自动建库建表
❓实现数据库随代码自动维护,包含建库建表操作自动建库
自动建库
引入依赖
<!-- mysql驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot jdbc框架-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- hutool db-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-db</artifactId>
<version>${hutool.version}</version>
</dependency>
通过监听SpringBoot的生命周期,在Environment准备完毕后调用建库方法
🎯目的
- 在建表前先判断是否有库,没有则建库,防止数据源导致报错
- 从Environment中获取application.yml中的数据库配置信息
- 将配置信息中的数据库名替换成默认一定存在的mysql库,用mysql数据源创建application.yml中配置的数据库
核心代码如下
@Slf4j
public class DBInitializer{
public DBInitializer(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
public void initialDB(){
String name = environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.name");
String url = environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.url");
String username = environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.username");
String password = environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.password");
//读取类路径下的文件
String mysqlUrl = url.replace(name, "mysql");
SimpleDataSource mysqlDb = new SimpleDataSource(mysqlUrl, username, password);
try {
List<Entity> schemaNameList = Db.use(mysqlDb).find(Entity.create("information_schema.SCHEMATA").set("SCHEMA_NAME", name));
if (schemaNameList.isEmpty()){//不存在该数据库
log.info("\n========================================\n" +
"db:{} does not exist begin to initialize\n" +
"========================================",name);
String createDbSql = "CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `"+name+"` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = `utf8` COLLATE `utf8_general_ci`;";
int execute = Db.use(mysqlDb).execute(createDbSql);
if (execute>0){
log.info("\n...create db : {} success, next step => switch dataSource and execute initSql...",name);
}
}else {
log.info("\n========================================\n" +
"db:{} has already existed \n" +
"========================================",name);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(ThrowableUtil.getStackTrace(e));
}
}
}
在生命周期中调用核心代码
@Slf4j
public class MySpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
public MySpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
}
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.starting(bootstrapContext);
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
new DBInitializer(environment).initialDB();
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.contextPrepared(context);
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.contextLoaded(context);
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.started(context, timeTaken);
}
@Override
public void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.ready(context, timeTaken);
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
SpringApplicationRunListener.super.failed(context, exception);
}
}
注册监听器
在resource目录下创建META-INF文件夹,并在该文件夹中创建spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=com.xxx.MySpringApplicationRunListener
自动建表
基于flyway
引入依赖
注意版本号,实测7.1.1可以兼容mysql5.7, springboot本身的依赖群中定义了flyway的版本号过高的话可能不兼容低版本的数据库
<!--指定flyway版本为7.1.1兼容Mysql5.7-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
<version>${flyway.version}</version>
</dependency>
配置说明
spring:
flyway:
# 启用或禁用 flyway
enabled: true
# SQL 脚本的目录,多个路径使用逗号分隔 默认值 classpath:db/migration
locations: classpath:db/migration
# metadata 版本控制信息表 默认 flyway_schema_history
table: flyway_schema_history
# 如果没有 flyway_schema_history 这个 metadata 表, 在执行 flyway migrate 命令之前, 必须先执行 flyway baseline 命令
# 设置为 true 后 flyway 将在需要 baseline 的时候, 自动执行一次 baseline。
baseline-on-migrate: true
# 指定 baseline 的版本号,默认值为 1, 低于该版本号的 SQL 文件, migrate 时会被忽略
baseline-version: 0
# 字符编码 默认 UTF-8
encoding: UTF-8
# 是否允许不按顺序迁移 开发建议 true 生产建议 false
out-of-order: false
# 需要 flyway 管控的 schema list,这里我们配置为flyway 缺省的话, 使用spring.datasource.url 配置的那个 schema,可以指定多个schema, 但仅会在第一个schema下建立 metadata 表, 也仅在第一个schema应用migration sql 脚本. 但flyway Clean 命令会依次在这些schema下都执行一遍. 所以 确保生产 spring.flyway.clean-disabled 为 true
# schemas: flyway
# 执行迁移时是否自动调用验证 checkNum 当你的 版本不符合逻辑 比如 你先执行了 DML 而没有 对应的DDL 会抛出异常
validate-on-migrate: true
# flyway 的 clean 命令会删除指定 schema 下的所有 table, 生产务必禁掉。这个默认值是 false 理论上作为默认配置是不科学的。
clean-disabled: true
#当发现校验错误时是否自动调用clean,默认false.
clean-on-validation-error: false
使用sql脚本来维护数据库
以上述配置文件为例,locations: classpath:db/migration定义了类路径下的db/migration为sql脚本的目录
在该目录下可以添加数据库迭代文件,常用的有两种
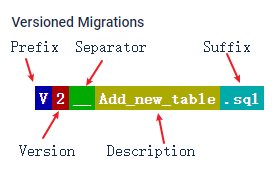
1.以V开头的具有明确版本号的sql脚本
格式:
- 前缀为
V - 后面跟着版本号,这里可以用日期
202401090000,也可以用数字1,2... - 然后是分隔符
__注意必须是双下划线 - 在后面是描述,添加新的表,插入新的数据等
- 后缀是
.sql
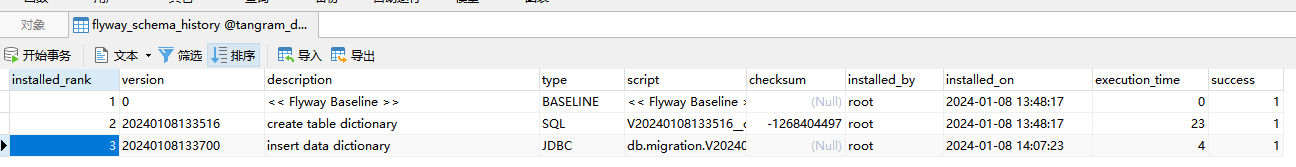
机制:
flyway的生态维护了一张flyway_schema_history的表格
只要项目中的sql脚本的版本号大于最后一条记录该脚本就会被执行
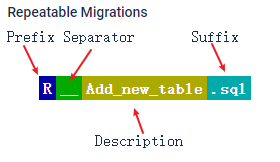
2.以R开头的可以重复执行的sql脚本
格式:
- 前缀为R
- 后面跟着分隔符号
__ - 描述
- 后缀
.sql
机制:
只要R开头的文件发生改变,flyway就会重新执行该sql脚本文件
注意,该脚本一定要具有可重复执行的特性
使用Java脚本来维护数据库
project
|- src
|- main
|- java
|-com
|-db
|-migration
|-Vxxx__type_do_something.java
在项目的src/main/java/com的同级目录,创建db/migration目录
并创建命名规则同上述所说的Java类,可以通过Java脚本的方式更加灵活的定制数据库维护策略
以下代码为示例:
@Slf4j
public class V20240108133700__insert_data_dictionary extends BaseJavaMigration {
@Override
public void migrate(Context context) throws Exception {
log.info("test flyway base java migration");
try (Statement statement = context.getConnection().createStatement()) {
try (ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from table_dictionary")) {
if (!resultSet.next()){//不存在数据
statement.execute("INSERT INTO `tangram_db`.`table_dictionary` ( `id`, `param_name`, `param_key`, `param_value`, `param_describe`, `sort` )\n" +
"VALUES\n" +
"\t( 1, '测试', 'test', 'test', '参数描述', 1 );");
}
}
}
}
}
基于jpa
引入依赖
<!-- jpa 用来维护表结构-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置说明
application.yml
spring:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
# ddl-auto:create----每次运行该程序,没有表格会新建表格,表内有数据会清空
# ddl-auto:create-drop----每次程序结束的时候会清空表
# ddl-auto:update----每次运行程序,没有表格会新建表格,表内有数据不会清空,只会更新
# ddl-auto:validate----运行程序会校验数据与数据库的字段类型是否相同,不同会报错
实体类配置
@Data//lombok
@Entity//标注实体类
@NoArgsConstructor//lombok 无参
@AllArgsConstructor//lombok 全参
@Table(name="user") //jpa自动创建表
@TableName(value = "user")//mybatis plus
public class User {
@Id//标注主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)//主键策略
@TableId//mybatis plus 标注主键
private Long id;
@Column(name = "username")//标注字段名
@TableField(value = "username")//mybatis plus
private String username;
@Column(name = "password")
@TableField(value = "password")
private String password;
@Column(name = "telephone_number",unique = true)
@TableField(value = "telephone_number")
private String telephoneNumber;
@Column(name = "age")
@TableField(value = "age")
private Integer age;
@Column(name = "create_time")
@TableField(value = "create_time")
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@Column(name = "update_time")
@TableField(value = "update_time")
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号