Map集合类型
- Map
- 特点:存储的键值对映射关系,根据key可以找到value
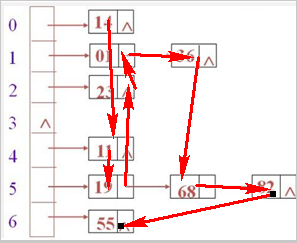
- HashMap
- 采用Hashtable哈希表存储结构(神奇的结构)
- 优点:添加速度快 查询速度快 删除速度快
- 缺点:key无序
- LinkedHashMap
- 采用哈希表存储结构,同时使用链表维护次序
- key有序(添加顺序)
![]()
![]()
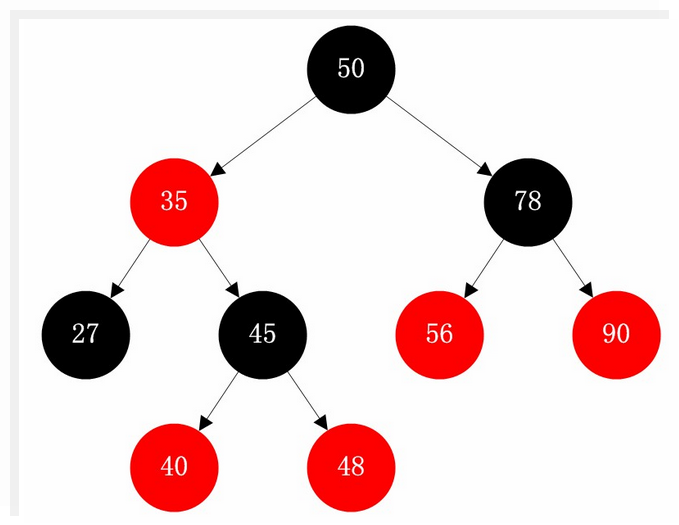
- TreeMap
- 采用二叉树(红黑树)的存储结构
- 优点:key有序 查询速度比List快(按照内容查询)
- 缺点:查询速度没有HashSet快
![]()
使用各种Map存储国家简称-国家名称映射
public class TestMap1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Map集合对象
//Map <String,String>map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//Map <String,String>map =
//new LinkedHashMap<String,String>();
Map<String, String> map = new TreeMap<String, String>();
//向Map集合中添加元素(key-value)
map.put("cn", "China");
map.put("jp", "Japan");
map.put("us", "the United States");
map.put("us", "America");
map.put("uk", "England");
map.put("en", "England");
//从Map中根据key获取value
System.out.println(map.size());
// System.out.println(map);
// System.out.println(map.keySet());//Set 得到所有的key
// System.out.println(map.values());//Collection 得到所有的value
// System.out.println(map.get("cn"));
// System.out.println(map.get("it"));
//Map的遍历
//思路1:先得到所有的key(Set),然后根据key找到value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key + "---->" + map.get(key));
}
//思路2:先得到所有的key-value组成的Set,
//然后输出每个key-value
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entrySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//取出一个Entry
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
//输出一个Entry
//System.out.println(entry);
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "->"+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
使用各种Map存储学号-学生映射
public class TestMap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Map对象用户存储key-value
Map<Integer,Student> map = new HashMap<Integer,Student>();
//Map <Integer,Student>map = new TreeMap<Integer,Student>();
//使用Map对象存储多个key-value
Student stu1 = new Student(1, "zhangsan", 23, 98.2);
Student stu2 = new Student(2, "zhangsan", 23, 98);
Student stu3 = new Student(3, "wangwu", 22, 98.5);
Student stu4 = new Student(1, "zhangsan", 23, 98.2);
map.put(stu1.getSno(), stu1);
map.put(stu2.getSno(), stu2);
map.put(stu3.getSno(), stu3);
map.put(stu4.getSno(), stu4);
//Map的其他方法
//map.remove(1);
//map.clear();
//map.replace(1, new Student(1, "zhaoliu", 23, 100));
map.containsKey(1);
map.containsValue(stu4);
map.isEmpty();
//从Map对象中根据学号找到对应的学生
Student stu = map.get(1);//key 学号
// List list = new ArrayList();;
// list.get(1);//索引
if(stu == null){
System.out.println("该学生不存在");
}else{
System.out.println(stu);
}
System.out.println(map.size());//
System.out.println(map.toString());
//遍历
Set<Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Entry<Integer,Student> entry:entrySet){
Student student = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号