WordCount 程序的实现
WordCount是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字数、单词数和行数。在本次项目中,要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有的WordCount.exe的功能,并加以扩充,统计出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。在此基础上,还实现了对某程序设计语言源文件的空行、代码行和注释行的统计。
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter][filename]
各个参数的意义
基本功能列表
wc.exe -c file.c 对字符数的统计
wc.exe -w file.c 对单词数的统计
wc.exe -l file.c: 对行数的统计
扩展功能
wc.exe -a 对空行、代码行和注释行的统计
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“}”。
代码行:本行包括多余一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。
本项目一共分成了四个模块:分别是字符统计模块、单词统计模块、行数统计模块和综合统计模块,综合统计模块包括代码行、空行和注释行的统计。设计如下:
void CharCount(); //字符统计函数 void WordCount(); //单词统计函数 void LineCount(); //行数统计函数 void Muiltiple(); //综合统计函数,包括代码行,空行,注释行
字符统计模块:
void CharCount() //字符统计函数 { FILE *fp; int c = 0; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { c ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } printf("char count is :%d.\n",c); fclose(fp); }
本模块以只读的方式打开在程序目录中的file.c文本文件,依次访问文本文件中的每个字符,统计变量依次加1,直到文本文件结束为止。
单词统计模块:
void WordCount() //单词统计函数 { FILE *fp; int w = 0; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if ((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')||(ch >= 'A'&&ch <='Z')||(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) { while ((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')||(ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z')||(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')||ch == '_') { ch = fgetc(fp); } w ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { ch = fgetc(fp); } } printf("word count is :%d.\n",w); fclose(fp); }
本模块统计的是以字母、数字和下划线组成,且首字母不为下划线的所有单词。统计过程同字符统计模块,此处不再赘述。
行数统计模块:
void LineCount() //行数统计函数 { FILE *fp; int l = 1; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if (ch == '\n') { l ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { ch = fgetc(fp); } } printf("line count is :%d.\n",l); fclose(fp); }
此模块行数的初始化为1,依次访问文本文件中的字符,遇到换行符依次加1,直到文本结束为止。
综合统计模块:
void Muiltiple() //综合统计函数,包括代码行,空行,注释行 { FILE *fp; char ch; int c=0,e=0,n=0; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if (ch == '{'||ch == '}') { e ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else if (ch == '\n') { ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch == '\n') { e ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } } else if (ch == '/') { ch = fgetc(fp); if (ch == '/') while(ch != '\n') { ch = fgetc(fp); } n ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { c ++; while (ch != '{'&&ch != '}'&&ch != '\n'&&ch != '/'&&ch != EOF) { ch = fgetc(fp); } } } printf("code line count is :%d.\n",c); printf("empt line count is :%d.\n",e); printf("note line count is :%d.\n",n); fclose(fp); }
此模块能够实现对空行、代码行和注释行的统计。依次访问文本文件中的字符,若该字符为“{”或“}”,则空行变量加1。若该字符为两个连续的“/”,则注释行变量加1。否则代码变量加1。依次循坏,直到文本结束为止。
总模块的设计:
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { CharCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-w") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { WordCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-l") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { LineCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-a") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { Muiltiple(); } return 0; }
总模块对命令行参数中字符串数组进行判断,第一个字符串数组为程序名,若第二个字符串为“-c”、“-w”、“-l”、“-a”,且第三个字符串数组为file.c,则依次调用CharCount、WordCount、LineCount、Muiltiple函数以实现对字符数、单词数、行数和空行数、代码行数和注释行数的统计。
程序运行测试:
需要统计的文本文件:
void main() //main { int x,y,s; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); s = Add(int x,int y); printf("x + y = %d.",s); } int Add(int x,int y) //Add { return x + y; }
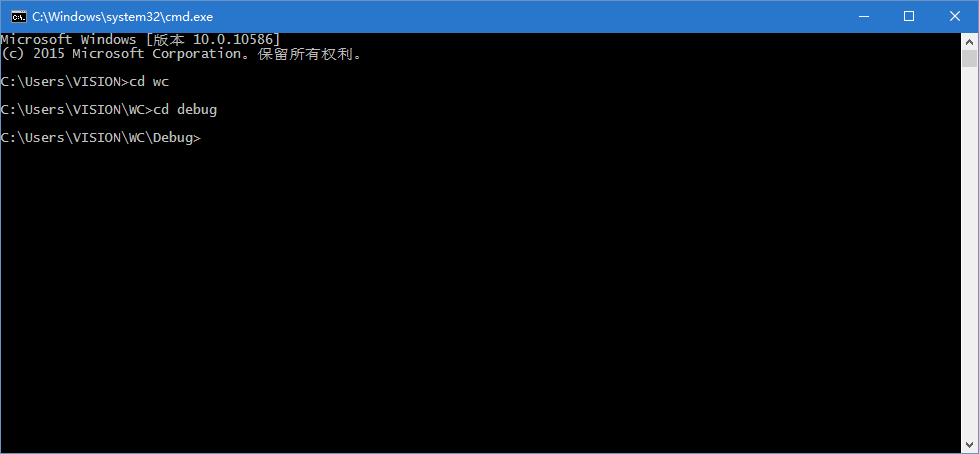
找到程序所在目录。注:需要统计的文本文件file.c在此目录中。
字符数的统计测试:
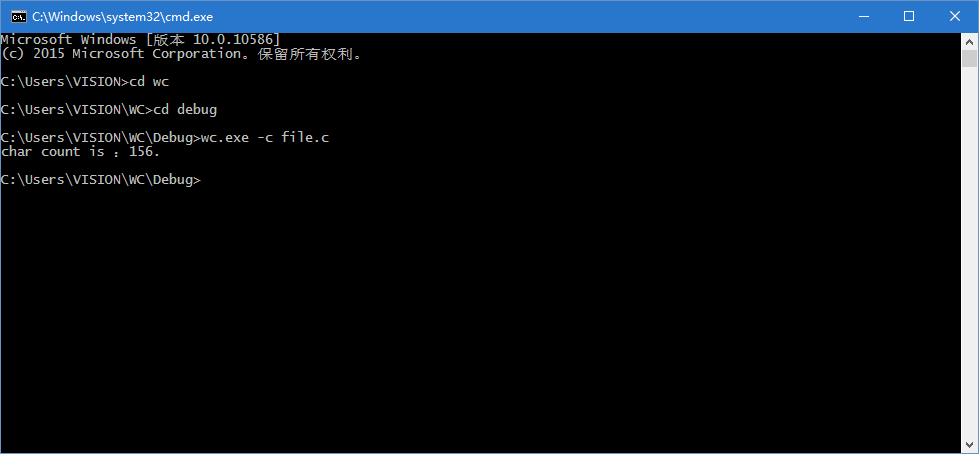
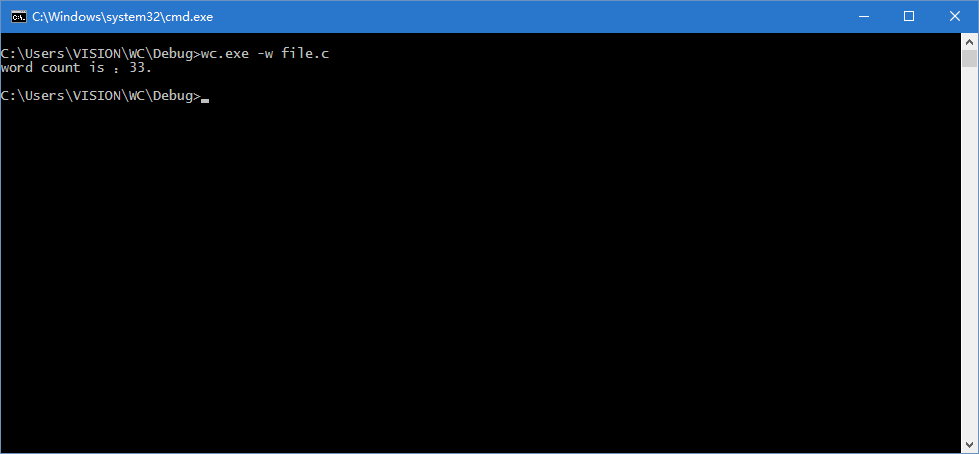
单词数的统计测试:
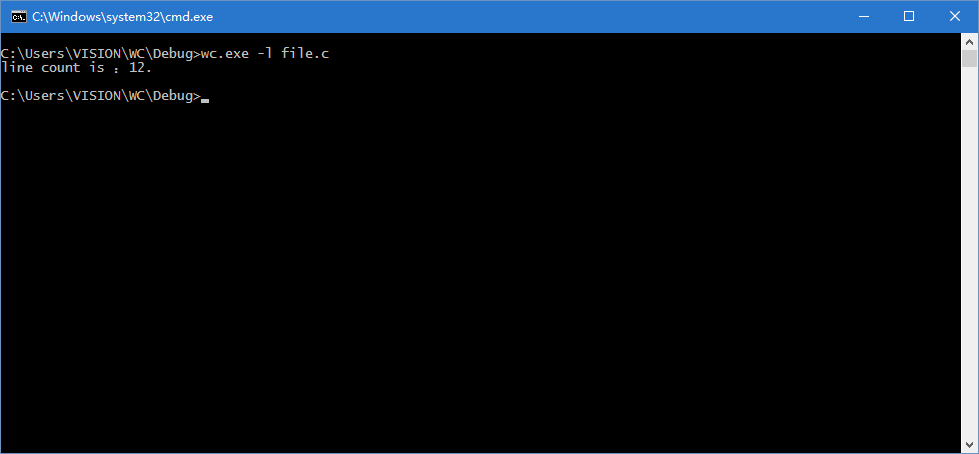
行数的统计测试:
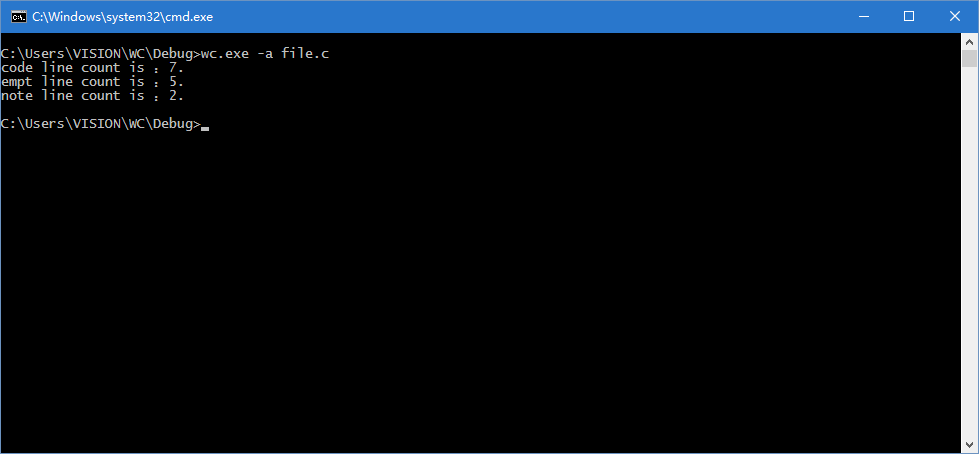
对空行数、代码行数、注释行数的统计测试:
本次项目任有没能实现的功能,wc.exe -s递归处理目录下符合条件的文件和wc.exe -x 显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。对于递归处理目录下符合的文件功能,暂时还没有能够很好解决的思想,所以等待下次作业的完善。对于显示图形界面的功能,由于还没有做图形界面的经历,再加上本次项目时间有些仓促,也是没能完美完成。
附上完整代码:
// WC.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" #include "string.h" void CharCount(); //字符统计函数 void WordCount(); //单词统计函数 void LineCount(); //行数统计函数 void Muiltiple(); //综合统计函数,包括代码行,空行,注释行 int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { CharCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-w") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) WordCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-l") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { LineCount(); } if ((strcmp(argv[1], "-a") == 0) && (strcmp(argv[2], "file.c") == 0)) { Muiltiple(); } return 0; } void CharCount() //字符统计函数 { FILE *fp; int c = 0; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { c ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } printf("char count is :%d.\n",c); fclose(fp); } void WordCount() //单词统计函数 { FILE *fp; int w = 0; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if ((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')||(ch >= 'A'&&ch <='Z')||(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) { while ((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')||(ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z')||(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')||ch == '_') { ch = fgetc(fp); } w ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { ch = fgetc(fp); } } printf("word count is :%d.\n",w); fclose(fp); } void LineCount() //行数统计函数 { FILE *fp; int l = 1; char ch; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if (ch == '\n') { l ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { ch = fgetc(fp); } } printf("line count is :%d.\n",l); fclose(fp); } void Muiltiple() //综合统计函数,包括代码行,空行,注释行 { FILE *fp; char ch; int c=0,e=0,n=0; if((fp = fopen("file.c","r")) == NULL) { printf("file read failure."); } ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch != EOF) { if (ch == '{'||ch == '}') { e ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else if (ch == '\n') { ch = fgetc(fp); while(ch == '\n') { e ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } } else if (ch == '/') { ch = fgetc(fp); if (ch == '/') while(ch != '\n') { ch = fgetc(fp); } n ++; ch = fgetc(fp); } else { c ++; while (ch != '{'&&ch != '}'&&ch != '\n'&&ch != '/'&&ch != EOF) { ch = fgetc(fp); } } } printf("code line count is :%d.\n",c); printf("empt line count is :%d.\n",e); printf("note line count is :%d.\n",n); fclose(fp); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号