hdu 1005
Number Sequence
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 127502 Accepted Submission(s): 30987
Problem Description
A number sequence is defined as follows:
f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(n) = (A * f(n - 1) + B * f(n - 2)) mod 7.
Given A, B, and n, you are to calculate the value of f(n).
f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(n) = (A * f(n - 1) + B * f(n - 2)) mod 7.
Given A, B, and n, you are to calculate the value of f(n).
Input
The
input consists of multiple test cases. Each test case contains 3
integers A, B and n on a single line (1 <= A, B <= 1000, 1 <= n
<= 100,000,000). Three zeros signal the end of input and this test
case is not to be processed.
Output
For each test case, print the value of f(n) on a single line.
Sample Input
1 1 3
1 2 10
0 0 0
Sample Output
2
5
题意:给你一个方程,求f[n],结果模7分析:1:对7取模,f[n-1],f[n-2],A,B固定,最多7*7=49种情况。
从3算到50,把所有的情况存起来
2:如果题目加难,模100000007,这种方法肯定不行,超时,当然,仅仅追求这个题目的初学者可以不用看第二份代码。
第二份代码思路:这是一个二维矩阵乘法,,,这就要一定功底去构造矩阵啦,然后使用快速幂取模。。。
代码一:
//这份代码就没什么好解释了,找循环节 #include <stdio.h> int main () { int f[51]; int a, b, n,i,T; while(scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&n),a||b||n) { f[1]=f[2]=1; for (i=3;i<50;i++) { f[i]=(a*f[i-1]+b*f[i-2])%7; if (f[i]==1&&f[i-1]==1) { break; } } T=i-2; f[0]=f[T]; printf ("%d\n", f[n%T]); } return 0; }
代码二:
/*记得当时刚学,不会这种高级方法,大神在旁边看了一眼,直接给构造了一个矩阵,交了我幂取模,满满的崇拜和感谢
刚开始学,朋友不多,有人教一个东西,感觉真幸运,自学可能又要好久吧*/
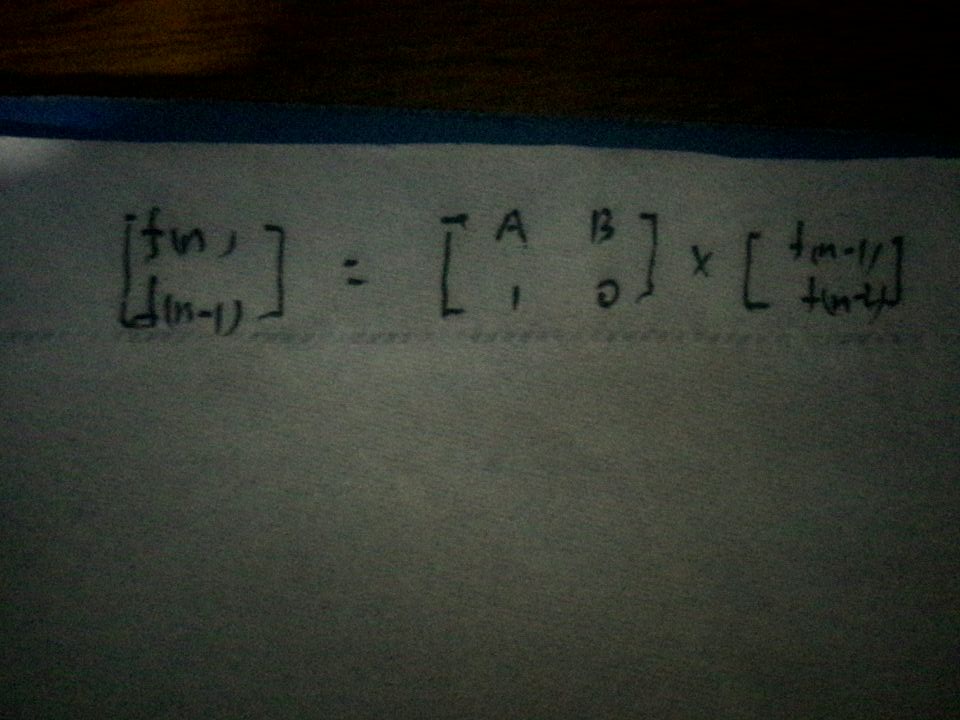
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; struct matrix{ int Q[10][10]; }; matrix mult_pow(matrix a,matrix b){//矩阵乘法 int i,j,k; matrix c; memset(c.Q,0,sizeof(c.Q)); for(i=1;i<=2;i++) for(j=1;j<=2;j++) for(k=1;k<=2;k++) c.Q[i][j]=(c.Q[i][j]+a.Q[i][k]*b.Q[k][j])%7; return c; } matrix mult_pow_mod(matrix a,int n){ matrix ret;//构造矩阵 ret.Q[1][1]=1; ret.Q[1][2]=0; ret.Q[2][1]=0; ret.Q[2][2]=1; while(n){//快速密取模 if(n&1) ret=mult_pow(ret,a); a=mult_pow(a,a); n/=2; } return ret; } int main(){ int a,b,n; while(cin>>a>>b>>n){ if(a==0) break; if(n<=2) { printf("1\n"); continue; } matrix A;//构造矩阵 A.Q[1][1]=a; A.Q[1][2]=b; A.Q[2][1]=1; A.Q[2][2]=0; A=mult_pow_mod(A,n-2); printf("%d\n",(A.Q[1][1]+A.Q[1][2])%7); } return 0; }





