:
{
"customerId": "CDICC",
"broker": "test",
"editUserId": "wadexu"
}
测试代码:
@Test public void testCreate() { final String bodyString = "{\"customerId\": \"CDICC\",\"broker\": \"test\",\"editUserId\": \"wadexu\"}"; given(). contentType("application/json"). request().body(bodyString). expect(). statusCode(200). body( "order.orderNumber", is(Number.class), "order.deleteDate", is(nullValue()), "success", equalTo(true)). when(). post("/order"); }
这时除了用到request().body
还多加了一个header 请求消息头 -- ContentType
set Headers 的方法有很多, 上面是其一, 你还可以按如下方式做:
given().header("Content-Type", "application/json")
given().headers("Accept", "application/json", "Content-Type", "application/json")
另外 注意到期望结果的比较没有, 这里用到org.hamcrest.Matchers的一些方法, 因为Order number 每次不一样,无法判断具体是多少,所以就看是否是数字就行了,删除日期是null value
hamcrest.Matchers 里的各种匹配器有兴趣的童鞋可以研究下, 对测试断言很有帮助。
转载注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wade-xu/p/4298819.html
e) 同样你还可以verify HTTP Status code
因为我这个service是需要Content-Type=application/json的, 而我的case里并没有赋值给contentType, 所以返回会报错 415
The server refused this request because the request entity is in a format not supported by the requested resource for the requested method.
@Test public void testOpenOrder_error() { final String orderNumber = "3017"; final String orderVersion = "1"; final String versionType = ""; final String editUserId = ""; final String customerId = ""; final String state = ""; given(). parameters( "orderNumber", orderNumber, "orderVersion", orderVersion, "versionType", versionType, "editUserId", editUserId, "customerId", customerId, "state", state). expect(). statusCode(415). when(). post("/order/open"); }
f) Cookies 其实都大同小异了
第一个没有set cookie 结果抛 403
"name":"Forbidden",
"detail":"The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it. Unlike a 401 Unauthorized response, authenticating will make no difference."
@Test public void testCookie() { expect(). statusCode(403). when(). get("/access"); given(). cookie("userName", "wadexu"). expect(). statusCode(200). when(). get("/access"); }
g) Authentication
如果你的service需要认证,则需要设置authentication()
否则401 -- Unauthorized
@Test public void testAuthentication() { expect(). statusCode(401). when(). get("/service/user"); expect(). statusCode(200). when(). with(). authentication().basic("wadexu", "123456"). get("/service/user"); }
H) Specification reuse 规范重用
@Test public void testSpecReuse() { ResponseSpecBuilder builder = new ResponseSpecBuilder(); builder.expectStatusCode(200); builder.expectBody("userInfo.userId", equalTo("wadexu")); builder.expectBody("userInfo.firstName", equalTo("Wade")); builder.expectBody("userInfo.lastName", equalTo("Xu")); builder.expectBody("success", equalTo(true)); ResponseSpecification responseSpec = builder.build(); //use this specification for test example -- a expect(). spec(responseSpec). when(). get("/user/login?userName=wadexu&password=NzrmRcIfIW4="); //now re-use for another example -- c that returns similar data given(). queryParam("userName", "wadexu"). queryParam("password", "NzrmRcIfIW4="). expect(). spec(responseSpec). when(). get("/user/login"); }
如果你还有更多的测试,返回期望结果又类似 则可以继续使用 specification, 达到重用的目的。
转载注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wade-xu/p/4298819.html
测试运行结果如下(不包含上面每一个用例):
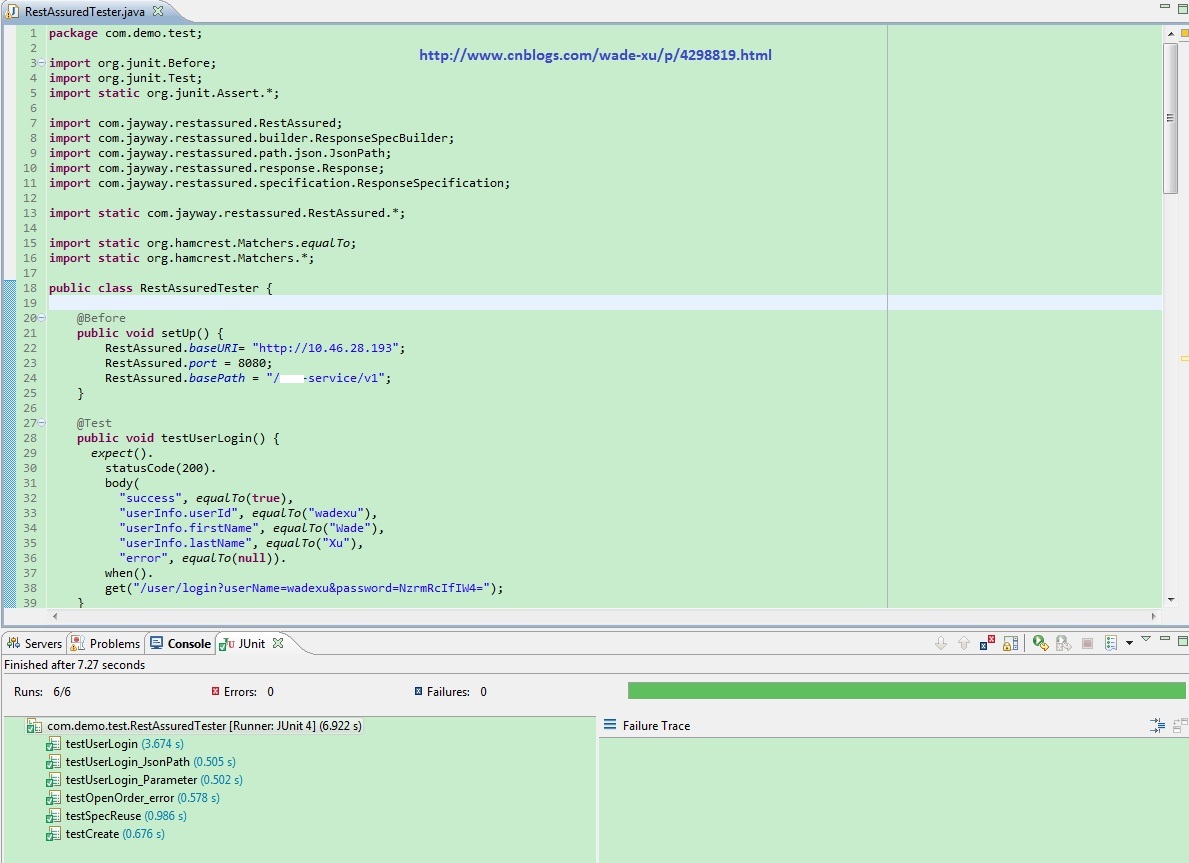
Troubleshooting
有些类需要Static imports
参考我的如下:
import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import com.jayway.restassured.RestAssured; import com.jayway.restassured.builder.ResponseSpecBuilder; import com.jayway.restassured.path.json.JsonPath; import com.jayway.restassured.response.Response; import com.jayway.restassured.specification.ResponseSpecification; import static com.jayway.restassured.RestAssured.*; import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo; import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
设置好你的请求url 路径, 默认http://localhost:8080
参考我的base path(即所以请求url 前面相同的部分) 配置如下:
@Before public void setUp() { RestAssured.baseURI= "http://10.46.28.193"; RestAssured.port = 8080; RestAssured.basePath = "/service/v1"; }
“WARNING: Cannot find parser for content-type: text/json — using default parser.”
– 需要注册相关的parser: e.g. RestAssured.registerParser(“text/json”, Parser.JSON);
参考来源
官方文档:https://code.google.com/p/rest-assured/
羊年第一篇文章,感谢阅读,如果您觉得本文的内容对您的学习有所帮助,您可以点击右下方的推荐按钮。您的鼓励是我创作的动力,祝大家羊年工作生活各方面洋洋得意!






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下