一、引入
在java的实际开发过程中,我们可能需要在spring实例化一个bean的过程中,使用到初始化一个对象(bean)后立即初始化(加载)一些数据,或者在销毁一个对象之前进行执行一些事情等等。
因此Spring为我们提供了一系列的方式:
| 方式 | 初始化 init | 销毁destroy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | @bean 注解,指定属性initMethod | @bean 注解,指定属性destroyMethod |
| 2 | xml形式,指定 init-method | xml形式,指定 destroy-method |
| 3 | 实现InitializingBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet方法 | 实现DisposableBean接口,重写destroy方法 |
| 4 | 注解@PostConstruct | 注解@PreDestroy |
二、方式详解
- @bean 注解
@Bean(name="user",initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public User user(String name) {
return new User(name);
}
- xml形式
<bean id="user" class="com.demo.user" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
- 接口InitializingBean和DisposableBean
实现InitializingBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet()方法
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
实现DisposableBean方法,重写destroy方法
/**
* Interface to be implemented by beans that want to release resources
* on destruction. A BeanFactory is supposed to invoke the destroy
* method if it disposes a cached singleton. An application context
* is supposed to dispose all of its singletons on close.
*
* <p>An alternative to implementing DisposableBean is specifying a custom
* destroy-method, for example in an XML bean definition.
* For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the BeanFactory javadocs.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 12.08.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#close
*/
public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* Invoked by a BeanFactory on destruction of a singleton.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors.
* Exceptions will get logged but not rethrown to allow
* other beans to release their resources too.
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
- @PostConstruct和@PreDestroy
//初始化后执行的方法,必须为voidlei'xing类型
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
***do someThing
}
//bean销毁前执行的方法
@PreDestroy
public void init() {
***do someThing
}
从Java EE 5规范开始,Servlet中增加了两个影响Servlet生命周期的注解:@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy。
被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Serclet的inti()方法。被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在构造函数之后,init()方法之前运行。
被@PreDestroy修饰的方法会在服务器卸载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Servlet的destroy()方法。被@PreDestroy修饰的方法会在destroy()方法之后运行,在Servlet被彻底卸载之前。
三、总结
一)对Spring版本的要求
-
xml和实现接口的方式是Spring最原始的方式,Spring任何版本均支持
-
@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy需要Spring2.5及以上版本
-
@bean :需要Spring 3.0以上版本支持
二)执行顺序不一样
其中
此处引入Spring中bean生命周期的介绍
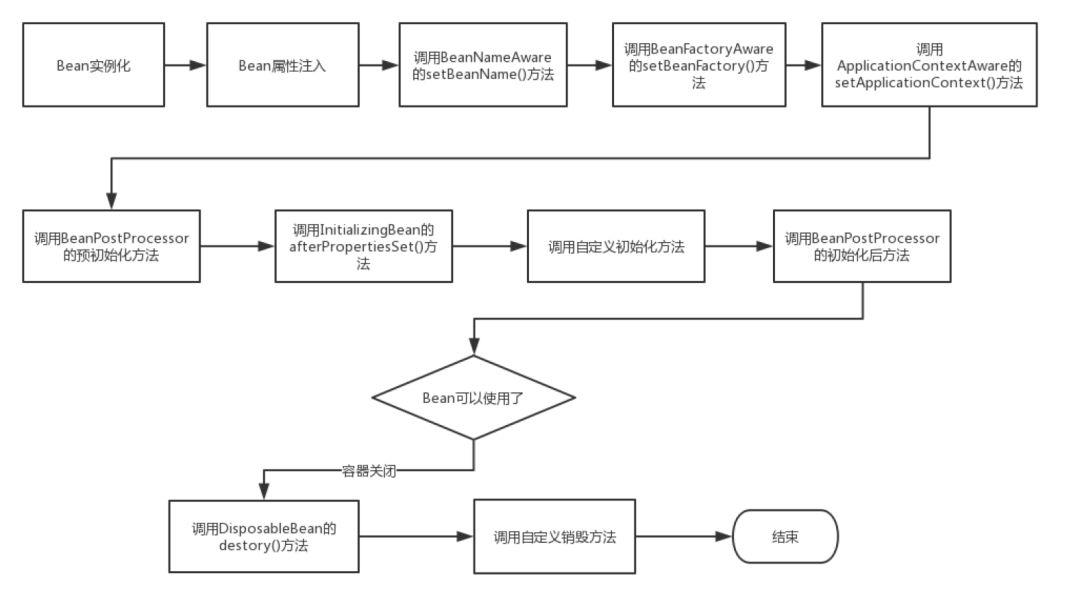 引自: 深究Spring中Bean的生命周期.
引自: 深究Spring中Bean的生命周期.
初始化之后执行顺序: @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > Beaninit-method(xml注解或者@Bean)
销毁之前执行顺序:@preDestroy > DisposableBean > destoryMethod(xml注解或者@Bean)





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2019-10-11 IDEA里maven不见了