
import numpy as np
from .metrics import accuracy_score
# accuracy_score方法:查看准确率
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Logistic Regression模型"""
self.coef_ = None
self.intercept_ = None
self._theta = None
def _sigmiod(self, t):
"""函数名首部为'_',表明该函数为私有函数,其它模块不能调用"""
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-t))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):
"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Logistic Regression模型"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
def J(theta, X_b, y):
y_hat = self._sigmiod(X_b.dot(theta))
try:
return - np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)) / len(y)
except:
return float('inf')
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
return X_b.T.dot(self._sigmiod(X_b.dot(theta)) - y) / len(X_b)
def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
cur_iter = 0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):
break
cur_iter += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict_proda(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回 X_predict 中的样本的发生的概率向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return self._sigmiod(X_b.dot(self._theta))
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的分类结果的向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
proda = self.predict_proda(X_predict)
# proda:单个待预测样本的发生概率
# proda >= 0.5:返回元素为布尔类型的向量;
# np.array(proda >= 0.5, dtype='int'):将布尔数据类型的向量转化为元素为 int 型的数组,则该数组中的 0 和 1 代表两种不同的分类类别;
return np.array(proda >= 0.5, dtype='int')
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
# 分类问题的化,查看标准是分类的准确度:accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
"""实例化类之后,输出显示 LogisticRegression()"""
return "LogisticRegression()"

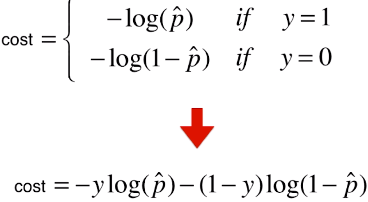
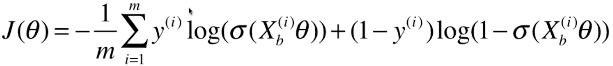
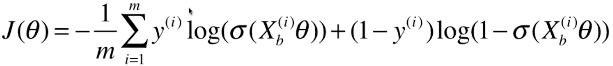
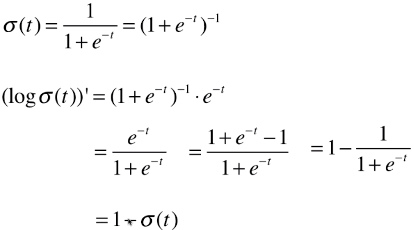
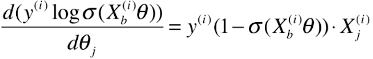

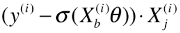
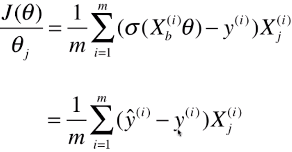

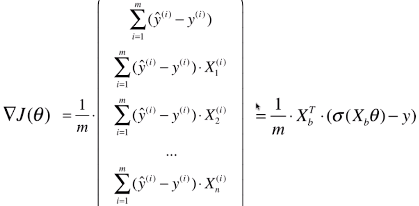


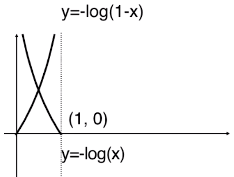
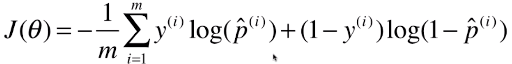
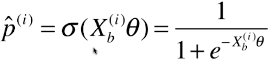

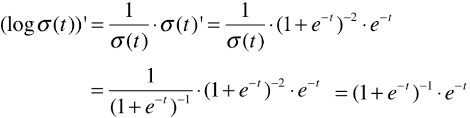
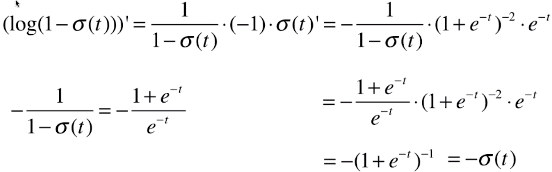




· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决