黑盒测试的等价类划分法软件测试
黑盒测试中,最理想的就是穷举输入测试了,然而这在现实中是不可能办到的。于是,找到一种正确而有效且实用性强的测试方法也就很重要了。在常见的黑盒测试中,有一种叫做等价类划分法。
所谓等价类是指输入域的某个互不相交的子集合,所有等价类的并集便是整个输入域。目的在于测试用例的无冗余性。分为有效等价类和无效等价类。
有效等价类:检验程序是否实现了规格说明预先规定的功能和性能。
无效等价类:检查软件功能和性能的实现是否有不符合规格说明要求的地方。
划分等价类( valid / invalid )
(1)有效等价类:检验程序是否实现了规格说明预先规定的功能和性能。
(2)无效等价类:检查软件功能和性能的实现是否有不符合规格说明要求的地方。
常用的等价类划分原则
(1)按区间划分
可以确定一个有效等价类、两个无效等价类。
(2)按数值划分
如果输入条件规定了输入数据的一组可能的值,而且程序是用不同的方式处理每一种值,则可为每一种值划分一个有效等价类,并划分一个无效等价类。
(3)按数值集合划分
规格说明中规定了输入值的集合,则可以确定一个有效等价类,并划分一个无效等价类。
(4)按限制条件或规则划分
规格说明中规定了输入数据必须遵守的规则和限制条件,则可以确立一个有效等价类(符合规则)和若干个(≥ 1)无效等价类(不同角度的违反规则)。
(5)细分等价类
如果我们确知,已划分的某等价类中的各元素(例子)在程序中的处理方式是不同的,则应据此将此等价类进一步划分成更小的等价类。
等价类测试用例设计
(1)在确立了等价类之后,可列出所有划分出的等价类表。
(2)为每一个等价类规定一个唯一的编号。
(3)设计一个新的测试用例,使其尽可能多地覆盖尚未覆盖的有效等价类。重复这一步,直到测试用例覆盖了所有的有效等价类。
(4)设计一个新的测试用例,使其覆盖且只覆盖一个尚未覆盖的无效等价类。重复这一步,直到测试用例覆盖了所有的无效等价类。
软件测试:
允许1到6个英文字符或数字,按提交结束。
有效等价类:
长度:1到6
字符:a-z,A-Z,0-9
无效等价类
长度:0,7
字符:英文/数字以外字符,控制字符,标点符号
等价类划分
| 编号 | 有效等价类 | 编号 | 无效等价类 |
| 1 | 长度<6 | 5 | 长度=0或>7 |
| 2 | 数字 | 6 | 控制字符,标点符号 |
| 3 | 小写英文字母 | ||
| 4 | 大写英文字母 |
测试用例
|
用例 |
覆盖等价类 | 结果 |
| asdf | 1,3 | |
| ASfdsf | 1,2,4 | |
| asd123 | 1,2,3 | |
| Ght555 | 1,2,3,4 | |
| 5 | ||
| 123!s | 1,2,3,6 | |
| yU12? | 1,2,3,4,6 | |
|
asdfghhh |
3,5 |





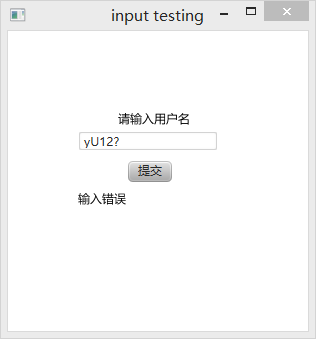


输入框与测试部分源码
1 import javafx.application.Application; 2 import javafx.event.ActionEvent; 3 import javafx.event.EventHandler; 4 import javafx.scene.Scene; 5 import javafx.scene.control.Button; 6 import javafx.scene.control.TextField; 7 import javafx.scene.layout.AnchorPane; 8 import javafx.scene.text.Text; 9 import javafx.stage.Stage; 10 11 12 public class testing extends Application { 13 14 public static void main(String[ ] args) { 15 testing.launch( args ); 16 } 17 public void start( Stage primaryStage ) { 18 primaryStage.setTitle( "input testing" ); 19 AnchorPane root = new AnchorPane(); 20 21 Text text = new Text("请输入用户名"); 22 final Text text2 = new Text(""); 23 24 final TextField intext = new TextField(""); 25 intext.setMaxSize(140, 20); 26 root.getChildren().addAll(text,text2,intext); 27 AnchorPane.setTopAnchor(text, 80.0); 28 AnchorPane.setLeftAnchor(text, 110.0); 29 AnchorPane.setTopAnchor(text2, 160.0); 30 AnchorPane.setLeftAnchor(text2, 70.0); 31 AnchorPane.setTopAnchor(intext, 100.0); 32 AnchorPane.setLeftAnchor(intext, 70.0); 33 Button btn = new Button("提交"); 34 root.getChildren().addAll(btn); 35 AnchorPane.setTopAnchor(btn, 130.0); 36 AnchorPane.setLeftAnchor(btn, 120.0); 37 38 btn.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() { 39 public void handle(ActionEvent arg0) { 40 if(check(intext.getText().toString())){ 41 text2.setText("输入正确"); 42 } 43 else{ 44 text2.setText("输入错误"); 45 } 46 } 47 }); 48 49 primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(root,300,300)); 50 primaryStage.show( ); 51 } 52 public boolean check(String str){ 53 char array[] = new char[str.length()]; 54 array = str.toCharArray(); 55 if (str.length() < 1 || str.length() > 6) 56 return false; 57 if (str.length() != 0){ 58 for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){ 59 if(!((array[i]>='a' && array[i]<='z')||(array[i]>='A' && array[i]<='Z')||(array[i]>='0' && array[i]<='9'))) 60 return false; 61 } 62 } 63 return true; 64 } 65 66 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号