设计模式之--原型模式
1.原型模式定义
原型模式非常简单,定义如下:
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象
2.通用类图
原型模式的核心是实现Cloneable接口,此接口为JDK提供的一个标识接口,只有实现了此接口的类才能被拷贝。
原型模式的通用类图如下;
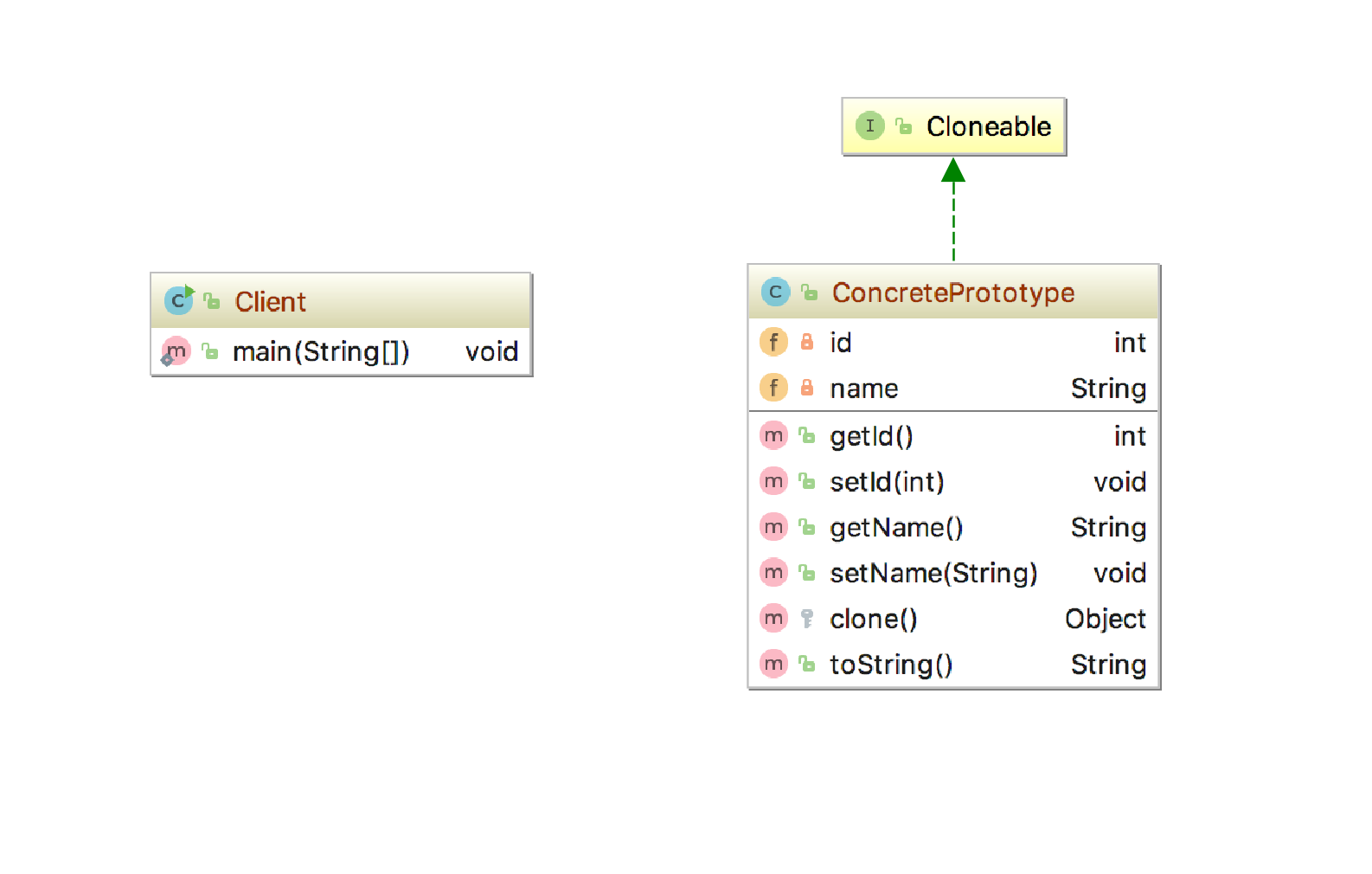
3.通用原型实现代码
原型类:
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable {
private int id;
private String name;
public ConcretePrototype() {
System.out.println("ConcretePrototype construct.");
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = null;
try {
concretePrototype = (ConcretePrototype) super.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return concretePrototype;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Client测试代码:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = new ConcretePrototype();
concretePrototype.setId(123);
concretePrototype.setName("test");
ConcretePrototype cloneType = (ConcretePrototype) concretePrototype.clone();
cloneType.setId(111);
cloneType.setName("test111");
System.out.println(concretePrototype);
System.out.println(cloneType);
}
}
输出结果如下:
ConcretePrototype construct.
ConcretePrototype{id=123, name='test'}
ConcretePrototype{id=111, name='test111'}
通过输出结果可以看出,通过clone方法拷贝了一个新的对象。
4.原型模式的优点
1.性能优良
原型模式是在内存中二进制流的拷贝,要比直接new一个对象快的多
2.通过3中的输出结果来看,在clone对象的时候构造函数不会执行,这对于一些需要在构造函数中做一些初始化的类来说可能称为约束
5.需要注意的点
在原型模式拷贝的时候需要注意可变引用类型的属性,下面通过一个例子来说明此问题:
拷贝对象:
public class DeepClone implements Cloneable{
private Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
public void addPair(String key, String value){
map.put(key, value);
}
public Map<String , Object> getMap(){
return map;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
DeepClone deepClone = null;
try {
deepClone = (DeepClone) super.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return deepClone;
}
}
Client类
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DeepClone deepClone = new DeepClone();
deepClone.addPair("key1", "value1");
DeepClone clone = (DeepClone) deepClone.clone();
clone.addPair("key2", "value2");
System.out.println(deepClone.getMap());
}
}
输出结果如下:
{key1=value1, key2=value2}
在使用clone方法拷贝对象的时候引用类型的属性不会继续做拷贝,而是多个拷贝对象使用同一个属性,这种被称为浅拷贝。
下面对clone方法重写完成深拷贝:
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
DeepClone deepClone = null;
try {
deepClone = (DeepClone) super.clone();
Map<String, Object> cloneMap = new HashMap<>();
cloneMap.putAll(this.map);
deepClone.map = cloneMap;
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return deepClone;
}
重新执行client输出结果为:
{key1=value1}




