4.Ceres官方教程-非线性最小二乘~Curve Fitting(曲线拟合)
1.Curve Fitting
到目前为止,我们看到的示例都是没有数据的简单优化问题。最小二乘和非线性最小二乘分析的原始目的是对数据进行曲线拟合。
接下来将介绍曲线拟合的问题。采样点是根据曲线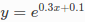 生成的,并且添加标准差σ=0.2的高斯噪声。我们用下列带未知参数的方程来拟合这些采样点:
生成的,并且添加标准差σ=0.2的高斯噪声。我们用下列带未知参数的方程来拟合这些采样点:
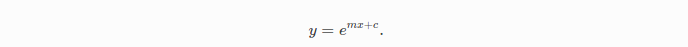
首先定义一个模板对象来计算残差。每一个观察值(采样点)都有一个残差。
struct ExponentialResidual {
ExponentialResidual(double x, double y)
: x_(x), y_(y) {}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const m, const T* const c, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = y_ - exp(m[0] * x_ + c[0]);
return true;
}
private:
// Observations for a sample.
const double x_;
const double y_;
};
假设观测数据是一个名为data的2n大小的的数组,为每一个观察值创建一个CostFunction的问题(problem)构造是一个简单的事。
double m = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < kNumObservations; ++i) {
CostFunction* cost_function =
new AutoDiffCostFunction<ExponentialResidual, 1, 1, 1>(
new ExponentialResidual(data[2 * i], data[2 * i + 1]));
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, nullptr, &m, &c);
}
// 与Hello World的f(x)=10−x对比:
struct CostFunctor {
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = T(10.0) - x[0];
return true;
}
};
CostFunction* cost_function =
new AutoDiffCostFunction<CostFunctor, 1, 1>(new CostFunctor);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL, &x);
/*
对比结果:
1.在Hello World中,CostFunctor中是没有(显式)构造函数的,也就同样没有了初始值。所以在构造对象时,可以直接New CostFunctor。而在本节的例子中,构造对象时还要加上初始值,即
new ExponentialResidual(data[2 * i], data[2 * i + 1]));
2.在AutoDiffCostFunction的模板中,本例中一共有三个1,而在Hello World中,只有两个1,即residual和x的维度。注意先是残差,后是输入参数,而且一一对应。
*/
示例代码在examples/curve_fitting.cc中
#include "ceres/ceres.h"
#include "glog/logging.h"
using ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction;
using ceres::CostFunction;
using ceres::Problem;
using ceres::Solver;
using ceres::Solve;
// Data generated using the following octave code.
// randn('seed', 23497);
// m = 0.3;
// c = 0.1;
// x=[0:0.075:5];
// y = exp(m * x + c);
// noise = randn(size(x)) * 0.2;
// y_observed = y + noise;
// data = [x', y_observed'];
const int kNumObservations = 67;
const double data[] = {
0.000000e+00, 1.133898e+00,
7.500000e-02, 1.334902e+00,
1.500000e-01, 1.213546e+00,
2.250000e-01, 1.252016e+00,
3.000000e-01, 1.392265e+00,
3.750000e-01, 1.314458e+00,
4.500000e-01, 1.472541e+00,
5.250000e-01, 1.536218e+00,
6.000000e-01, 1.355679e+00,
6.750000e-01, 1.463566e+00,
7.500000e-01, 1.490201e+00,
8.250000e-01, 1.658699e+00,
9.000000e-01, 1.067574e+00,
9.750000e-01, 1.464629e+00,
1.050000e+00, 1.402653e+00,
1.125000e+00, 1.713141e+00,
1.200000e+00, 1.527021e+00,
1.275000e+00, 1.702632e+00,
1.350000e+00, 1.423899e+00,
1.425000e+00, 1.543078e+00,
1.500000e+00, 1.664015e+00,
1.575000e+00, 1.732484e+00,
1.650000e+00, 1.543296e+00,
1.725000e+00, 1.959523e+00,
1.800000e+00, 1.685132e+00,
1.875000e+00, 1.951791e+00,
1.950000e+00, 2.095346e+00,
2.025000e+00, 2.361460e+00,
2.100000e+00, 2.169119e+00,
2.175000e+00, 2.061745e+00,
2.250000e+00, 2.178641e+00,
2.325000e+00, 2.104346e+00,
2.400000e+00, 2.584470e+00,
2.475000e+00, 1.914158e+00,
2.550000e+00, 2.368375e+00,
2.625000e+00, 2.686125e+00,
2.700000e+00, 2.712395e+00,
2.775000e+00, 2.499511e+00,
2.850000e+00, 2.558897e+00,
2.925000e+00, 2.309154e+00,
3.000000e+00, 2.869503e+00,
3.075000e+00, 3.116645e+00,
3.150000e+00, 3.094907e+00,
3.225000e+00, 2.471759e+00,
3.300000e+00, 3.017131e+00,
3.375000e+00, 3.232381e+00,
3.450000e+00, 2.944596e+00,
3.525000e+00, 3.385343e+00,
3.600000e+00, 3.199826e+00,
3.675000e+00, 3.423039e+00,
3.750000e+00, 3.621552e+00,
3.825000e+00, 3.559255e+00,
3.900000e+00, 3.530713e+00,
3.975000e+00, 3.561766e+00,
4.050000e+00, 3.544574e+00,
4.125000e+00, 3.867945e+00,
4.200000e+00, 4.049776e+00,
4.275000e+00, 3.885601e+00,
4.350000e+00, 4.110505e+00,
4.425000e+00, 4.345320e+00,
4.500000e+00, 4.161241e+00,
4.575000e+00, 4.363407e+00,
4.650000e+00, 4.161576e+00,
4.725000e+00, 4.619728e+00,
4.800000e+00, 4.737410e+00,
4.875000e+00, 4.727863e+00,
4.950000e+00, 4.669206e+00,
};
struct ExponentialResidual {
ExponentialResidual(double x, double y)
: x_(x), y_(y) {}
template <typename T> bool operator()(const T* const m,
const T* const c,
T* residual) const {
residual[0] = y_ - exp(m[0] * x_ + c[0]);
return true;
}
private:
const double x_;
const double y_;
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
double m = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < kNumObservations; ++i) {
problem.AddResidualBlock(
new AutoDiffCostFunction<ExponentialResidual, 1, 1, 1>(
new ExponentialResidual(data[2 * i], data[2 * i + 1])),
NULL,
&m, &c);
}
Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 25;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
Solver::Summary summary;
Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << "\n";
std::cout << "Initial m: " << 0.0 << " c: " << 0.0 << "\n";
std::cout << "Final m: " << m << " c: " << c << "\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果如下
iter cost cost_change |gradient| |step| tr_ratio tr_radius ls_iter iter_time total_time
0 1.211734e+02 0.00e+00 3.61e+02 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 1.00e+04 0 3.02e-04 3.58e-04
1 2.334822e+03 -2.21e+03 0.00e+00 7.52e-01 -1.87e+01 5.00e+03 1 1.20e-04 5.07e-04
2 2.331438e+03 -2.21e+03 0.00e+00 7.51e-01 -1.86e+01 1.25e+03 1 1.20e-05 5.27e-04
3 2.311313e+03 -2.19e+03 0.00e+00 7.48e-01 -1.85e+01 1.56e+02 1 9.55e-06 5.41e-04
4 2.137268e+03 -2.02e+03 0.00e+00 7.22e-01 -1.70e+01 9.77e+00 1 8.88e-06 5.54e-04
5 8.553131e+02 -7.34e+02 0.00e+00 5.78e-01 -6.32e+00 3.05e-01 1 2.82e-05 5.86e-04
6 3.306595e+01 8.81e+01 4.10e+02 3.18e-01 1.37e+00 9.16e-01 1 3.10e-04 9.01e-04
7 6.426770e+00 2.66e+01 1.81e+02 1.29e-01 1.10e+00 2.75e+00 1 2.64e-04 1.17e-03
8 3.344546e+00 3.08e+00 5.51e+01 3.05e-02 1.03e+00 8.24e+00 1 2.63e-04 1.44e-03
9 1.987485e+00 1.36e+00 2.33e+01 8.87e-02 9.94e-01 2.47e+01 1 2.68e-04 1.71e-03
10 1.211585e+00 7.76e-01 8.22e+00 1.05e-01 9.89e-01 7.42e+01 1 2.63e-04 1.98e-03
11 1.063265e+00 1.48e-01 1.44e+00 6.06e-02 9.97e-01 2.22e+02 1 2.63e-04 2.25e-03
12 1.056795e+00 6.47e-03 1.18e-01 1.47e-02 1.00e+00 6.67e+02 1 2.63e-04 2.52e-03
13 1.056751e+00 4.39e-05 3.79e-03 1.28e-03 1.00e+00 2.00e+03 1 2.62e-04 2.78e-03
trust_region_minimizer.cc:707 Terminating: Function tolerance reached. |cost_change|/cost: 3.541695e-08 <= 1.000000e-06
Ceres Solver Report: Iterations: 14, Initial cost: 1.211734e+02, Final cost: 1.056751e+00, Termination: CONVERGENCE
Initial m: 0 c: 0
Final m: 0.291861 c: 0.131439
参数的初始值为m=0,c=0,代价函数为1.211734e+02。最后的解是m=0.291861,c=0.131439,代价函数值是1.056751e+00。
这些解和原始值m=0.3,c=0.1有一些细微的差别,但是是合理的(因为添加了高斯噪声)。当从噪声数据重建曲线时,我们预计会看到这样的偏差。
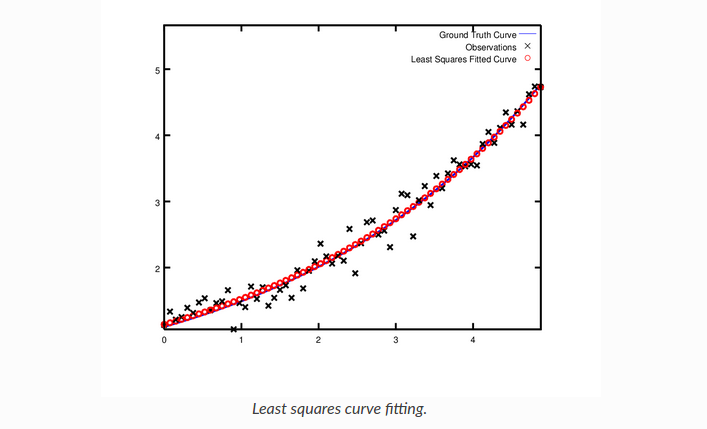
实际上,如果您要对m=0.3,c=0.1的目标函数进行评估,那么当目标函数值为1.082425时,拟合效果会更差。下图说明了适合度。
2.Robust Curve Fitting
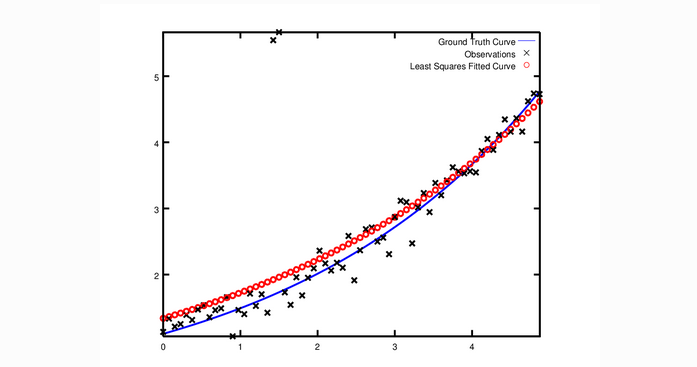
现在假设我们给出的数据有一些异常值,也就是说,我们有一些点不服从噪声模型。如果我们使用上面的代码来拟合这些数据,我们将得到如下所示的拟合结果。请注意拟合曲线是如何偏离实际情况的。
处理异常值的标准方法是使用LossFunction。损失函数降低了残差高的残差块(通常是与异常值对应的残差块)的影响。为了将损失函数与残差块联系起来,我们改变
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, nullptr , &m, &c);
改变为:
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, new CauchyLoss(0.5) , &m, &c);
CauchyLoss是Ceres Solver附带的损失函数之一。 参数0.5指定了损失函数的规模。拟合结果如下,通过与上图的对比,发现拟合曲线更接近真实曲线。
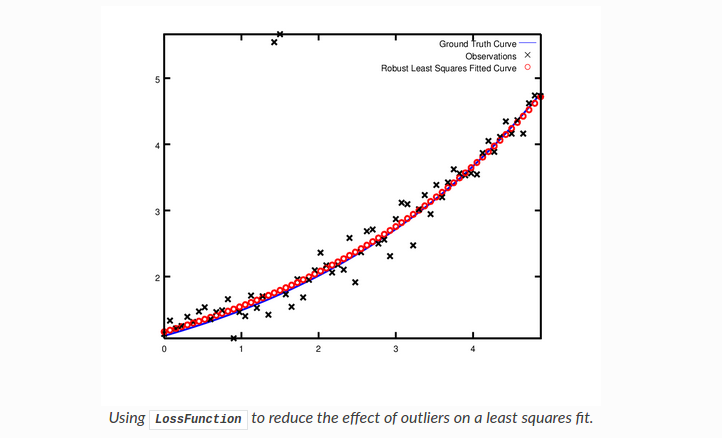
源代码在examples/robust_curve_fitting.cc中
#include "ceres/ceres.h"
#include "glog/logging.h"
// Data generated using the following octave code.
// randn('seed', 23497);
// m = 0.3;
// c = 0.1;
// x=[0:0.075:5];
// y = exp(m * x + c);
// noise = randn(size(x)) * 0.2;
// outlier_noise = rand(size(x)) < 0.05;
// y_observed = y + noise + outlier_noise;
// data = [x', y_observed'];
const int kNumObservations = 67;
const double data[] = {
0.000000e+00, 1.133898e+00,
7.500000e-02, 1.334902e+00,
1.500000e-01, 1.213546e+00,
2.250000e-01, 1.252016e+00,
3.000000e-01, 1.392265e+00,
3.750000e-01, 1.314458e+00,
4.500000e-01, 1.472541e+00,
5.250000e-01, 1.536218e+00,
6.000000e-01, 1.355679e+00,
6.750000e-01, 1.463566e+00,
7.500000e-01, 1.490201e+00,
8.250000e-01, 1.658699e+00,
9.000000e-01, 1.067574e+00,
9.750000e-01, 1.464629e+00,
1.050000e+00, 1.402653e+00,
1.125000e+00, 1.713141e+00,
1.200000e+00, 1.527021e+00,
1.275000e+00, 1.702632e+00,
1.350000e+00, 1.423899e+00,
1.425000e+00, 5.543078e+00, // Outlier point
1.500000e+00, 5.664015e+00, // Outlier point
1.575000e+00, 1.732484e+00,
1.650000e+00, 1.543296e+00,
1.725000e+00, 1.959523e+00,
1.800000e+00, 1.685132e+00,
1.875000e+00, 1.951791e+00,
1.950000e+00, 2.095346e+00,
2.025000e+00, 2.361460e+00,
2.100000e+00, 2.169119e+00,
2.175000e+00, 2.061745e+00,
2.250000e+00, 2.178641e+00,
2.325000e+00, 2.104346e+00,
2.400000e+00, 2.584470e+00,
2.475000e+00, 1.914158e+00,
2.550000e+00, 2.368375e+00,
2.625000e+00, 2.686125e+00,
2.700000e+00, 2.712395e+00,
2.775000e+00, 2.499511e+00,
2.850000e+00, 2.558897e+00,
2.925000e+00, 2.309154e+00,
3.000000e+00, 2.869503e+00,
3.075000e+00, 3.116645e+00,
3.150000e+00, 3.094907e+00,
3.225000e+00, 2.471759e+00,
3.300000e+00, 3.017131e+00,
3.375000e+00, 3.232381e+00,
3.450000e+00, 2.944596e+00,
3.525000e+00, 3.385343e+00,
3.600000e+00, 3.199826e+00,
3.675000e+00, 3.423039e+00,
3.750000e+00, 3.621552e+00,
3.825000e+00, 3.559255e+00,
3.900000e+00, 3.530713e+00,
3.975000e+00, 3.561766e+00,
4.050000e+00, 3.544574e+00,
4.125000e+00, 3.867945e+00,
4.200000e+00, 4.049776e+00,
4.275000e+00, 3.885601e+00,
4.350000e+00, 4.110505e+00,
4.425000e+00, 4.345320e+00,
4.500000e+00, 4.161241e+00,
4.575000e+00, 4.363407e+00,
4.650000e+00, 4.161576e+00,
4.725000e+00, 4.619728e+00,
4.800000e+00, 4.737410e+00,
4.875000e+00, 4.727863e+00,
4.950000e+00, 4.669206e+00
};
using ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction;
using ceres::CostFunction;
using ceres::CauchyLoss;
using ceres::Problem;
using ceres::Solve;
using ceres::Solver;
struct ExponentialResidual {
ExponentialResidual(double x, double y)
: x_(x), y_(y) {}
template <typename T> bool operator()(const T* const m,
const T* const c,
T* residual) const {
residual[0] = y_ - exp(m[0] * x_ + c[0]);
return true;
}
private:
const double x_;
const double y_;
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
double m = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < kNumObservations; ++i) {
CostFunction* cost_function =
new AutoDiffCostFunction<ExponentialResidual, 1, 1, 1>(
new ExponentialResidual(data[2 * i], data[2 * i + 1]));
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function,
new CauchyLoss(0.5),
&m, &c);
}
Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
Solver::Summary summary;
Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << "\n";
std::cout << "Initial m: " << 0.0 << " c: " << 0.0 << "\n";
std::cout << "Final m: " << m << " c: " << c << "\n";
return 0;
}
结果
iter cost cost_change |gradient| |step| tr_ratio tr_radius ls_iter iter_time total_time
0 1.815138e+01 0.00e+00 2.04e+01 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 1.00e+04 0 2.75e-04 5.29e-04
1 2.259471e+01 -4.44e+00 0.00e+00 5.48e-01 -7.74e-01 5.00e+03 1 3.61e-05 5.99e-04
2 2.258929e+01 -4.44e+00 0.00e+00 5.48e-01 -7.73e-01 1.25e+03 1 1.53e-05 6.21e-04
3 2.255683e+01 -4.41e+00 0.00e+00 5.48e-01 -7.68e-01 1.56e+02 1 1.38e-05 6.41e-04
4 2.225747e+01 -4.11e+00 0.00e+00 5.41e-01 -7.16e-01 9.77e+00 1 1.31e-05 6.59e-04
5 1.784270e+01 3.09e-01 8.54e+01 4.72e-01 5.44e-02 5.72e+00 1 2.61e-04 9.25e-04
6 7.557353e+00 1.03e+01 1.13e+02 1.06e-01 2.07e+00 1.72e+01 1 2.92e-04 1.22e-03
7 2.674796e+00 4.88e+00 7.69e+01 5.41e-02 1.78e+00 5.15e+01 1 2.53e-04 1.48e-03
8 1.946177e+00 7.29e-01 1.61e+01 5.00e-02 1.23e+00 1.54e+02 1 2.52e-04 1.74e-03
9 1.904587e+00 4.16e-02 2.20e+00 2.64e-02 1.11e+00 4.63e+02 1 2.53e-04 2.00e-03
10 1.902929e+00 1.66e-03 2.28e-01 6.94e-03 1.12e+00 1.39e+03 1 2.52e-04 2.26e-03
11 1.902884e+00 4.51e-05 1.49e-02 1.27e-03 1.14e+00 4.17e+03 1 2.53e-04 2.52e-03
trust_region_minimizer.cc:707 Terminating: Function tolerance reached. |cost_change|/cost: 5.631229e-07 <= 1.000000e-06
Ceres Solver Report: Iterations: 12, Initial cost: 1.815138e+01, Final cost: 1.902884e+00, Termination: CONVERGENCE
Initial m: 0 c: 0
Final m: 0.287605 c: 0.151213





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!