Activity的生命周期
我们已经多次使用Activity,今天我们来讲讲一个重要的概念,Activity的生命周期。
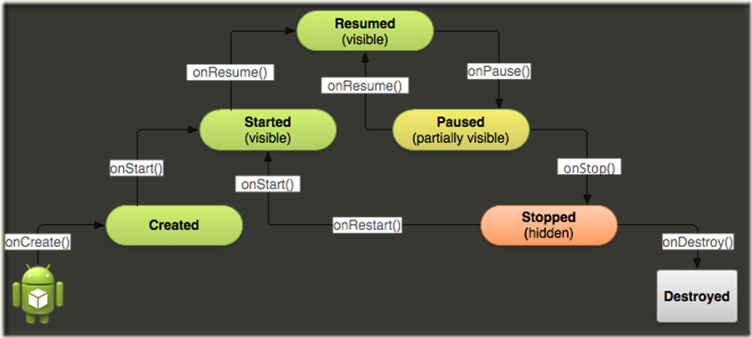
Activity的创建,暂停,销毁等动作,都是由Android系统统一管理的(在Framework里有一个叫ActivityManager的Service). 我们来看一张图:
这是一张Activity的生命周期图,Activity一共有六个状态:
Created,Started,Resumed,Paused,Stopped,Destoryed
关键的是这三个:
Resumed 这个时候,Activity是在最前面的,并且用户可以与之交互。
Paused 这个状态是指,当需要切换到另外一个Activity的时候,当前界面正在消失又未完全消失时(部分可见)。在这个状态下,Activity是不会接收用户事件和执行代码的。
Stopped 这个状态时,界面是完全不可见了。此时Activity的状态信息会被保留起来,但是不会执行任何代码。
当有一个Intent 要启动某个Activity而且这时并没有该Activity的对象实现时,onCreate方法会被调用,我们一般会在onCreate方法中做一些初始化的工作,例如设置ContentView, 为View变量获取实例,然后onStart(), onResume()会被调用,需要注意的是在onStart(), onResume()方法中, 不宜放置耗时的代码。在到达started状态后, Activity就变成可见了。
所有onXXXX的都是Activity类里面有的方法,子类可以重载。
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); } @Override protected void onRestart() { super.onRestart(); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); }
注意: