OAuth2 密码模式下结合JWT
OAuth2 密码模式下结合JWT
前言
还记得在OAuth2概念的这张图吗?
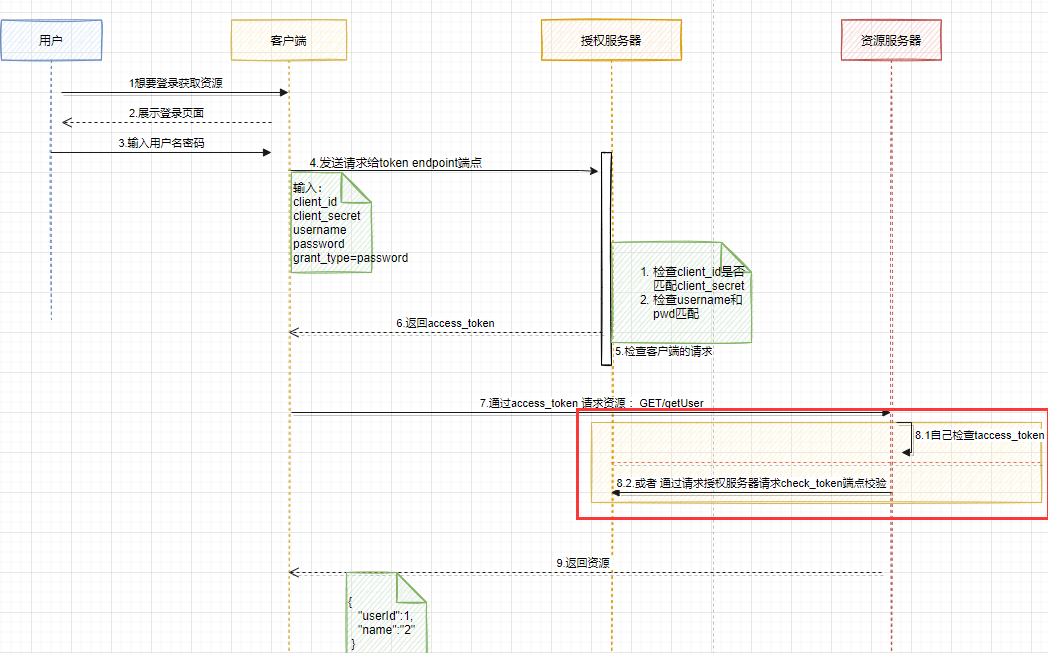
看到红框里面的,前面在写的代码是通过远程调用check_token 来进行校验access_token的,但是如果每次校验都交给授权服务器的话,会加重授权服务器的重担,所以资源服务器其实是可以自己校验的(图中8.1小点),例如通过JWT,(jwt相关的知识可以参考:jwt概念 jwt的生成)
一般来讲token的存储可以有如下几种:
- InMemoryTokenStore
- JdbcTokenStore
- JwtTokenStore
- RedisTokenStore
同样,代码先行的方式介绍Oauth2结合jwt
首先还是准备两个服务
授权服务
- SpringSecurity配置
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//密码管理器,可以认为是时间戳加盐的一种方式
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManager();
}
// @Bean
// public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(){
// return this.userDetailsService();
// }
/**
* 配置authenticationManager->providerManager->authenticationProvider->UserdetailServices->userDetails(存放的是用户信息)-》最终设置到
* SpringSecurityContextHolder
* 所以我们可以通过UserDetailService来得到用户信息,也可以将用信息存储在内存中,
* 像下面这样:可以在这里配置一些用户名和密码,以及用户所对应的权限
*
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().
withUser("hxx").
password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).authorities(Collections.emptyList())
.and().
withUser("wm").
password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).
authorities(new ArrayList<>(0));
}
//配置http
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//任何请求都需要验证
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
//配置web资源
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
super.configure(web);
}
}
- 授权服务配置,授权服务配置对比之前的配置就加了jwtTokenStore和jwtAccessTokenConverter
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
// @Autowired
// private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
//配置客户端
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory().
withClient("client1"). //客户端id
secret(passwordEncoder.encode("client_secret")) //客户端密码
.scopes("all")
.authorizedGrantTypes("password"); // 密码模式
}
//配置安全约束
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
security.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()").//<1> 访问check_token 不需要认证
tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()") //<2> 访问 token端点 不需要认证
.allowFormAuthenticationForClients();
}
//配置授权端点等配置
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)
.tokenStore(jwtTokenStore())
.accessTokenConverter(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter(){
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("hxx_key"); //<3> 设置 sign_key
return converter;
}
@Bean
public TokenStore jwtTokenStore(){
return new JwtTokenStore(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
}
资源服务
资源服务配置,对比之前的资源服务配置,也只是多了jwtTokenStore和jwtAccessTokenConverter
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourcesServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
// 配置资源服务的安全约束
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
//配置和授权服务器一样的tokenStore
resources.tokenStore(jwtTokenStore());
}
@Bean
public JwtTokenStore jwtTokenStore(){
return new JwtTokenStore(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter(){
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("hxx_key");
return converter;
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//任何请求都需要认证
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
测试
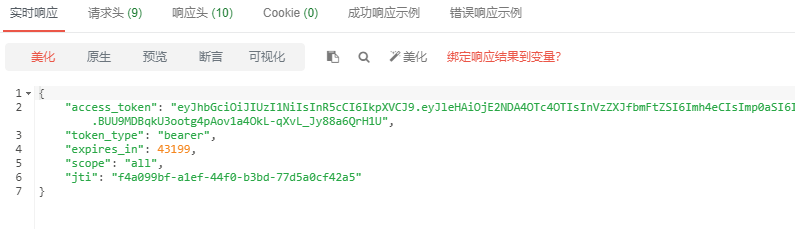
- 请求/oauth/token
返回
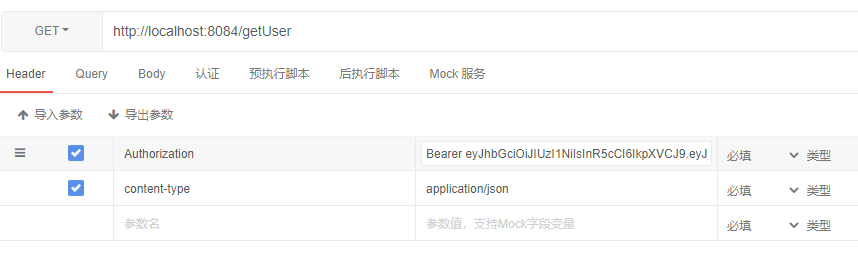
- 请求资源
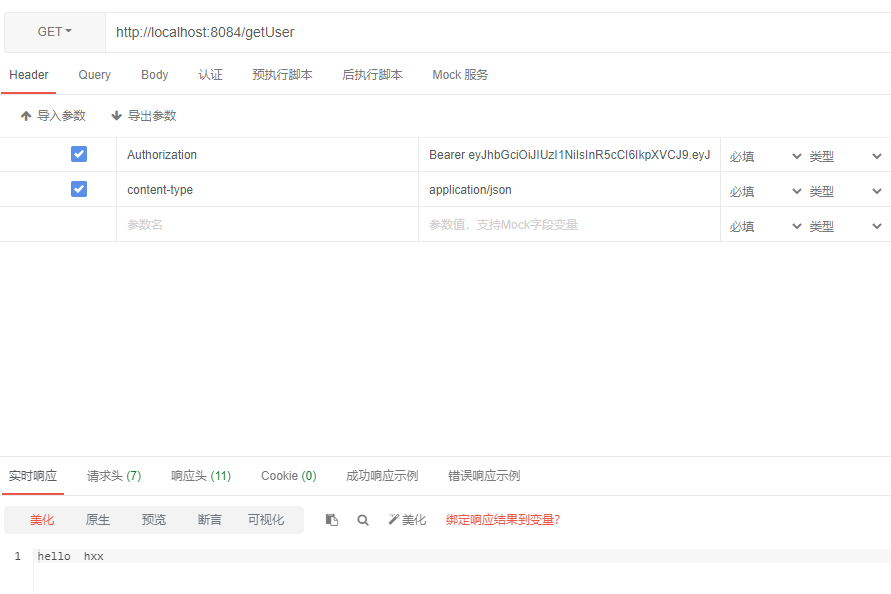
返回hello hxx
源码分析
请求/oauth/token
主要分析的是为什么通过jwtTokenStore就实现了生成token,和校验token的过程
生成token和之前在OAuth2 密码模式分析/oauth/token这一部分源码差不多,再认证成功后,看一下后面生成access_token的方法,重点看看DefaulTokenService的createAccessToken方法
public class DefaultTokenServices implements AuthorizationServerTokenServices, ResourceServerTokenServices,
ConsumerTokenServices, InitializingBean {
...//省略
private TokenStore tokenStore;
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
private TokenEnhancer accessTokenEnhancer;
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
/**
* Initialize these token services. If no random generator is set, one will be created.
*/
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(tokenStore, "tokenStore must be set");
}
@Transactional
public OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OAuth2AccessToken existingAccessToken = tokenStore.getAccessToken(authentication);
OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = null;
if (existingAccessToken != null) {
if (existingAccessToken.isExpired()) {
if (existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken() != null) {
refreshToken = existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken();
// The token store could remove the refresh token when the
// access token is removed, but we want to
// be sure...
tokenStore.removeRefreshToken(refreshToken);
}
tokenStore.removeAccessToken(existingAccessToken);
}
else {
// Re-store the access token in case the authentication has changed
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(existingAccessToken, authentication);
return existingAccessToken;
}
}
// Only create a new refresh token if there wasn't an existing one
// associated with an expired access token.
// Clients might be holding existing refresh tokens, so we re-use it in
// the case that the old access token
// expired.
if (refreshToken == null) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
// But the refresh token itself might need to be re-issued if it has
// expired.
else if (refreshToken instanceof ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) {
ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken expiring = (ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) refreshToken;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > expiring.getExpiration().getTime()) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
}
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = createAccessToken(authentication, refreshToken);//<1>
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(accessToken, authentication); //<2>
// In case it was modified
refreshToken = accessToken.getRefreshToken();
if (refreshToken != null) {
tokenStore.storeRefreshToken(refreshToken, authentication);
}
return accessToken;
}
...//省略
}
<1>通过DefaultTokenService 生成accessToken;
<2>通过JwtTokenStore存储token,但是实际上JwtTokenStore并不存储token,下面storeAccessToken实际上是一个空方法
@Override
public void storeAccessToken(OAuth2AccessToken token, OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
}
仔细看下DefaultTokenService#createAccessToken
private OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication, OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken) {
DefaultOAuth2AccessToken token = new DefaultOAuth2AccessToken(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
int validitySeconds = getAccessTokenValiditySeconds(authentication.getOAuth2Request());
if (validitySeconds > 0) {
token.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + (validitySeconds * 1000L)));
}
token.setRefreshToken(refreshToken);
token.setScope(authentication.getOAuth2Request().getScope());
return accessTokenEnhancer != null ? accessTokenEnhancer.enhance(token, authentication) : token;
}
因为在授权配置里面配置了相应的accessTokenConverter :
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter(){
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("hxx_key"); //<3> 设置 sign_key
return converter;
}
所以token的生成会由这个accessTokenEnhancer.enhance(token, authentication)来创建,具体看看acessTokenEnhancer.enhance()这个方法
public class JwtAccessTokenConverter implements TokenEnhancer, AccessTokenConverter, InitializingBean {
...//省略
public OAuth2AccessToken enhance(OAuth2AccessToken accessToken, OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
DefaultOAuth2AccessToken result = new DefaultOAuth2AccessToken(accessToken);
Map<String, Object> info = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(accessToken.getAdditionalInformation());
String tokenId = result.getValue();
if (!info.containsKey(TOKEN_ID)) {
info.put(TOKEN_ID, tokenId);
}
else {
tokenId = (String) info.get(TOKEN_ID);
}
result.setAdditionalInformation(info);
result.setValue(encode(result, authentication)); // <1>
OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = result.getRefreshToken();
if (refreshToken != null) {
DefaultOAuth2AccessToken encodedRefreshToken = new DefaultOAuth2AccessToken(accessToken);
encodedRefreshToken.setValue(refreshToken.getValue());
// Refresh tokens do not expire unless explicitly of the right type
encodedRefreshToken.setExpiration(null);
try {
Map<String, Object> claims = objectMapper
.parseMap(JwtHelper.decode(refreshToken.getValue()).getClaims());
if (claims.containsKey(TOKEN_ID)) {
encodedRefreshToken.setValue(claims.get(TOKEN_ID).toString());
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
}
Map<String, Object> refreshTokenInfo = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(
accessToken.getAdditionalInformation());
refreshTokenInfo.put(TOKEN_ID, encodedRefreshToken.getValue());
refreshTokenInfo.put(ACCESS_TOKEN_ID, tokenId);
encodedRefreshToken.setAdditionalInformation(refreshTokenInfo);
DefaultOAuth2RefreshToken token = new DefaultOAuth2RefreshToken(
encode(encodedRefreshToken, authentication));
if (refreshToken instanceof ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) {
Date expiration = ((ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) refreshToken).getExpiration();
encodedRefreshToken.setExpiration(expiration);
token = new DefaultExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken(encode(encodedRefreshToken, authentication), expiration);
}
result.setRefreshToken(token);
}
return result;
}
...//省略
}
<1>result.setValue(encode(result, authentication)), 这个就是来设置access_token的值的,通过JwtHelper工具类来生成这个access_token(这样就完成了对access_token的加密)。后面我们调用来验证前端传递的access_token的时候,是靠什么来校验的呢?
protected String encode(OAuth2AccessToken accessToken, OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
String content;
try {
content = objectMapper.formatMap(tokenConverter.convertAccessToken(accessToken, authentication));
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot convert access token to JSON", e);
}
String token = JwtHelper.encode(content, signer).getEncoded();
return token;
}
其实看到前面的关于Jwt的文章可以知道,它最终是靠JwtHelper.decodeAndVerify()方法解密的,解析access_token
protected Map<String, Object> decode(String token) {
try {
Jwt jwt = JwtHelper.decodeAndVerify(token, verifier);
String claimsStr = jwt.getClaims();
Map<String, Object> claims = objectMapper.parseMap(claimsStr);
if (claims.containsKey(EXP) && claims.get(EXP) instanceof Integer) {
Integer intValue = (Integer) claims.get(EXP);
claims.put(EXP, new Long(intValue));
}
this.getJwtClaimsSetVerifier().verify(claims);
return claims;
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new InvalidTokenException("Cannot convert access token to JSON", e);
}
}
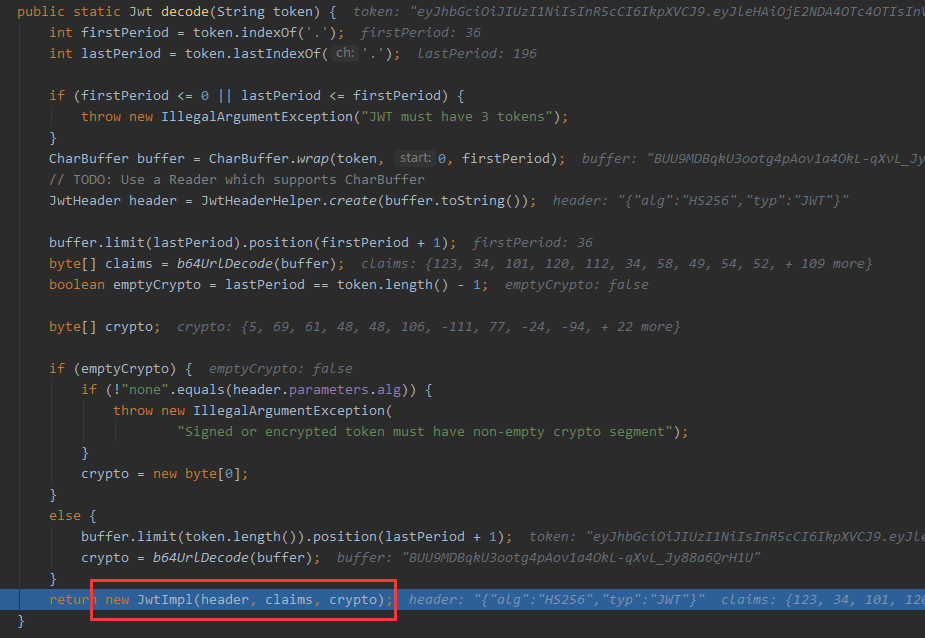
然后再通过生成的jwt里面的crypto和计算出的signingInput() 进行比对:verifier.verify(signingInput(), crypto);
public static Jwt decodeAndVerify(String token, SignatureVerifier verifier) {
Jwt jwt = decode(token); // <1> 解析计算出jwt,三个部分都计算出来,并给crypto赋值,crypto可以认为就是
签名signature部分
jwt.verifySignature(verifier); // <2> 校验比对签名
return jwt;
}
@Override
public void verifySignature(SignatureVerifier verifier) {
verifier.verify(signingInput(), crypto);
}
private byte[] signingInput() {
return concat(b64UrlEncode(header.bytes()), JwtHelper.PERIOD,
b64UrlEncode(content));
}
请求资源 GET: /getUser header: Authorization Bearer access_token
我们知道在SpringSecurity中,任何请求都逃不过OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter过滤器,任何请求都经过它,
public class OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter implements Filter, InitializingBean {
...//省略
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException,
ServletException {
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
final HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
final HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
Authentication authentication = tokenExtractor.extract(request);
if (authentication == null) {
if (stateless && isAuthenticated()) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Clearing security context.");
}
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("No token in request, will continue chain.");
}
}
else {
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_VALUE, authentication.getPrincipal());
if (authentication instanceof AbstractAuthenticationToken) {
AbstractAuthenticationToken needsDetails = (AbstractAuthenticationToken) authentication;
needsDetails.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
}
Authentication authResult = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication success: " + authResult);
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(authResult);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
}
}
catch (OAuth2Exception failed) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed);
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationFailure(new BadCredentialsException(failed.getMessage(), failed),
new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken("access-token", "N/A"));
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(failed.getMessage(), failed));
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
...// 省略
}
看看tokenExtractor#extract 方法,就是用它来进行解析我们前端的access_token 。
public class BearerTokenExtractor implements TokenExtractor {
private final static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(BearerTokenExtractor.class);
@Override
public Authentication extract(HttpServletRequest request) {
String tokenValue = extractToken(request);
if (tokenValue != null) {
PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken authentication = new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken(tokenValue, "");
return authentication;
}
return null;
}
protected String extractToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
// first check the header...
String token = extractHeaderToken(request);
// bearer type allows a request parameter as well
if (token == null) {
logger.debug("Token not found in headers. Trying request parameters.");
token = request.getParameter(OAuth2AccessToken.ACCESS_TOKEN);
if (token == null) {
logger.debug("Token not found in request parameters. Not an OAuth2 request.");
}
else {
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_TYPE, OAuth2AccessToken.BEARER_TYPE);
}
}
return token;
}
/**
* Extract the OAuth bearer token from a header.
*
* @param request The request.
* @return The token, or null if no OAuth authorization header was supplied.
*/
protected String extractHeaderToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
Enumeration<String> headers = request.getHeaders("Authorization");
while (headers.hasMoreElements()) { // typically there is only one (most servers enforce that)
String value = headers.nextElement();
if ((value.toLowerCase().startsWith(OAuth2AccessToken.BEARER_TYPE.toLowerCase()))) {
String authHeaderValue = value.substring(OAuth2AccessToken.BEARER_TYPE.length()).trim();
// Add this here for the auth details later. Would be better to change the signature of this method.
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_TYPE,
value.substring(0, OAuth2AccessToken.BEARER_TYPE.length()).trim());
int commaIndex = authHeaderValue.indexOf(',');
if (commaIndex > 0) {
authHeaderValue = authHeaderValue.substring(0, commaIndex);
}
return authHeaderValue;
}
}
return null;
}
}
如果我们是头部放了access_token,就会用这个extractHeaderToken方法来解析了,不过这段代码也很简单就是通过header来获取accessToken 然后返回这个access_token字符串而已。
获取到access_token成功后,通过Authentication类封装,然后交由SpringSecurity去校验真伪:authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);
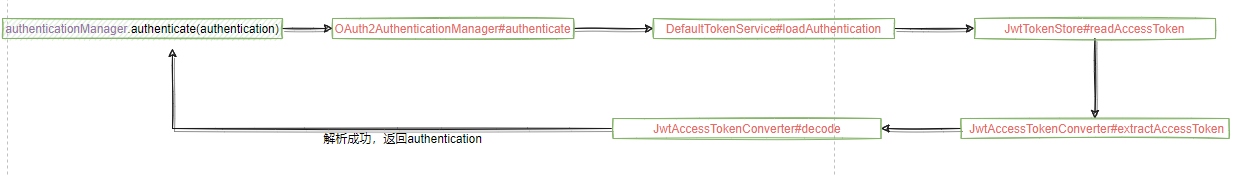
这样后面会写到SpringSecurity相关的内容,推荐江南一点雨关于SpringSecurity的文章
本文作者:hu_volsnow
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/volsnow/p/15752221.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步