大数据学习笔记——Hadoop编程之SequenceFile
SequenceFile(Hadoop序列文件)基础知识与应用
上篇编程实战系列中本人介绍了基本的使用HDFS进行文件读写的方法,这一篇将承接上篇重点整理一下SequenceFile的相关知识及应用
1. SequenceFile简介
SequenceFile是Hadoop自带的一种键值对文件格式,它具有以下几个特点:
1. 由于该文件类型是Hadoop自带的,因此对Hadoop环境具有最强的兼容性
2. 由于Hadoop不适合存储大量小文件,SequenceFile作为容器文件,能够封装大量的小文件为一个大文件,很好地解决了这个问题
3. 该文件类型具有可切割性,因此可实现数据本地化
2. SequenceFile编程实战
首先介绍一下SequenceFile的基本组成部分
1. SequenceFile的版本号,包括3个字节的SEQ,和它的版本号
2. key的类名
3. value的类名
4. 一个用来表示是否压缩的boolean值
5. 一个用来表示是否是块压缩的boolean值
6. 指定一个压缩编解码器
7. 元数据
8. 同步点:用来定位数据的边界
2.1 SequenceFile的基本读写操作
//测试使用SequenceFile进行文件的写出 @Test public void testWrite() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个写入器 SequenceFile.Writer writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/1.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class); //传入1000个hello做测试 for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){ IntWritable key = new IntWritable(i); Text value = new Text("hello" + i); writer.append(key,value); } //关闭资源 writer.close(); } //测试使用SequenceFile进行文件内容的读取 @Test public void testRead() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个读取器 SequenceFile.Reader reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(fs, new Path("/1.seq"), conf); //初始化两个对象作为容器存放读取到的数据 IntWritable key = new IntWritable(); Text value = new Text(); for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){ reader.next(key,value); System.out.println("key: " + key + "\t" + "value: " + value); } //关闭资源 reader.close(); }
2.2 SequenceFile的sort和merge操作
sort操作
由于需要使用到排序方法,因此首先我们需要准备一个乱序的seq文件
//准备一个乱序的seq文件 @Test public void testWrite2() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个写入器 SequenceFile.Writer writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/in1.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class); //传入1000个hello做测试,但是是乱序输出的 Random r = new Random(); for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){ IntWritable key = new IntWritable(r.nextInt(1000)); Text value = new Text("hello" + key); writer.append(key,value); } //关闭资源 writer.close(); } //测试排序方法 @Test public void testSort() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个排序器 SequenceFile.Sorter sorter = new SequenceFile.Sorter(fs, IntWritable.class, Text.class, conf); //使用sorter对象的sort方法对key进行排序 sorter.sort(new Path("/in1.seq"),new Path("/out1.seq")); }
排序前,可用hdfs dfs -text /in1.seq进行SequenceFile的查看,查看结果如下:
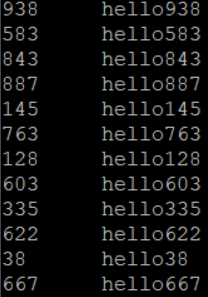
排序后,使用hdfs dfs -text /out1.seq进行查看,结果如下,排序成功!
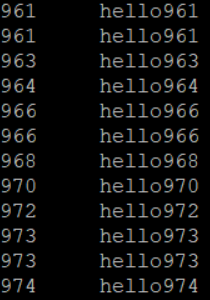
merge操作
//准备另一个seq文件用来进行merge操作 @Test public void testWrite3() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个写入器 SequenceFile.Writer writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/in2.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class); //传入1000个hello做测试,但是是乱序输出的 Random r = new Random(); for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){ IntWritable key = new IntWritable(r.nextInt(1000)); Text value = new Text("helloworld" + key); writer.append(key,value); } //关闭资源 writer.close(); } //演示merge方法合并两个seq文件 @Test public void testMerge() throws Exception{ //进行用户设置 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); //Configuration对象 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //FileSystem对象 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //新建一个排序器,然后调用排序器的merge方法 SequenceFile.Sorter sorter = new SequenceFile.Sorter(fs, IntWritable.class, Text.class, conf); Path path1 = new Path("/in1.seq"); Path path2 = new Path("/in2.seq"); Path[] paths = {path1,path2}; sorter.merge(paths,new Path("/merge.seq")); }
2.3 SequenceFile三种压缩方式比较
SequenceFile一共有三种不同的压缩方式:
1. None:不压缩
2. Record:记录压缩,只压缩value
3. Block:块压缩,将多个K-V对聚集在一起,超过指定大小后(1000000字节,近似于1M)将其压缩
package com.seq; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.junit.Test; /* 测试几种不同的压缩方式最终产生的文件大小 */ public class TestCompress { @Test public void testCompression() throws Exception{ System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root"); Configuration conf = new Configuration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //分别新建三个不同的写出器,之后查看文件大小 SequenceFile.Writer writer1 = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/none.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class, SequenceFile.CompressionType.NONE); SequenceFile.Writer writer2 = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/record.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class, SequenceFile.CompressionType.RECORD); SequenceFile.Writer writer3 = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, new Path("/block.seq"), IntWritable.class, Text.class, SequenceFile.CompressionType.BLOCK); //写入10000个hello作比较 for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ IntWritable key = new IntWritable(i); Text value = new Text("hellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohello" + key); writer1.append(key,value); writer2.append(key,value); writer3.append(key,value); } //关闭资源 writer1.close(); writer2.close(); writer3.close(); } }
查看文件大小,可得:不压缩文件大小 > 记录压缩文件大小 > 块压缩文件大小
![]()
![]()
![]()
2.4 压缩编解码器性能对比
目前常用的压缩编解码器主要有这几种:gzip, bzip2, lz4, lzo, Snappy等,关于性能的讨论,主要分为两派,一是追求较高的压缩比,但要付出时间的代价,二是追求较高的速度,但相对的,压缩比会小一些,对于lzo来说,首先需要导入相关依赖,依赖如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.anarres.lzo</groupId> <artifactId>lzo-hadoop</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>
测试代码如下:
package com.codec; import com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*; import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; /** * 综合测试压缩时间 解压时间 压缩大小 */ public class TestCodec { public static void main(String[] args) { Class[] classes = { GzipCodec.class, DefaultCodec.class, Lz4Codec.class, BZip2Codec.class, LzopCodec.class, SnappyCodec.class }; for (Class clazz : classes) { testCompress(clazz,"d:/test.log"); testDecompress(clazz,"d:/test.log"); } } /** * 测试压缩 * @throws Exception */ public static void testCompress(Class clazz, String path) { try { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //通过hadoop的反射工具类,获取压缩编解码器的实例 CompressionCodec codec = (CompressionCodec)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, conf); //获取编解码器默认扩展名 String ext = codec.getDefaultExtension(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //输入流读取本地文件 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path); //输出流加压缩 CompressionOutputStream cos = codec.createOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path + ext)); IOUtils.copyBytes(fis,cos,1024); System.out.println(ext + "压缩时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() -start)); File f = new File(path+ext); long length = f.length(); System.out.println(ext + "压缩大小:" + length); fis.close(); cos.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 测试解压 * @throws Exception */ public static void testDecompress(Class clazz, String path){ try { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //通过hadoop的反射工具类,获取压缩编解码器的实例 CompressionCodec codec = (CompressionCodec)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, conf); //获取编解码器默认扩展名 String ext = codec.getDefaultExtension(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //输入流解压文件 CompressionInputStream cis = codec.createInputStream(new FileInputStream(path+ext)); //输出流加压缩 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path + ext + ".log"); IOUtils.copyBytes(cis,fos,1024); System.out.println(ext + "解压时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() -start)); cis.close(); fos.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
测试结果公布:
压缩大小
bzip2 < gzip < deflate < lz4 < lzo
压缩时间
lz4 < lzo < deflate < gzip < bzip2
328 576 1106 2653 20599
解压时间
lzo < lz4 < deflate < gzip < bzip2
404 427 437 524 4694
优化压缩比可选用:
bzip2
gzip
deflate
优化压缩速度可选用:
lz4
lzo


