Java 多线程三、线程间的通信
一、线程通信
多线程之间是可以相互通信的,当一个线程使用 wait() 阻塞当前线程时,另一个线程可以用 notify() 或 notifyAll() 方法来唤醒正在阻塞的线程,从而实现线程通信。
示例:
使用两个线程打印 1~100 中的数字,实现交替打印,即先线程1打印,在线程2打印,再线程1,再线程2... 以此类推。
代码如下:
public class ThreadNotifyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number num = new Number();
Thread t1 = new Thread(num);
Thread t2 = new Thread(num);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Number implements Runnable {
private int number = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
//唤醒被阻塞的线程,之前线程1被阻塞,线程2进来notify线程1唤醒
this.notify();
// this.notifyAll();//唤醒所有正在被wait的线程
if (number <= 100) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
number++;
//wait当前线程,即阻塞当前线程
try {
wait();//一旦执行wait,会释放锁,例如当线程2进来后走到这里,释放了锁之后,线程1才能再次进来
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
打印结果如下:
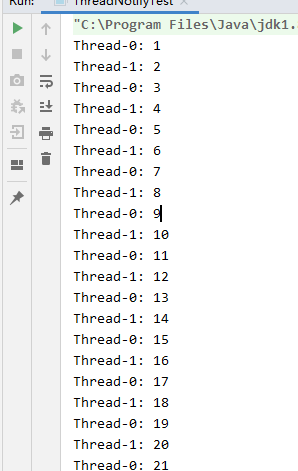
说明:
-
- 使用
wait()方法,用于阻塞当前线程,这个方法执行时会释放当前锁,而sleep()不会释放当前锁。
- 使用
-
- 使用
notify()方法,通知正在被阻塞的线程,将其唤醒,如果有多个线程被wait(),则优先唤醒优先级高的那个。
- 使用
-
- 使用
notifyAll()方法,通知并唤醒所有被wait()的线程。
- 使用
注意:
- 这几个方法,必须都在同步代码块,或者同步方法中。
- 这三个方法,调用者必须是 同步代码块 或 同步同步方法 中的 同步监视器。
例如:上述码中调用
notify和wait都是在this对象下的,即用的是this当锁的,如果重新起一个obj对象,this还是锁,使用obj.wait()肯定是不行的。
简单的来说,就是调用
notify和wait的对象,必须是当前锁对象。
- 这三个方法,不是在
Thread类中定义的,这三个方法,是在Object 类中定义的。因为任何一个对象都有这几个方法,即这几个方法在最终父类中。
如下代码:演示notify和 wait,必须是在当前锁对象下。
public class ThreadNotifyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number2 num = new Number2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(num);
Thread t2 = new Thread(num);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Number2 implements Runnable {
private int number = 1;
//使用obj对象充当当前锁。
Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (obj) {
obj.notify();
// this.notifyAll();//唤醒所有正在被wait的线程
if (number <= 100) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
number++;
try {
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
二、面试题
sleep 和wait有什么异同?
-
1.相同点:一旦执行方法,都可以使得当前线程进入阻塞状态。
-
2.不同点:
- 1)两个方法声明的位置不同,
Thread类中声明sleep(),Object类中声明wait() -
- 调用的要求不同:
sleep()可以在任何需要的场景下调用,wait()必须在同步代码块或同步方法中。
- 调用的要求不同:
-
- 如果两个方法都在同步监视器或同步方法中,
sleep不会释放锁,而wait会释放锁。
- 如果两个方法都在同步监视器或同步方法中,
- 1)两个方法声明的位置不同,


