图的基本方法(BFS 和DFS 的 遍历)
图的形式如下所示:
分别使用 BFS DFS 来对图进行遍历;并利用BFS 来求 无权重图的无向图 的最短路径
1 #!/usr/bin/python 2 # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- 3 graph ={ 4 'A':['B','C'], 5 'B':['A','C','D'], 6 'C':['A','B','D','E'], 7 'D':['B','C','E','F'], 8 'E':['C','D'], 9 'F':['D'] 10 } 11 def BFS(graph,start): 12 queue = [] 13 visted = set() 14 queue.append(start) 15 visted.add(start) 16 layer = [] 17 while(len(queue) >0): 18 node = queue.pop(0) 19 neighbors = graph[node] 20 for v in neighbors: 21 if v not in visted: 22 queue.append(v) 23 visted.add(v) 24 layer.append(node) 25 return layer 26 layer = BFS(graph,'A') 27 print(layer) 28 29 def BFS_withLayer(graph,start): 30 queue = [] 31 visted = set() 32 queue.append(start) 33 visted.add(start) 34 layers = [] 35 while(len(queue) >0): 36 len_queue = len(queue) 37 layer = [] 38 for i in range(len_queue): 39 node = queue.pop(0) 40 layer.append(node) 41 visted.add(start) 42 neighbors = graph[node] 43 for v in neighbors: 44 if v not in visted: 45 queue.append(v) 46 visted.add(v) 47 layers.append(layer) 48 return layers 49 layers = BFS_withLayer(graph,'A') 50 print(layers) 51 print('----------------------------------') 52 53 def DFS(graph,start): 54 stack = [] 55 visted = set() 56 stack.append(start) 57 visted.add(start) 58 layer = [] 59 while(len(stack) >0): 60 node = stack.pop() 61 neighbors = graph[node] 62 for v in neighbors: 63 if v not in visted: 64 stack.append(v) 65 visted.add(v) 66 layer.append(node) 67 return layer 68 layer = DFS(graph,'A') 69 print(layer) 70 71 print("=============================") 72 ### 利用BFS来求无权值的无向图的最短路径问题: 73 def BFS_Short_Path(graph,start): 74 queue = [] 75 visted = set() 76 parent = {} 77 queue.append(start) 78 visted.add(start) 79 parent[start] = None 80 while(len(queue) >0): 81 node =queue.pop(0) 82 neighbors = graph[node] 83 for v in neighbors: 84 if v not in visted: 85 queue.append(v) 86 visted.add(v) 87 parent[v] = node 88 # print(node) 89 return parent 90 parents = BFS_Short_Path(graph,'A') 91 print(parents) 92 ## 则从 A 到E的路径为 93 v = 'E' 94 path = [] 95 path.append(v) 96 while parents[v] != None: 97 path.append(parents[v]) 98 v = parents[v] 99 print(path) 100 print(path[::-1])
输出的结果为:
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']
[['A'], ['B', 'C'], ['D', 'E'], ['F']]
----------------------------------
['A', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F', 'B']
=============================
{'A': None, 'E': 'C', 'C': 'A', 'B': 'A', 'D': 'B', 'F': 'D'}
['E', 'C', 'A']
['A', 'C', 'E']
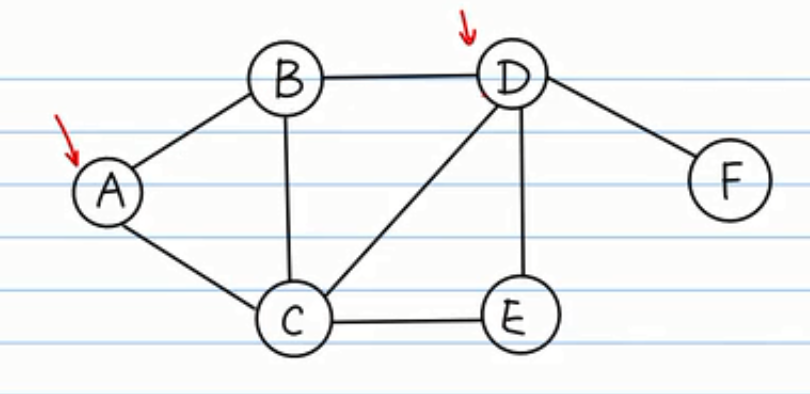
若图是如下所示,应如何实现:
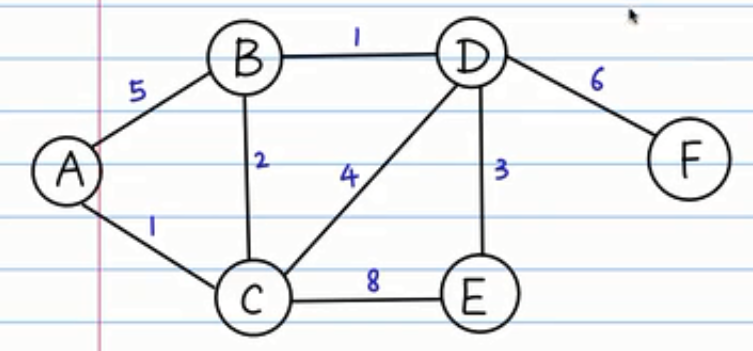
具体的代码如下 :
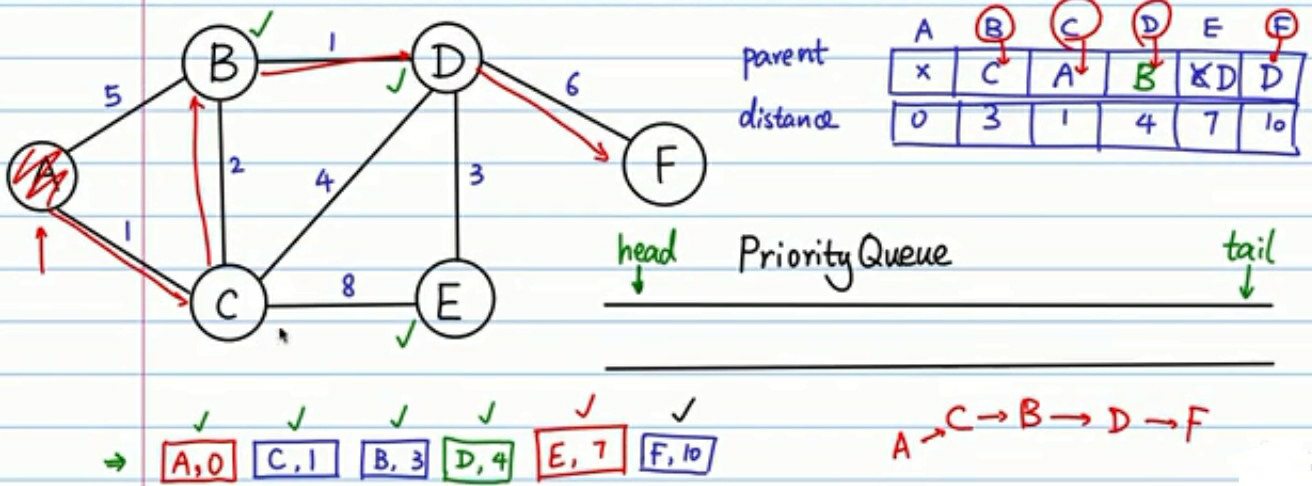
1 #!/usr/bin/python 2 # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- 3 import heapq 4 import math 5 graph ={ 6 'A':{'B':5,'C':1}, 7 'B':{'A':5,'C':2,'D':1}, 8 'C':{'A':1,'B':2,'D':4,'E':8}, 9 'D':{'B':1,'C':4,'E':3,'F':6}, 10 'E':{'C':8,'D':3}, 11 'F':{'D':6} 12 } 13 def init_distnce(graph,start): 14 distance ={} 15 for v in graph.keys(): 16 if v !=start: 17 distance[v] = 999999 18 else: 19 distance[v] = 0 20 return distance 21 # t = init_distnce(graph,'A') 22 # print(t) 23 def dijkstra(graph,start): 24 pqueue = [] 25 heapq.heappush(pqueue,(0,start)) 26 visted = set() 27 distance = init_distnce(graph,start) 28 parent = {start:None} 29 while(len(pqueue)>0): 30 pair = heapq.heappop(pqueue) 31 dist = pair[0] 32 node = pair[1] 33 visted.add(node) 34 neighbors = graph[node].keys() 35 for w in neighbors: 36 if w not in visted: 37 if dist + graph[node][w] < distance[w]: 38 heapq.heappush(pqueue,(dist + graph[node][w],w)) 39 parent[w] = node 40 distance[w] = dist + graph[node][w] 41 return distance,parent 42 43 distance,parent = dijkstra(graph,'A') 44 print("Parent: ",parent) 45 print("Distance: ",distance)
结果:
Parent: {'F': 'D', 'C': 'A', 'E': 'D', 'D': 'B', 'A': None, 'B': 'C'}
Distance: {'F': 10, 'C': 1, 'E': 7, 'D': 4, 'A': 0, 'B': 3}





