cookie与session
一、cookie
1.cookie的产生
由于http协议无法保持状态,但实际情况,我们却又需要“保持状态”,因此cookie就是在这样一个场景下诞生。它能够记住每次用户端访问的状态信息,从而避免了每次都要登录验证。
2.cookie工作原理
服务器产生内容(相当于给当前访问的用户一个身份证),浏览器收到请求后保存在本地;当浏览器再次访问时,浏览器会自动带上cookie,这样服务器就能通过cookie的内容来判断这个是“谁”了。
3.cookie优点与缺点
优点:保存用户状态信息
缺点:cookie最大支持4096字节,而且cookie本身保存在客户端,这样可能会被拦截和窃取。因此,它的安全性不高。
4.cookie示例
下面,我们通过Django来简单模拟一下用户的登陆验证
前端登陆页面:(login.html)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>登陆页面</h1> <form action="/login/" method="POST"> {% csrf_token %} <p>姓名:<input type="text" name="username"/></p> <p>密码:<input type="password" name="password"/></p> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
登陆后的跳转页面:(index.html)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>登陆成功</h1> </body> </html>
后台的处理逻辑:
def index(request): is_login = request.COOKIES.get("chenwei1230", None) if is_login: return render(request, 'index.html') else: return redirect('/login/') def login(request): print(request) if request.method == 'POST': user = request.POST.get('username') pwd = request.POST.get('password') if user == 'chenwei' and pwd == '123': obj = redirect('/index/') obj.set_cookie("chenwei1230", '1212121213132',max_age=30) return obj return render(request, 'login.html')
下面,先来描述一下过程:
1.我们在前端输入用户名和密码,登陆成功后,服务端会将cookie和响应的页面一起发回给客户端。
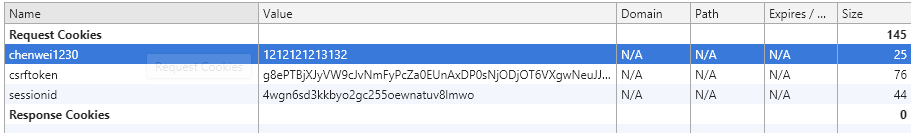
2.我们想直接访问登陆后的页面,可以直接输入http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/,而如果我们换一个浏览器来登陆index,会直接跳转到login.html页面,这是因为在该浏览器中并没有记录我们登陆过的验证信息,也就是cookie信息,所有当我们尝试失败。
二、session
session的产生是为了解决cookie的不足:它能支持更多的字节,并且他保存在服务器,有较高的安全性。
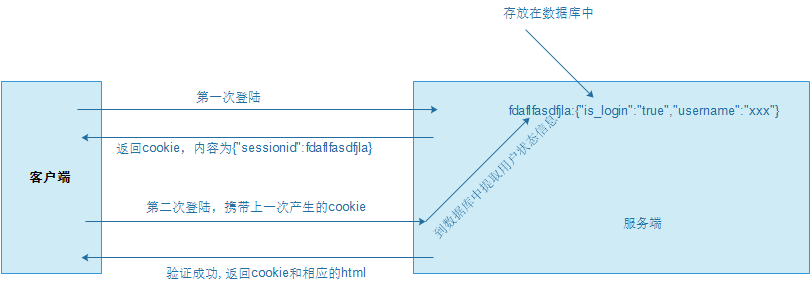
session存在与服务端,它在用户验证信息成功后,返回一个id给客户端,這个id被封装到了cookie中,用户下次登陆,携带该cookie,取出该id去数据库中找到用户之前的登陆状态信息。
三、cookie与session实现用户认证应用
大致流程如下图:
实例代码:
前端html代码:(index.html)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>登陆成功</h1> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>登陆页面</h1> <form action="/login/" method="POST"> {% csrf_token %} <p>姓名:<input type="text" name="username"/></p> <p>密码:<input type="password" name="password"/></p> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
后台处理逻辑:
def index(request): is_login = request.session.get("Is_login", False) if is_login: return render(request, 'index.html') else: return redirect('/login/') def login(request): print(request) if request.method == 'POST': user = request.POST.get('username') pwd = request.POST.get('password') if user == 'chenwei' and pwd == '123': obj = redirect('/index/') request.session['Is_login'] = True request.session['username'] = 'chenwei' obj.set_cookie("chenwei1230", '1212121213132',max_age=30) return obj return render(request, 'login.html')


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号